Months-Long Lingering Of Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment In Buildings

Table of Contents
Pathways of Chemical Intrusion into Buildings
The toxic plume from the Ohio train derailment didn't simply vanish. Hazardous chemicals found their way into buildings through various pathways, creating a persistent source of contamination.
Airborne Contamination
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate, readily evaporate and disperse through the air. Wind patterns played a significant role in carrying these chemicals over considerable distances, impacting buildings even those some distance from the derailment site. Inadequate building ventilation systems allowed these VOCs to accumulate indoors, severely compromising indoor air quality.
- Examples of VOCs: Vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, benzene, and other less well-known compounds.
- Impact on Indoor Air Quality: Elevated VOC levels lead to headaches, nausea, respiratory irritation, and other serious health problems.
- Methods of Detection: Air quality testing using specialized equipment is essential to identify and quantify VOC concentrations.
Surface Contamination
Chemicals also deposited directly onto building surfaces, both exterior and interior. These chemicals can leach into various building materials over time. Drywall, carpeting, furniture, and even exterior siding can absorb and retain these toxins, creating long-lasting contamination.
- Types of Surfaces Affected: Exterior walls, roofs, windows, flooring, furniture upholstery, and drywall.
- Persistence of Chemicals on Different Materials: Porous materials like carpeting and drywall absorb chemicals more readily and release them slowly, making remediation more challenging.
- Difficulty of Remediation: Complete removal of chemicals from porous materials is often difficult and may require extensive and costly remediation efforts.
Groundwater Contamination
Contaminated groundwater poses another significant pathway for chemical intrusion. Subsurface migration of chemicals can lead to contamination of building foundations, basements, and even utility systems. This poses a risk of continuous exposure through contaminated water sources and structural damage.
- Potential for Subsurface Migration: The extent of groundwater contamination depends on soil type, hydrological conditions, and the chemical properties of the contaminants.
- Impact on Building Structures: Chemical exposure can weaken building foundations, leading to structural damage and instability over time.
- Risks Associated with Contaminated Water Sources: Ingestion of contaminated groundwater can have severe health consequences.
Health and Environmental Impacts of Lingering Chemicals
The lingering presence of toxic chemicals in buildings poses substantial long-term health risks and significant environmental damage.
Respiratory Issues
Exposure to VOCs is strongly linked to various respiratory problems. The irritation caused by these chemicals can trigger or exacerbate asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like children and the elderly.
- Symptoms: Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness.
- Long-Term Effects: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), reduced lung function.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions are at significantly higher risk.
Neurological Effects
Certain chemicals released during the derailment, such as vinyl chloride, have been linked to neurological damage. This can manifest in various ways, ranging from subtle cognitive impairments to severe neurological disorders.
- Specific Chemicals with Neurological Impacts: Vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and other neurotoxins.
- Symptoms of Neurological Damage: Headaches, dizziness, memory loss, difficulty concentrating, tremors, seizures.
- Diagnostic Challenges: Establishing a direct link between chemical exposure and neurological damage can be challenging, requiring thorough medical evaluation.
Environmental Contamination
The environmental consequences extend far beyond the immediate vicinity of the derailment. Soil and water contamination can have devastating long-term ecological effects, impacting wildlife populations and the overall health of the ecosystem.
- Long-Term Ecological Effects: Disruption of aquatic ecosystems, soil degradation, and potential harm to plant and animal life.
- Impact on Wildlife: Toxic chemicals can accumulate in the food chain, causing harm to various species.
- Remediation Strategies: Soil remediation, water treatment, and habitat restoration are crucial for mitigating environmental damage.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the lingering effects of toxic chemicals in affected buildings requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach.
Air Quality Testing and Remediation
Thorough air quality testing is the first step in determining the extent of contamination. This involves identifying the specific VOCs present and their concentrations. Remediation strategies may include air filtration systems, enhanced ventilation, and in some cases, complete building evacuation until proper remediation is completed.
- Types of Air Quality Tests: VOC analysis, particle counting, and other specialized tests.
- Effective Remediation Techniques: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration, improved ventilation, and air scrubbing systems.
- Cost Considerations: Remediation costs can vary significantly depending on the extent of contamination and the chosen remediation methods.
Surface Decontamination
Cleaning and decontaminating affected building surfaces is crucial to remove or neutralize the lingering chemicals. Methods vary depending on the material and the type of contamination. This might involve specialized cleaning solutions, surface sealing, or even material replacement in severe cases.
- Different Cleaning Methods: Vacuuming, wet cleaning, steam cleaning, and specialized decontamination techniques.
- Effectiveness on Various Materials: Effectiveness varies depending on material porosity and chemical properties.
- Safety Precautions: Specialized personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential during decontamination efforts.
Groundwater Remediation
Addressing groundwater contamination requires a combination of techniques such as pump-and-treat systems, bioremediation, or in-situ chemical oxidation. Long-term monitoring is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the remediation efforts and to protect building integrity.
- Remediation Techniques: Pump-and-treat systems, bioremediation, in-situ chemical oxidation.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Regular groundwater testing is necessary to track progress and identify any potential resurgences.
- Associated Costs: Groundwater remediation is typically a long-term and expensive undertaking.
Conclusion: Addressing the Long-Term Impacts of the Ohio Train Derailment's Chemical Lingering
The Ohio train derailment's impact extends far beyond the immediate aftermath. The months-long lingering of toxic chemicals in buildings presents a significant and ongoing threat to public health and the environment. Comprehensive testing, aggressive remediation efforts, and long-term monitoring are absolutely crucial. Government support and transparent communication with affected communities are paramount. We must learn from this tragedy and advocate for stronger regulations and preventative measures to avoid similar disasters in the future. Learn more about the months-long lingering of toxic chemicals in buildings after the Ohio train derailment and how you can help.

Featured Posts
-
 1 Mayis Kocaeli Kutlamalarda Meydana Gelen Arbede Hakkinda Bilgiler
May 03, 2025
1 Mayis Kocaeli Kutlamalarda Meydana Gelen Arbede Hakkinda Bilgiler
May 03, 2025 -
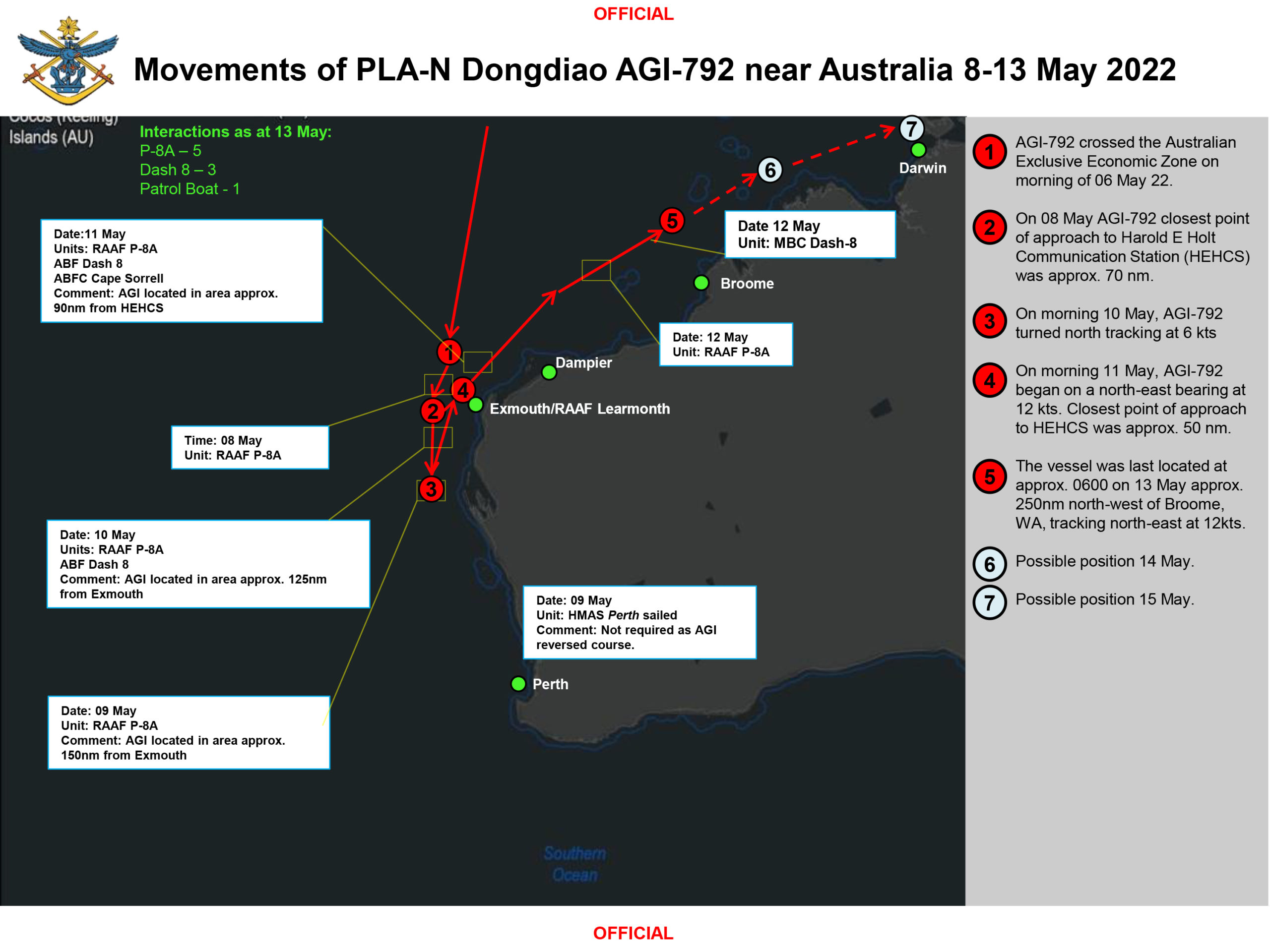 Chinese Naval Activity Off Sydney What Australians Need To Know
May 03, 2025
Chinese Naval Activity Off Sydney What Australians Need To Know
May 03, 2025 -
 Is That Really Christina Aguilera New Pictures Spark Photoshop Debate
May 03, 2025
Is That Really Christina Aguilera New Pictures Spark Photoshop Debate
May 03, 2025 -
 Navigating This Country Practical Tips And Advice
May 03, 2025
Navigating This Country Practical Tips And Advice
May 03, 2025 -
 Lotto 6aus49 Ergebnisse Mittwoch 9 April 2025
May 03, 2025
Lotto 6aus49 Ergebnisse Mittwoch 9 April 2025
May 03, 2025
