Mitigating Urban Heat Island Effect In India Through Innovative Construction Materials
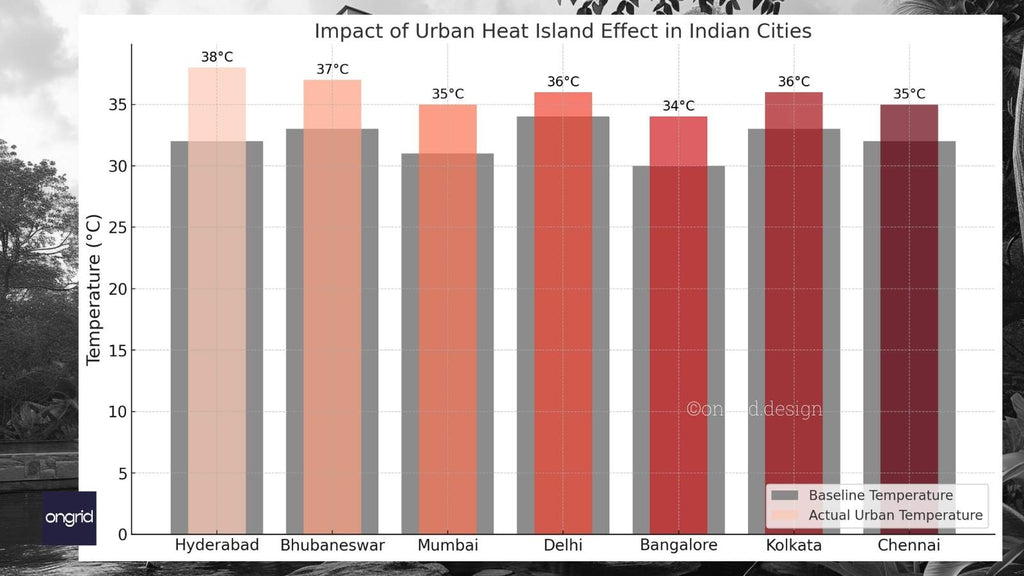
Table of Contents
Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect in India
The UHI effect in India is a complex issue stemming from the interplay of various factors. Rapid urbanization leads to reduced vegetation cover, increased impervious surfaces (like concrete and asphalt), and altered airflow patterns. These changes trap heat, resulting in significantly higher temperatures in urban areas compared to their surroundings. This phenomenon exacerbates climate change impacts, creating a vicious cycle of rising temperatures and increased energy consumption.
- Higher temperatures in urban areas: Indian cities experience significantly elevated temperatures, impacting the comfort and health of their residents.
- Increased energy demand for cooling: The need for air conditioning increases dramatically, placing a strain on the power grid and contributing to higher energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Negative impacts on human health: Heat stress, respiratory illnesses, and cardiovascular problems are aggravated by the UHI effect, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations like the elderly and children.
- Contribution to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions: Increased energy consumption for cooling and the use of certain construction materials contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, further impacting environmental health and quality.
Innovative Construction Materials for UHI Mitigation
Fortunately, innovative construction materials offer a potent arsenal of tools to combat the UHI effect in India. By strategically choosing materials with specific thermal properties, we can significantly reduce heat absorption and improve energy efficiency within buildings and across entire urban landscapes.
Cool Roofs
Cool roofs, characterized by their high albedo (reflectivity), play a crucial role in mitigating the UHI effect. These roofs reflect a significant portion of solar radiation back into the atmosphere, preventing heat absorption and reducing surface temperatures.
- White or light-colored coatings: Applying reflective coatings to existing roofs is a cost-effective way to improve their thermal performance.
- Cool roofing tiles: Specialized tiles designed to reflect sunlight are increasingly available and can be incorporated into new construction.
- Green roofs (extensive and intensive): Green roofs, while more complex to implement, offer exceptional cooling benefits through evapotranspiration and shading. Extensive green roofs use shallow soil depths while intensive green roofs can support deeper planting and a wider range of vegetation.
- Reduced energy consumption for cooling: The use of cool roofs dramatically reduces the energy needed for air conditioning, leading to cost savings and lower carbon emissions.
High Thermal Mass Materials
Materials with high thermal mass absorb and store heat during the day, releasing it slowly at night. This moderates temperature fluctuations within buildings, providing improved thermal comfort and reducing the reliance on artificial cooling and heating.
- Concrete with embedded phase-change materials: Incorporating phase-change materials into concrete further enhances its thermal mass capabilities, allowing for more efficient temperature regulation.
- Earth-based construction materials (rammed earth, adobe): Traditional earth-based construction techniques utilize readily available materials, boasting excellent thermal mass properties and reduced embodied carbon.
- Improved thermal comfort within buildings: High thermal mass materials create a more stable and comfortable indoor environment, reducing energy consumption and enhancing occupant well-being.
Green Building Materials
Sustainable and locally sourced materials play a critical role in reducing the embodied carbon of buildings – the carbon emissions associated with material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, and construction. Choosing these materials also often promotes cooler environments.
- Bamboo: A rapidly renewable resource, bamboo offers excellent structural strength and thermal properties.
- Recycled materials: Utilizing recycled materials reduces waste and minimizes the environmental impact of construction.
- Locally sourced stone and timber: Minimizing transportation distances reduces fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
- Reduced transportation emissions: Sourcing materials locally significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with material transport.
Other Innovative Materials
Emerging technologies are constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in sustainable construction.
- Aerogel insulation: Aerogel, a highly efficient insulator, minimizes heat transfer, leading to significant energy savings.
- Radiation-reflective paints: Specialized paints with high solar reflectance properties can reduce heat absorption on building surfaces.
- Development and adoption of new, sustainable materials: Ongoing research continues to explore and develop novel materials with enhanced thermal properties and reduced environmental impact.
Policy and Implementation Strategies for Widespread Adoption
To ensure widespread adoption of these innovative construction materials, a multi-pronged approach involving government policies, industry collaboration, and public awareness is essential.
- Building codes incorporating thermal performance standards: Updated building codes should mandate the use of materials with superior thermal properties.
- Financial incentives for using sustainable materials: Subsidies and tax breaks can encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly construction materials.
- Training programs for construction workers: Providing training on the proper installation and use of these new materials is crucial for successful implementation.
- Public awareness campaigns on UHI mitigation: Educating the public about the benefits of sustainable construction practices is essential to foster widespread support and adoption.
Conclusion
Innovative construction materials offer a significant opportunity to mitigate the UHI effect in Indian cities, leading to improved public health, reduced energy consumption, and a more sustainable built environment. The adoption of cool roofs, high thermal mass materials, and green building materials, coupled with supportive government policies, is crucial for creating climate-resilient cities. By embracing these strategies and fostering collaboration between stakeholders, India can create cooler, healthier, and more sustainable urban spaces for future generations. Let’s work together to mitigate the urban heat island effect in India through responsible and innovative construction practices, paving the way for a sustainable urban future.

Featured Posts
-
 El Plan De Trump Para Controlar Los Precios De Los Boletos De Ticketmaster La Orden Ejecutiva Explicada
May 30, 2025
El Plan De Trump Para Controlar Los Precios De Los Boletos De Ticketmaster La Orden Ejecutiva Explicada
May 30, 2025 -
 Jon Joness Injury The Hasbulla Fights Hidden Cost
May 30, 2025
Jon Joness Injury The Hasbulla Fights Hidden Cost
May 30, 2025 -
 Cibc Report 64 Billion Economic Injection From Carneys Military Spending
May 30, 2025
Cibc Report 64 Billion Economic Injection From Carneys Military Spending
May 30, 2025 -
 The B C Billionaire Buying Hudsons Bay Unveiling Weihong Lius Strategy
May 30, 2025
The B C Billionaire Buying Hudsons Bay Unveiling Weihong Lius Strategy
May 30, 2025 -
 Viral Gym Photos Bts V And Jungkook Show Off Post Military Physiques
May 30, 2025
Viral Gym Photos Bts V And Jungkook Show Off Post Military Physiques
May 30, 2025
