Middle Managers: The Bridge Between Leadership And Workforce
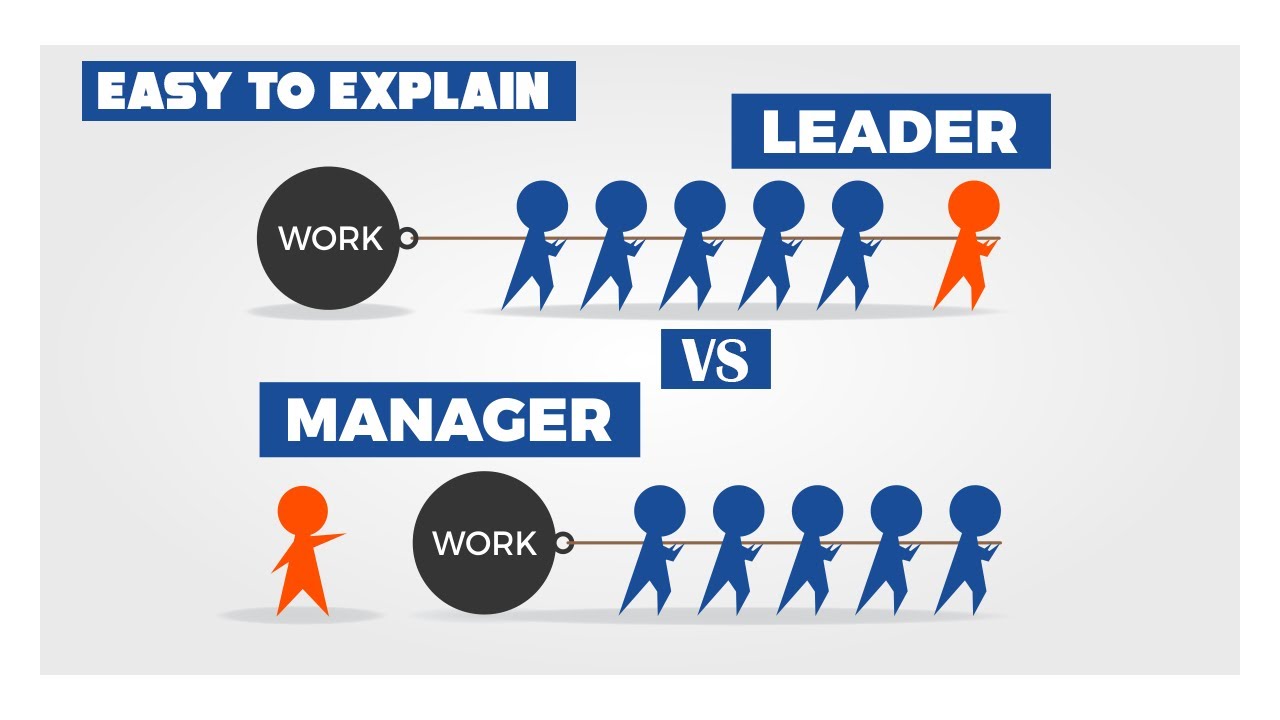
Table of Contents
The Critical Role of Middle Managers in Communication
Effective communication is the lifeblood of any successful organization, and middle managers are central to this process. They are responsible for ensuring that strategic goals set by upper management are clearly understood and effectively implemented by their teams.
Translating Vision into Action
Middle managers translate the often-abstract vision of senior leadership into concrete action plans for their teams. This requires exceptional communication skills and a deep understanding of both the strategic objectives and the capabilities of their employees. Effective middle management communication strategies are crucial for bridging this gap.
- Examples of effective communication strategies: Utilizing clear and concise language, employing various communication channels (e.g., meetings, emails, one-on-one conversations), and using visual aids to clarify complex information.
- Overcoming communication barriers: Identifying and addressing language barriers, cultural differences, and technological limitations to ensure that all team members receive and understand the message.
- Fostering transparency: Openly communicating updates, challenges, and successes to build trust and keep employees informed.
Gathering Feedback and Reporting Upwards
Middle managers act as a vital conduit for feedback, conveying employee concerns, suggestions, and performance data to senior leadership. This upward communication is essential for identifying potential problems early, improving processes, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Methods for gathering employee feedback: Regular team meetings, anonymous surveys, one-on-one conversations, and performance reviews.
- Techniques for effective upward communication: Preparing concise and well-structured reports, presenting data clearly and objectively, and actively participating in leadership meetings.
- Providing constructive criticism: Offering insightful and actionable feedback that helps improve processes and address issues within the organization.
Middle Managers: Driving Performance and Productivity
Beyond communication, middle managers play a pivotal role in driving performance and productivity within their teams. They are responsible for mentoring, training, and motivating their employees to achieve organizational goals.
Mentoring and Team Development
Effective middle managers act as mentors and coaches, guiding their team members' professional development and creating a supportive work environment. Investing in employee development is key to improving team performance.
- Importance of mentorship: Providing guidance, support, and feedback to help team members develop their skills and reach their full potential.
- Effective team building strategies: Organizing team-building activities, fostering open communication, and creating a collaborative work environment.
- Fostering a positive work environment: Promoting a culture of respect, trust, and recognition to motivate employees and improve morale.
Implementing Strategies and Monitoring Progress
Middle managers are responsible for ensuring that strategic initiatives are effectively implemented at the ground level. This involves effective project management, performance monitoring, and adapting to changing circumstances.
- Project management skills: Defining project scopes, creating timelines, assigning tasks, and tracking progress effectively.
- Performance monitoring techniques: Using key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress towards goals and identifying areas for improvement.
- Adapting to changes in strategy: Remaining flexible and adjusting plans as needed to respond to unforeseen challenges or changing priorities.
Challenges Faced by Middle Managers and Solutions
The role of a middle manager is demanding, requiring a unique blend of skills and abilities. They often face pressure from both above and below, requiring excellent conflict resolution skills and adeptness at navigating organizational politics.
The Pressure from Above and Below
Middle managers are caught in the middle, balancing the expectations of senior leadership with the needs and concerns of their teams. This can create significant pressure and requires strong leadership skills.
- Balancing competing priorities: Effectively prioritizing tasks, delegating responsibilities, and managing resources to meet multiple deadlines.
- Managing conflict: Addressing interpersonal conflicts, mediating disagreements, and resolving disputes fairly and efficiently.
- Navigating organizational politics: Understanding the dynamics of the organization, building strong relationships with colleagues, and effectively advocating for their teams.
Developing Essential Skills for Success
To excel as a middle manager, certain essential skills are crucial. Investment in leadership training and professional development is critical for success.
- Communication skills: Effectively conveying information, actively listening, and providing constructive feedback.
- Leadership skills: Motivating and inspiring teams, delegating effectively, and creating a positive work environment.
- Problem-solving skills: Identifying challenges, analyzing situations, and developing creative solutions.
- Conflict resolution skills: Mediating disputes, resolving disagreements, and finding mutually beneficial outcomes.
- Emotional intelligence: Understanding and managing emotions, building relationships, and working effectively with diverse personalities.
Conclusion
Middle managers are the unsung heroes of many organizations. Their ability to effectively communicate, drive performance, and navigate challenges is critical to organizational success. They translate leadership vision into actionable plans, provide crucial feedback, and mentor their teams to achieve shared goals. However, they also face significant pressures and require a diverse skillset to thrive.
Investing in effective middle management training and development is crucial for building a high-performing organization. Understand the critical role of your middle managers and empower them to succeed. By recognizing and supporting the valuable contributions of middle managers, organizations can unlock their full potential and achieve their strategic objectives. The success of any organization rests, in part, on the strength of its middle management team.

Featured Posts
-
 Adult Adhd Next Steps After A Suspected Diagnosis
Apr 29, 2025
Adult Adhd Next Steps After A Suspected Diagnosis
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Novak Djokovics Upset Loss To Alejandro Tabilo At Monte Carlo Masters 2025
Apr 29, 2025
Novak Djokovics Upset Loss To Alejandro Tabilo At Monte Carlo Masters 2025
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Mine Managers Testimony Refusal Sparks Contempt Threat In Yukon
Apr 29, 2025
Mine Managers Testimony Refusal Sparks Contempt Threat In Yukon
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyt Strands Solutions Hints And Answers For February 27 2025
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Strands Solutions Hints And Answers For February 27 2025
Apr 29, 2025 -
 La Efectividad Goleadora De Alberto Ardila Olivares Datos Y Estadisticas
Apr 29, 2025
La Efectividad Goleadora De Alberto Ardila Olivares Datos Y Estadisticas
Apr 29, 2025
