M&S Cyberattack: A £300 Million Hit To The Bottom Line
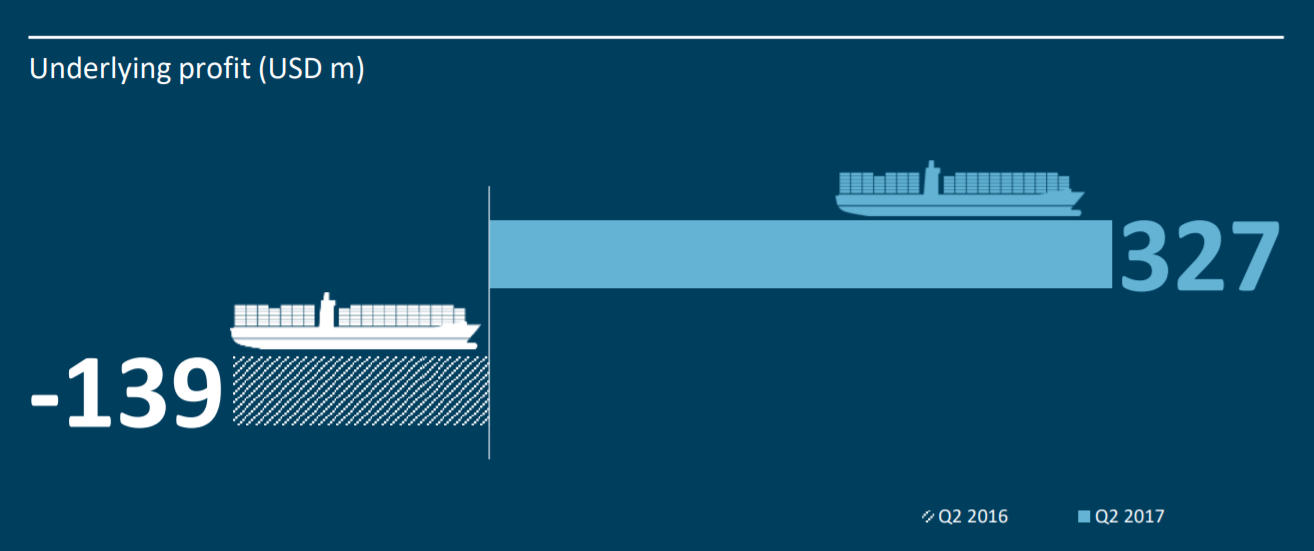
Table of Contents
The Scale of the Breach: Understanding the £300 Million Loss
The reported £300 million loss from the M&S cyberattack represents a significant blow to the company's financial health. While the exact nature of the attack remains undisclosed in its specifics by M&S, the financial implications are clear and far-reaching. This figure encompasses both direct and indirect costs.
- Direct Financial Losses: These include the immediate costs associated with the incident response, such as ransom payments (if any were made), forensic investigations to determine the extent of the breach, legal fees, and the cost of notifying affected customers.
- Indirect Financial Losses: The indirect costs are arguably even more substantial. These include lost revenue due to operational disruptions, the cost of repairing damaged systems and restoring data, the expense of implementing enhanced security measures, and the potentially significant drop in customer confidence leading to decreased sales.
- Reputational Damage and Loss of Investor Confidence: Beyond the immediate financial impact, the M&S cyberattack caused considerable reputational damage. The news of a major data breach can erode customer trust, impacting future sales and brand loyalty. Similarly, it can lead to a decline in investor confidence, resulting in stock price fluctuations and decreased investment opportunities. The long-term effects on M&S's brand image and market standing could be substantial. While precise figures for these indirect losses are difficult to quantify, they undoubtedly contribute significantly to the overall £300 million figure.
The attack's impact extended far beyond mere financials; it disrupted operations, damaged M&S's reputation, and shook investor confidence. The precise percentage decrease in profits and stock price fluctuations remain confidential, but the overall impact on the company's bottom line is undeniably severe.
Causes of the M&S Cyberattack: Identifying Vulnerabilities
Pinpointing the exact cause of the M&S cyberattack requires access to confidential internal investigations. However, analyzing similar attacks in the retail sector reveals several potential vulnerabilities that could have been exploited:
- Phishing Attacks: These are a common entry point for cybercriminals. Sophisticated phishing emails designed to mimic legitimate M&S communications could have tricked employees into revealing credentials or downloading malware.
- Malware Infections: Once malware is installed, it can compromise systems, steal data, and disrupt operations. This could have been introduced through phishing, infected attachments, or vulnerabilities in software.
- Insider Threats: Though less likely to be the sole cause, an insider with malicious intent could have exploited their access to sensitive systems and data.
- Outdated Security Systems: Using outdated software and infrastructure leaves organizations vulnerable to known exploits. M&S's security systems, if not regularly updated and patched, might have contained exploitable weaknesses.
Potential vulnerabilities exploited could include inadequate data encryption, weak access controls, and insufficient employee training on recognizing and reporting phishing attempts. A lack of robust multi-factor authentication could also have played a role.
The Aftermath: Response, Recovery, and Lessons Learned
M&S likely activated its incident response team immediately upon detecting the cyberattack. This would have involved collaborating with law enforcement, engaging forensic specialists, and notifying affected customers. The recovery process involved:
- Restoring Systems: Rebuilding compromised systems, restoring data from backups, and implementing new security measures.
- Regaining Customer Trust: This would have involved transparent communication with customers about the breach, measures taken to mitigate the risk, and steps to protect their data.
- Strengthening Cybersecurity Infrastructure: M&S has undoubtedly invested heavily in upgrading its cybersecurity infrastructure since the attack. This includes implementing stronger authentication protocols, enhancing data encryption, improving access controls, and bolstering its overall security posture.
Key lessons learned likely include: the critical need for comprehensive employee cybersecurity training, proactive threat detection, and the importance of continuous monitoring and vulnerability assessments.
Preventing Future M&S Cyberattacks: Best Practices for Retailers
Preventing future cyberattacks requires a multi-layered approach. Retailers should adopt the following best practices:
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: These help identify vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
- Robust Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: These systems provide real-time monitoring and analysis of security events, enabling prompt detection of suspicious activity.
- Employee Awareness Training: Regular training programs are vital in educating employees about phishing scams, social engineering attacks, and best practices for password security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Conclusion: Protecting Against Future Cyberattacks – Learning from the M&S Cyberattack
The M&S cyberattack serves as a stark reminder of the devastating financial consequences of inadequate cybersecurity. The £300 million loss underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures for businesses of all sizes, particularly within the retail sector. Proactive security strategies, including regular security audits, employee training, and the implementation of multi-factor authentication, are crucial for mitigating the risk of future attacks and protecting against substantial financial losses. Learn more about protecting your business from cyber threats by researching cybersecurity best practices and considering consulting services specializing in preventing data breaches and mitigating the impact of a potential M&S-style cyberattack. Investing in robust cybersecurity is not just a cost; it's an investment in the long-term health and security of your organization.

Featured Posts
-
 Tulsa King Season 3 A New Set Photo Featuring Sylvester Stallone
May 23, 2025
Tulsa King Season 3 A New Set Photo Featuring Sylvester Stallone
May 23, 2025 -
 Remont Pivdennogo Mostu Pidryadniki Provadzhennya Ta Koshti
May 23, 2025
Remont Pivdennogo Mostu Pidryadniki Provadzhennya Ta Koshti
May 23, 2025 -
 Mn Hw Ilyas Rwdryjyz Almshtbh Bh Fy Mqtl Mwzfy Alsfart Alisrayylyt Fy Washntn
May 23, 2025
Mn Hw Ilyas Rwdryjyz Almshtbh Bh Fy Mqtl Mwzfy Alsfart Alisrayylyt Fy Washntn
May 23, 2025 -
 Crawley Batsman Steals Gloucestershire Victory
May 23, 2025
Crawley Batsman Steals Gloucestershire Victory
May 23, 2025 -
 Vklad Eleny Rybakinoy V Razvitie Zhenskogo Tennisa V Kazakhstane
May 23, 2025
Vklad Eleny Rybakinoy V Razvitie Zhenskogo Tennisa V Kazakhstane
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Neal Mc Donoughs Role In The Last Rodeo
May 23, 2025
Neal Mc Donoughs Role In The Last Rodeo
May 23, 2025 -
 Smart Shopping For Memorial Day 2025 Best Sales And Deals
May 23, 2025
Smart Shopping For Memorial Day 2025 Best Sales And Deals
May 23, 2025 -
 Dallas Welcomes The Usa Film Festival Free Movies And Star Guests
May 23, 2025
Dallas Welcomes The Usa Film Festival Free Movies And Star Guests
May 23, 2025 -
 Dc Legends Of Tomorrow The Ultimate Fans Resource
May 23, 2025
Dc Legends Of Tomorrow The Ultimate Fans Resource
May 23, 2025 -
 Usa Film Festival In Dallas A Celebration Of Cinema With Free Screenings
May 23, 2025
Usa Film Festival In Dallas A Celebration Of Cinema With Free Screenings
May 23, 2025
