Kodiak Shellfish Harvest Under Threat: Second Harmful Algal Bloom Reported
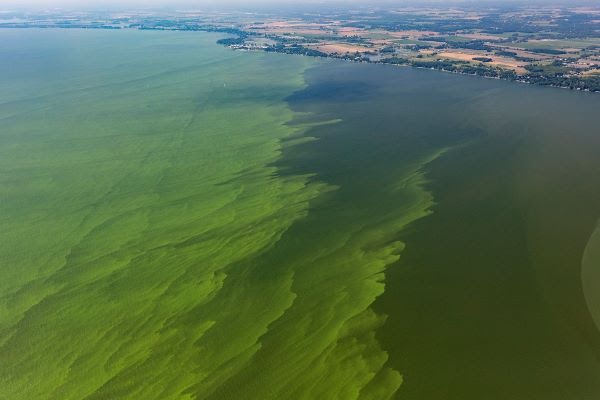

Table of Contents
Understanding the Current Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB) in Kodiak
The current crisis stems from a bloom of Alexandrium catenella, a species of dinoflagellate known to produce potent neurotoxins responsible for paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). PSP can cause severe illness and even death in humans who consume contaminated shellfish. This bloom's geographical extent currently encompasses [Insert specific geographical areas affected], posing a significant threat to shellfish populations across a wide area. The severity of the bloom is [Insert details on severity – e.g., toxin levels measured, density of algae].
- Current monitoring efforts: The Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation (ADEC) and other local agencies are actively monitoring the bloom's progression using satellite imagery, water sampling, and shellfish tissue analysis.
- Areas most affected: [List specific areas with the highest concentration of the bloom and closures].
- Latest updates on shellfish harvesting closures: [Provide the most up-to-date information on closures and any potential reopening timelines]. Check the ADEC website for the latest official updates on shellfish safety.
Economic Impact of the Kodiak Shellfish Harvest Closure
The closure of the Kodiak shellfish harvest has far-reaching economic consequences. The industry supports hundreds of jobs, directly impacting fishermen, processing plants, and related businesses like restaurants and tourism operators. Preliminary estimates suggest a revenue loss of [Insert estimated dollar amount] for the current season. This figure doesn't fully account for the ripple effect on related industries.
- Estimated revenue loss for the shellfish industry: [Provide more specific figures, if available, broken down by shellfish type].
- Impact on related businesses (tourism, retail): The closure affects tourism, as many visitors come to Kodiak specifically for seafood experiences. Retail businesses that rely on shellfish sales also suffer.
- Long-term economic consequences of repeated HABs: The recurring nature of these blooms creates long-term economic uncertainty and threatens the sustainability of the entire Kodiak shellfish industry. Financial assistance programs from state and federal governments are crucial to help businesses weather this crisis.
Environmental Factors Contributing to HABs in Kodiak
The increased frequency and intensity of HABs in Kodiak are likely linked to a complex interplay of environmental factors. Climate change, with its rising ocean temperatures and altered current patterns, plays a significant role. Nutrient runoff from land-based sources, such as agriculture and urban development, also contributes to the blooms by providing excess nutrients that fuel algal growth.
- Role of rising ocean temperatures: Warmer waters create ideal conditions for the growth of Alexandrium catenella and other harmful algae species.
- Impact of aquaculture practices: While not definitively linked, some research suggests that certain aquaculture practices can potentially exacerbate HABs. Further investigation is needed to understand this relationship fully.
- Effects on other marine species beyond shellfish: HABs impact the entire marine ecosystem, affecting other shellfish, finfish, and marine mammals through toxin exposure or habitat disruption.
Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies for Future Kodiak Shellfish Harvest Protection
Effective monitoring and mitigation strategies are crucial for protecting the Kodiak shellfish harvest. This includes improving early warning systems, implementing better water quality management, and developing resilient aquaculture practices. Current monitoring involves advanced technologies such as satellite remote sensing and sophisticated toxin detection methods.
- Advanced technologies used for HAB detection: [Describe specific technologies used, e.g., satellite imagery analysis, automated sensor networks, molecular techniques].
- Community involvement in monitoring efforts: Citizen science initiatives can supplement official monitoring programs, providing valuable data and promoting public awareness.
- Long-term strategies for sustainable shellfish harvesting: This requires a multi-faceted approach, including responsible land management practices, improved wastewater treatment, and research into climate change adaptation strategies for shellfish aquaculture.
Conclusion: Protecting the Future of the Kodiak Shellfish Harvest
The recurring harmful algal blooms pose a significant and immediate threat to the Kodiak shellfish harvest, causing substantial economic losses and environmental damage. The urgency of the situation cannot be overstated. Continued research into the causes of HABs, coupled with robust monitoring and mitigation strategies, is critical for safeguarding this vital industry and ecosystem. We must act now to protect the future of the Kodiak shellfish harvest. Learn more about HABs, support sustainable seafood practices, and contact your representatives to advocate for increased funding for HAB research and mitigation in the Kodiak region. Protecting the Kodiak shellfish industry and its surrounding ecosystem is our collective responsibility.

Featured Posts
-
 Le 9 Mai 2025 Arcelor Mittal La Russie Et Les Analyses De Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Le 9 Mai 2025 Arcelor Mittal La Russie Et Les Analyses De Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
 Sncf Greve 8 Mai Dernieres Informations Et Analyses
May 30, 2025
Sncf Greve 8 Mai Dernieres Informations Et Analyses
May 30, 2025 -
 New Guillermo Del Toro Documentary Sangre Del Toro To Launch At Cannes
May 30, 2025
New Guillermo Del Toro Documentary Sangre Del Toro To Launch At Cannes
May 30, 2025 -
 Del Toros Frankenstein Movie Unexpected Themes Revealed In Recent Teaser
May 30, 2025
Del Toros Frankenstein Movie Unexpected Themes Revealed In Recent Teaser
May 30, 2025 -
 Remote Lodge Break In Leads To Caribou Poaching Investigation In Northern Canada
May 30, 2025
Remote Lodge Break In Leads To Caribou Poaching Investigation In Northern Canada
May 30, 2025
