Is Our Mental Health Care System Failing? A Comprehensive Analysis
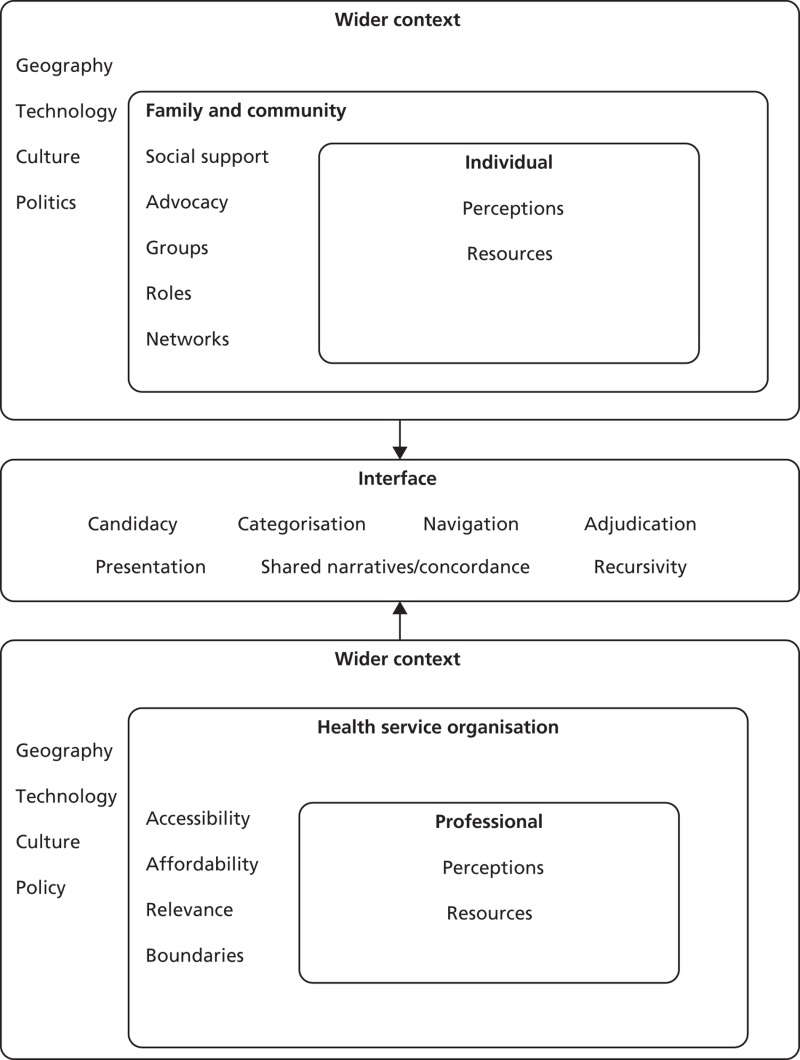
Table of Contents
Limited Access to Affordable and Quality Mental Healthcare
The current mental healthcare system is riddled with barriers that prevent many from accessing the help they desperately need. These obstacles manifest in several key areas:
Geographic Disparities
The unequal distribution of mental health professionals creates significant geographic disparities in access to care. Rural areas and underserved communities often face a severe shortage of psychiatrists, psychologists, and therapists. This translates to:
- Lack of specialists: Limited availability of specialized care for conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe depression.
- Long waiting lists: Individuals often face lengthy delays before receiving an appointment, exacerbating their distress.
- Limited transportation options: Lack of public transport or personal vehicles can make it impossible for individuals to reach distant treatment centers.
Statistics reveal stark differences. For example, while urban areas may have an abundance of mental health professionals, rural counties might have only one psychiatrist for every 100,000 residents, leading to inadequate mental health services and longer wait times for appointments.
High Cost of Treatment
The high cost of mental healthcare acts as a significant barrier for many individuals, particularly those lacking adequate insurance coverage. This includes:
- Lack of insurance coverage: Many insurance plans have limited coverage for mental health services, resulting in high out-of-pocket expenses.
- High deductibles and copays: Even with insurance, the cost of therapy sessions, medication, and hospitalization can be prohibitive.
- Unaffordable private practices: Many private practices charge exorbitant fees, making treatment inaccessible for individuals with low or moderate incomes.
Data indicates that a substantial percentage of uninsured individuals with mental health needs forgo treatment due to financial constraints. This underscores the critical need for affordable and accessible mental health insurance coverage.
Navigating the System
The complexities inherent in navigating the mental healthcare system often deter individuals from seeking help. These include:
- Bureaucratic hurdles: Dealing with insurance paperwork, referrals, and authorizations can be overwhelming and time-consuming.
- Lack of clear information: Finding appropriate services and understanding the different types of mental health professionals can be confusing.
- Difficulties in coordinating care: Integrating mental healthcare with other aspects of healthcare can be challenging, particularly for individuals with multiple health conditions.
Streamlining processes, simplifying paperwork, and providing clear, accessible information about available services are crucial steps towards improving access to mental healthcare.
Insufficient Funding and Resources
The chronic underfunding of mental health programs is a major contributor to the current crisis. This leads to:
Underfunded Public Programs
Public mental health programs are consistently underfunded, resulting in:
- Understaffed hospitals and clinics: A lack of resources leads to inadequate staffing levels, long wait times, and limited treatment options.
- Lack of community-based services: Insufficient funding hinders the development and maintenance of crucial community-based services, such as support groups and crisis intervention centers.
- Limited funding for research: Underinvestment in mental health research hampers the development of new and more effective treatments.
A comparison of funding levels for mental health compared to other areas of healthcare reveals a significant disparity, emphasizing the urgent need for increased investment.
Shortage of Mental Health Professionals
The severe shortage of mental health professionals further exacerbates the problem. Factors contributing to this shortage include:
- Burnout: The demanding nature of the work, coupled with high caseloads, leads to significant burnout among mental health professionals.
- Low salaries: Mental health professionals often receive lower salaries compared to their counterparts in other medical fields.
- Lack of training opportunities: Insufficient funding for training programs and residencies limits the number of new professionals entering the field.
Addressing these issues requires a multi-pronged approach, including increasing salaries, improving working conditions, and expanding training opportunities to attract and retain qualified mental health professionals.
Stigma and Societal Attitudes
Negative societal attitudes and stigma surrounding mental illness significantly impact help-seeking behavior and treatment outcomes.
The Impact of Stigma
The stigma associated with mental illness leads to:
- Fear of discrimination: Individuals fear being judged, ostracized, or discriminated against if they disclose their mental health condition.
- Reluctance to seek help: Fear of stigma often prevents individuals from seeking professional help, leading to delayed or inadequate treatment.
- Social isolation: Individuals may withdraw from social activities and relationships due to shame and fear of judgment.
Successful stigma-reduction campaigns emphasize education, empathy, and the normalization of mental health challenges.
Lack of Public Awareness
A lack of public awareness and education about mental health contributes to the problem. Addressing this requires:
- Improved mental health literacy: Educating the public about mental health conditions, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial.
- Promoting early intervention: Early identification and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with mental illness.
- Challenging misconceptions: Addressing misconceptions and stereotypes surrounding mental illness is essential to fostering understanding and support.
Investing in comprehensive public awareness campaigns is essential to destigmatize mental illness and promote help-seeking behavior.
Potential Solutions and Reforms
Overcoming the challenges facing our mental health care system requires a multifaceted approach involving increased funding, policy reforms, and integration of care.
Increased Funding and Investment
Significant increases in government funding are crucial to expand access to mental healthcare services. This includes:
- Investing in community-based programs: Expanding access to community-based services, such as support groups, crisis hotlines, and mobile crisis teams.
- Increasing the number of mental health professionals: Investing in training programs and providing incentives to attract and retain qualified professionals.
- Improving access to telehealth: Expanding access to telehealth services to overcome geographic barriers and improve access to care in rural and underserved areas.
Policy Reforms
Policy changes are needed to address systemic issues impacting access and affordability. This includes:
- Expanding insurance coverage: Mandating comprehensive mental health coverage under all insurance plans.
- Reducing administrative burdens: Streamlining the process of accessing mental health services and reducing unnecessary paperwork.
- Improving the coordination of care: Facilitating better communication and collaboration between mental health providers and other healthcare professionals.
Integration of Mental and Physical Healthcare
Integrating mental health services into primary care settings is essential for early detection and intervention. This involves:
- Collaborative care models: Implementing collaborative care models that integrate mental health providers into primary care teams.
- Improved screening and early intervention in primary care: Implementing routine mental health screenings in primary care settings to identify and address mental health issues early on.
Conclusion
The evidence overwhelmingly suggests that our mental health care system is failing to adequately address the needs of millions. Limited access to affordable and quality care, insufficient funding and resources, and pervasive stigma all contribute to this crisis. The central question—Is our mental health care system failing?—is undeniably answered with a resounding yes. However, the solutions are within reach. By increasing funding, enacting policy reforms, and addressing societal attitudes, we can create a more equitable and effective mental health care system. We must demand better from our mental health care system. Let's work together to build a future where everyone can access the comprehensive mental healthcare services they need. Let's reform our mental health care system to ensure that mental health is prioritized and treated with the same urgency and importance as physical health.

Featured Posts
-
 Daisy May Cooper Engaged To Boyfriend Anthony Huggins Confirmation And Details
May 02, 2025
Daisy May Cooper Engaged To Boyfriend Anthony Huggins Confirmation And Details
May 02, 2025 -
 Sanchajuje 2027 Metais Laukiama Hario Poterio Teminis Parkas
May 02, 2025
Sanchajuje 2027 Metais Laukiama Hario Poterio Teminis Parkas
May 02, 2025 -
 The Story Of Pancake Day From Shrove Tuesday To Modern Celebrations
May 02, 2025
The Story Of Pancake Day From Shrove Tuesday To Modern Celebrations
May 02, 2025 -
 England Women Vs Spain Lineup Predictions And Match Preview
May 02, 2025
England Women Vs Spain Lineup Predictions And Match Preview
May 02, 2025 -
 Increase Your Commission 1 500 Flight Credit Incentive On Paul Gauguin Cruises By Ponant
May 02, 2025
Increase Your Commission 1 500 Flight Credit Incentive On Paul Gauguin Cruises By Ponant
May 02, 2025
