Investor Guide: Understanding And Interpreting Stock Market Valuations (BofA)
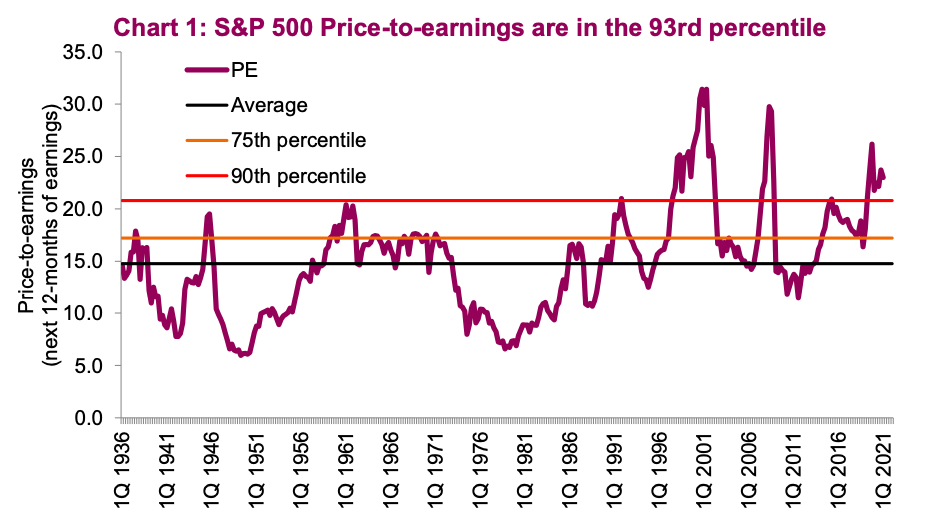
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics: A Deep Dive
Several key metrics are used to assess a company's valuation. Let's explore some of the most important ones.
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E)
The Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E ratio) is arguably the most widely used valuation metric. It represents the market price of a company's stock relative to its earnings per share (EPS). The calculation is straightforward: P/E Ratio = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share. A high P/E ratio (e.g., above 25) generally suggests that investors are willing to pay a premium for each dollar of earnings, often indicating expectations of strong future growth (growth stocks). Conversely, a low P/E ratio (e.g., below 15) might signify that the market perceives the stock as undervalued (value stocks), potentially due to slower growth prospects or higher risk.
- Advantages of using P/E ratio: Easily understood and widely used, readily available data, provides a quick comparison between companies.
- Disadvantages of using P/E ratio: Can be distorted by one-time events (e.g., asset sales), earnings manipulation, not suitable for companies with negative earnings, different accounting practices can influence EPS.
- Variations include the forward P/E ratio, which uses projected future earnings instead of past earnings.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B)
The Price-to-Book ratio (P/B ratio) compares a company's market capitalization to its book value of equity. The calculation is: P/B Ratio = Market Capitalization / Book Value of Equity. Book value represents the net asset value of a company – its assets minus its liabilities. The P/B ratio is particularly useful for valuing companies with substantial tangible assets, such as those in the financial or industrial sectors. However, it's less relevant for companies with primarily intangible assets, like technology firms, where intellectual property holds significant value but isn't fully reflected in book value.
- Limitations of P/B ratio: Doesn't account for future growth potential, intangible assets are often undervalued, different accounting methods can impact book value.
- It's crucial to distinguish between tangible book value (physical assets) and intangible assets (brand value, intellectual property).
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S)
The Price-to-Sales ratio (P/S ratio) compares a company's market capitalization to its annual revenue. The calculation is: P/S Ratio = Market Capitalization / Annual Revenue. This metric is useful for companies that are not yet profitable or have fluctuating earnings. It focuses on the revenue generation capacity of the business, offering a valuation benchmark even when earnings are negative. This makes it particularly useful for valuing early-stage companies or loss-making companies experiencing rapid top-line growth.
- Advantages of P/S ratio: Applicable to companies with negative earnings, provides a simple measure of revenue valuation.
- Disadvantages of P/S ratio: Doesn't consider profitability, ignores expenses and profit margins, less informative than P/E for established profitable companies.
Dividend Yield
The dividend yield is the annual dividend per share expressed as a percentage of the current market price. The calculation is: Dividend Yield = (Annual Dividend per Share / Market Price per Share) * 100. It's a crucial metric for income-oriented investors, showing the return on investment from dividends alone. A high dividend yield can be attractive but also indicates potential risks, such as the sustainability of the dividend payments and the overall health of the company.
- Risks associated with high dividend yields: Companies might cut dividends if earnings decline, high yields can sometimes signal financial distress.
- Importance of dividend sustainability: Analyze the dividend payout ratio (dividends paid relative to earnings) to assess the long-term sustainability of the dividend.
Analyzing Valuation in Context: Beyond the Numbers
While individual valuation metrics provide valuable insights, it's crucial to consider them within a broader context.
Industry Benchmarks
Comparing a company's valuation to its industry peers is essential. This involves analyzing industry average P/E, P/B, and P/S ratios to determine whether a company is trading at a premium or discount to its competitors. Identifying appropriate industry benchmarks requires careful consideration of the company’s business model and competitive landscape.
- How to identify industry benchmarks: Use financial databases (like Bloomberg or Refinitiv) to identify companies with similar business models, revenue streams, and market positions.
- Use of industry average P/E, P/B, and P/S ratios: These averages offer a point of reference for assessing whether a company's valuation is relatively high or low.
Growth Prospects
Future growth expectations significantly impact current valuations. High-growth companies typically command higher valuation multiples (P/E, P/B, P/S) than slower-growing companies. Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis is a more sophisticated valuation method that estimates a company's intrinsic value by discounting its future cash flows back to the present value. This approach integrates growth projections explicitly into the valuation.
- How growth rates affect valuation multiples: Higher anticipated growth rates lead to higher valuation multiples.
- The role of qualitative factors: Factors like management quality, competitive advantages, and market position significantly impact growth prospects and valuations.
Economic Conditions
Macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth significantly influence stock valuations. Rising interest rates generally put downward pressure on valuations, while periods of high inflation and economic uncertainty can lead to market corrections. Central bank policies play a critical role in shaping these conditions and their impact on asset prices.
- How economic downturns can affect valuations: Economic recessions often lead to lower valuations due to reduced earnings and increased uncertainty.
- The role of central bank policies: Monetary policy decisions (e.g., interest rate changes) can dramatically impact market sentiment and asset valuations.
Practical Application and BofA Resources
Integrating these valuation metrics into your investment decision-making process requires a structured approach.
Building a Valuation Framework
Developing a robust investment strategy involves considering multiple valuation metrics, performing thorough due diligence, and combining quantitative data with qualitative analysis of the company and its industry. No single metric provides a complete picture, and a holistic approach is vital.
- Consideration of multiple valuation metrics: Use several metrics in conjunction to gain a comprehensive view of a company’s valuation.
- Importance of qualitative analysis: Analyze factors like management quality, competitive landscape, and industry trends beyond quantitative metrics.
Utilizing BofA Research
BofA provides a wide range of research reports, market data, and analytical tools to aid investors in their valuation analysis. Our team of experienced analysts offers insightful perspectives and helps you navigate the market's complexities. [Insert links to relevant BofA research resources here].
- Examples of BofA resources for valuation analysis: Analyst reports, equity research, market data platforms.
Conclusion: Mastering Stock Market Valuations for Informed Investing
This guide has highlighted the importance of understanding key valuation metrics like the P/E ratio, P/B ratio, P/S ratio, and dividend yield. However, it is crucial to remember that effective stock market valuation requires a holistic approach that considers these metrics within their broader context – industry benchmarks, growth prospects, and prevailing economic conditions. By combining quantitative analysis with qualitative insights, investors can make more informed decisions and build robust investment strategies. Learn more about utilizing BofA's resources for effective stock market valuation and significantly improve your investment strategies using these techniques to understand and interpret stock market valuations.

Featured Posts
-
 The One Controller To Almost Rule Them All A Comprehensive Guide
May 12, 2025
The One Controller To Almost Rule Them All A Comprehensive Guide
May 12, 2025 -
 Comment Jose Aldo A Appris A S Adapter Pour Reussir
May 12, 2025
Comment Jose Aldo A Appris A S Adapter Pour Reussir
May 12, 2025 -
 Cardinals In The Running For Next Pope A Conclave Preview
May 12, 2025
Cardinals In The Running For Next Pope A Conclave Preview
May 12, 2025 -
 Increased Resistance To Ev Mandates From Car Dealerships
May 12, 2025
Increased Resistance To Ev Mandates From Car Dealerships
May 12, 2025 -
 How To Watch The Celtics Vs Knicks Game Live Stream And Tv Broadcast Details
May 12, 2025
How To Watch The Celtics Vs Knicks Game Live Stream And Tv Broadcast Details
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Top Australian Prospect Commits To Oregon Coach Graves Recruiting Success
May 13, 2025
Top Australian Prospect Commits To Oregon Coach Graves Recruiting Success
May 13, 2025 -
 Finding Information On Angela Swartz
May 13, 2025
Finding Information On Angela Swartz
May 13, 2025 -
 Angela Swartz In The Spotlight
May 13, 2025
Angela Swartz In The Spotlight
May 13, 2025 -
 The Angela Swartz Story
May 13, 2025
The Angela Swartz Story
May 13, 2025 -
 Angela Swartz News And Updates
May 13, 2025
Angela Swartz News And Updates
May 13, 2025
