Investigation Into Persistent Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following Ohio Train Derailment

Table of Contents
Types of Persistent Toxic Chemicals Released and Their Health Impacts
The Ohio train derailment released a cocktail of hazardous chemicals, many known for their toxicity and potential for long-term health problems. Key among these are vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate, both classified as volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These persistent organic pollutants are not easily broken down in the environment, posing a significant threat to human health.
-
Vinyl Chloride: A colorless gas used in the production of PVC plastics, vinyl chloride is a known carcinogen. Exposure, even at low levels, is linked to an increased risk of several cancers, including liver cancer, brain cancer, and leukemia. Long-term exposure can also lead to liver damage and other serious health consequences.
-
Butyl Acrylate: This colorless liquid is used in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. Acute exposure to butyl acrylate causes eye, skin, and respiratory irritation. However, the potential long-term health effects of low-level exposure remain under investigation, with concerns regarding respiratory problems and other systemic effects.
Other chemicals released during the derailment are also undergoing investigation for their potential long-term health impacts. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provide valuable resources and ongoing updates on the health effects of these chemicals. [Insert links to CDC and EPA resources here]. Understanding the specific properties and health risks associated with each chemical is critical for effective environmental testing and building remediation.
Methods Used to Investigate Chemical Contamination in Buildings
Investigating chemical contamination in buildings following the Ohio train derailment requires sophisticated methods for detection and quantification. A multi-pronged approach is necessary to accurately assess the extent of contamination and guide remediation efforts.
-
Air Sampling: Specialized pumps and filters are used to collect air samples, allowing for the identification and quantification of airborne pollutants. This method is crucial for determining the concentration of VOCs and other volatile chemicals in the indoor environment.
-
Surface Wipe Sampling: Surface wipe sampling involves using absorbent materials to collect residues from surfaces such as floors, walls, and furniture. This technique helps identify persistent toxic chemicals that may have settled on surfaces.
-
Water Sampling: Water samples are collected to analyze for dissolved contaminants. This is particularly important for buildings with potential for water contamination, such as those with compromised plumbing or proximity to contaminated water sources.
-
Laboratory Analysis: Collected samples are analyzed in accredited laboratories using advanced techniques like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to precisely identify and quantify the various chemicals present. This sophisticated environmental testing is crucial for accurate contamination assessment. Keywords: environmental testing, chemical analysis, contamination assessment.
Assessment of Long-Term Health Risks to Building Occupants
The long-term health risks to residents and workers in buildings affected by the derailment are a major concern. Ongoing assessment involves a combination of approaches:
-
Epidemiological Studies: Longitudinal epidemiological studies will be necessary to track the health of exposed populations over time, looking for increased rates of specific illnesses. This will help determine the long-term health effects of exposure to the released chemicals.
-
Biomonitoring: Biomonitoring techniques, such as blood and urine tests, can help detect the presence of chemicals or their metabolites in the bodies of exposed individuals. This provides direct evidence of exposure and can be linked to potential health outcomes.
Potential long-term health problems related to even low-level exposure include:
- Increased cancer rates
- Respiratory illnesses (asthma, chronic bronchitis)
- Neurological effects (cognitive impairment, neurological disorders)
- Reproductive health concerns
These concerns highlight the critical need for comprehensive long-term health monitoring and support for affected communities. Keywords: long-term health effects, epidemiological studies, public health risk.
Remediation Strategies for Contaminated Buildings
Remediation of buildings affected by the chemical spill requires tailored strategies depending on the type and extent of contamination. Several approaches are being employed:
-
Air Scrubbing and Filtration: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and air scrubbers can remove airborne contaminants, improving indoor air quality.
-
Surface Cleaning and Decontamination: Thorough cleaning and decontamination of surfaces using specialized cleaning agents can remove chemical residues.
-
Specialized Waste Disposal: Contaminated materials must be properly disposed of according to hazardous waste regulations to prevent further environmental contamination.
-
Building Demolition: In severe cases of contamination, building demolition may be necessary to ensure complete removal of hazardous materials.
Effective building remediation requires careful planning, rigorous testing, and adherence to safety protocols. Keywords: building remediation, environmental cleanup, decontamination procedures.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Investigation into Persistent Toxic Chemicals in Buildings Following the Ohio Train Derailment
The Ohio train derailment has underscored the devastating consequences of accidental chemical releases and the urgent need for robust remediation efforts. The investigation into persistent toxic chemicals in affected buildings is ongoing, and the potential long-term consequences for public health are significant. Ongoing monitoring, transparent communication, and proactive remediation strategies are vital to protect the health and well-being of affected communities. We must remain vigilant and advocate for a comprehensive response to this environmental disaster. Stay informed about the ongoing investigation into persistent toxic chemical cleanup efforts and demand accountability for the safety and health of all those affected by the Ohio train derailment. Let's work together to ensure effective building safety and promote a healthy future for our communities.

Featured Posts
-
 David Rosenberg Bank Of Canadas Timid Monetary Policy Under Fire
Apr 29, 2025
David Rosenberg Bank Of Canadas Timid Monetary Policy Under Fire
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Navigate Adhd Naturally Lifestyle Changes For Better Management
Apr 29, 2025
Navigate Adhd Naturally Lifestyle Changes For Better Management
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyr Porsche Macan Allt Um Fyrstu Rafutgafuna
Apr 29, 2025
Nyr Porsche Macan Allt Um Fyrstu Rafutgafuna
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Federal Intervention In Minnesota The Transgender Sports Debate
Apr 29, 2025
Federal Intervention In Minnesota The Transgender Sports Debate
Apr 29, 2025 -
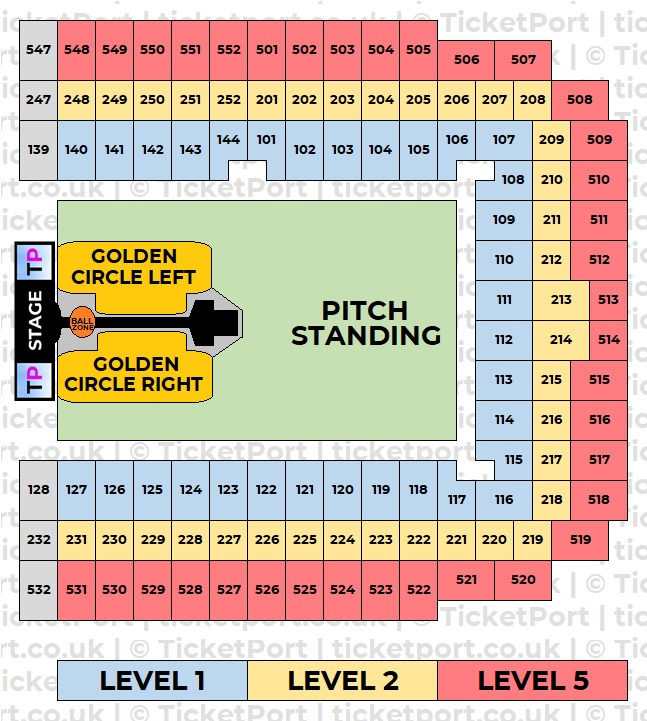 Getting Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets The Ultimate Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Getting Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets The Ultimate Guide
Apr 29, 2025
 50 Godini Praznuva Lyubimetst Na Milioni
50 Godini Praznuva Lyubimetst Na Milioni
