Interest Rate Differentials: Why The Fed Won't Follow Other Central Banks
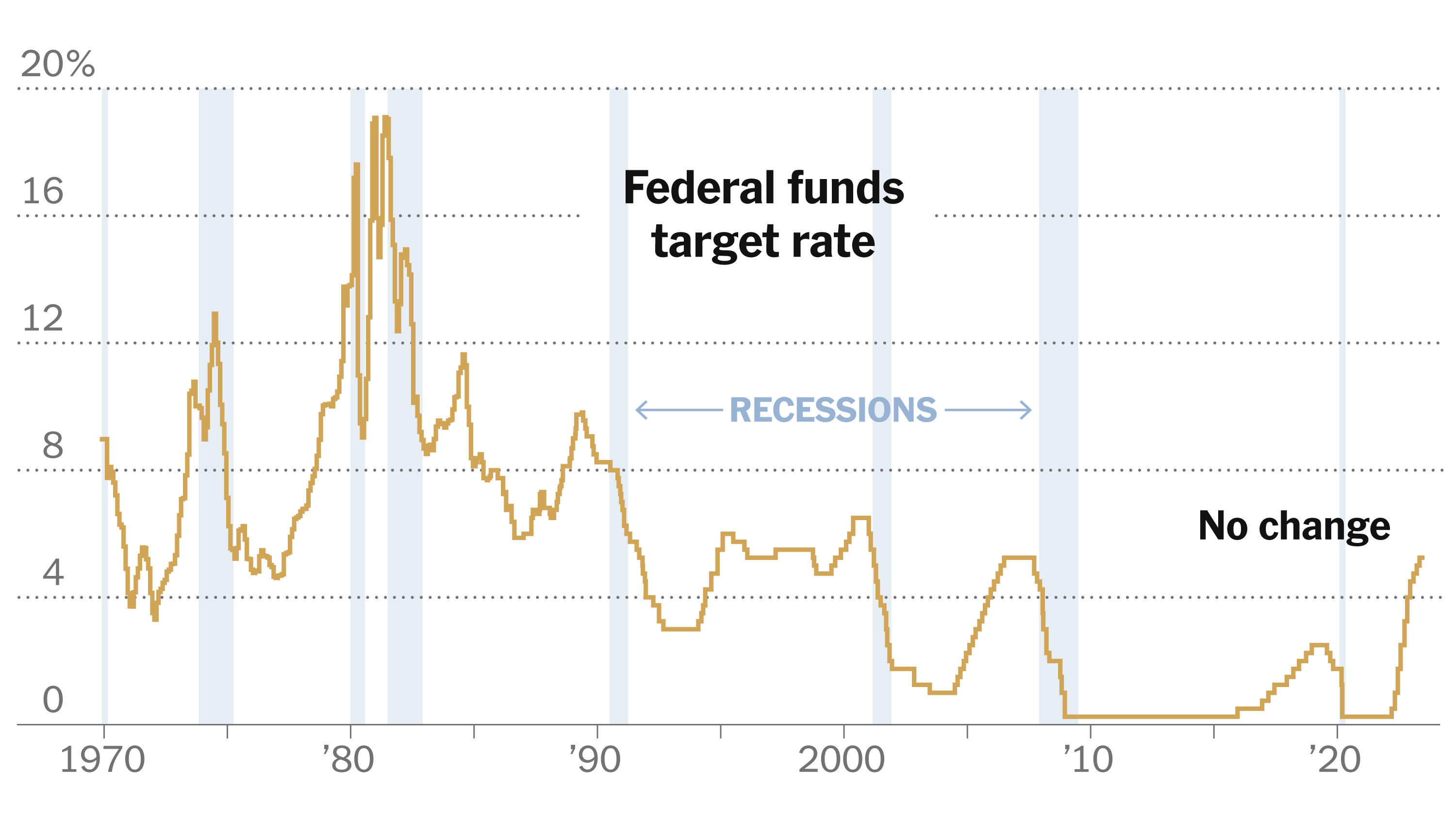
Table of Contents
Unique Economic Conditions in the US
The US economic landscape presents unique challenges that necessitate a distinct approach to monetary policy compared to other nations. This explains, in part, the widening interest rate differentials observed globally.
Inflationary Pressures
The US faces particularly stubborn inflationary pressures, significantly impacting interest rate differentials. These pressures differ from those in other developed economies, leading the Fed to adopt a more aggressive stance.
- Higher inflation rates compared to other developed economies: The US has experienced consistently higher inflation rates than many of its global counterparts, necessitating more forceful intervention to curb rising prices. This contrast in inflation rates directly contributes to the widening interest rate differentials.
- Strong domestic demand contributing to price pressures: Robust consumer spending and business investment fuel demand-pull inflation, adding to the price pressures the Fed must address through interest rate adjustments. This domestic demand differs from the more subdued demand seen in some other economies, influencing interest rate differential analysis.
- Supply chain bottlenecks impacting goods availability and costs: Ongoing supply chain disruptions continue to constrain the supply of goods, contributing to cost-push inflation and widening the gap in interest rate differentials. The US, while recovering, still faces significant supply-side constraints.
- Wage growth outpacing productivity gains: Rapid wage growth, while positive for workers, can exacerbate inflationary pressures if not matched by corresponding productivity increases. This creates a unique challenge for the Fed, contributing to the divergence in interest rate differentials.
Robust Labor Market
The US boasts a historically tight labor market, a factor influencing the Fed's approach to interest rate differentials. This low unemployment rate offers the Fed more flexibility in raising rates than central banks in countries facing higher unemployment.
- Low unemployment rate allows for higher interest rates without immediate recessionary fears: The strong labor market provides a buffer against immediate recessionary risks, allowing the Fed to pursue more aggressive interest rate hikes than central banks in economies with higher unemployment.
- Strong wage growth, potentially fueling inflation: High employment and strong wage growth, while positive, can contribute to a wage-price spiral, further fueling inflation and prompting the Fed's interest rate adjustments. This contributes to significant interest rate differentials compared to nations with weaker wage growth.
- Potential for wage-price spiral necessitates proactive monetary policy: The potential for a wage-price spiral necessitates a proactive monetary policy response from the Fed to preemptively curb inflationary pressures before they become entrenched. This explains the more aggressive interest rate hikes compared to other economies, which are often less concerned about wage-price pressures.
Differing Monetary Policy Strategies
The Fed's monetary policy strategy differs significantly from other central banks, creating noticeable interest rate differentials. This difference in approach is based on data dependency and forward guidance.
Data Dependency
The Fed's emphasis on a data-dependent approach to monetary policy sets it apart from other central banks. This flexibility allows the Fed to respond to changing economic conditions more nimbly.
- Focus on inflation data, employment figures, and other economic indicators: The Fed closely monitors a range of economic indicators to inform its policy decisions, resulting in a more reactive approach to interest rate adjustments. This reactive approach contrasts with some banks that rely more on pre-set targets or timelines.
- Flexibility to adjust interest rates based on evolving economic conditions: The data-dependent approach provides flexibility to adjust interest rates as new economic data emerges, allowing for a more nuanced response to changing circumstances. This contributes to the dynamism of the interest rate differentials.
- Less reliance on pre-set targets or timelines: Unlike some central banks that may adhere to pre-determined interest rate paths, the Fed’s data-dependent approach makes its trajectory less predictable, creating unpredictable interest rate differentials.
Forward Guidance
The Fed's communication strategy regarding future monetary policy also contributes to the divergence in interest rate differentials. Its less precise forward guidance allows for greater flexibility.
- Ambiguity in future policy announcements allows for greater adaptability: The less precise forward guidance allows the Fed to adapt its policy to unforeseen economic events or shifts in the data without being constrained by previous commitments. This is a key differentiator, impacting interest rate differentials.
- Reduces the risk of market misinterpretations and overly strong reactions: The less precise guidance aims to avoid market misinterpretations that could lead to overly strong reactions to policy announcements. This contributes to more stable markets, though interest rate differentials may remain volatile.
- Enables more nuanced adjustments to monetary policy based on new data: The absence of rigid commitments through forward guidance enables the Fed to make more nuanced adjustments to monetary policy as new data become available, resulting in more flexible interest rate differentials.
Global Economic Interdependencies and Geopolitical Factors
Global economic interdependencies and geopolitical factors also play a significant role in explaining the divergence in interest rate differentials.
Global Uncertainty
The current geopolitical landscape introduces significant uncertainty, influencing the Fed’s decision-making regarding interest rate differentials.
- Geopolitical risks affecting global supply chains and inflation: The war in Ukraine, for example, has disrupted global supply chains and exacerbated inflationary pressures worldwide, making it challenging to predict the long-term economic impact and adjust interest rate differentials accordingly.
- Uncertainty surrounding the duration and impact of the war in Ukraine: The ongoing war creates significant uncertainty about future economic growth and inflation, making it difficult for the Fed to set a clear path for interest rate adjustments and manage interest rate differentials.
- Energy price volatility impacting economic growth and inflation: Fluctuations in energy prices add to the uncertainty and complicate the Fed’s task in managing inflation and setting appropriate interest rates. This uncertainty contributes to the dynamics of global interest rate differentials.
Dollar's Reserve Currency Status
The US dollar's role as the world's reserve currency significantly influences the Fed's monetary policy decisions and the resulting interest rate differentials.
- Strong dollar can impact global trade balances and exchange rates: Raising interest rates strengthens the dollar, which can affect global trade balances and exchange rates, requiring careful consideration of international repercussions. This is a major factor impacting interest rate differentials.
- Increased capital flows into the US can create imbalances: Higher US interest rates attract capital inflows, potentially creating imbalances in global capital markets. The Fed must consider the global implications of its actions when setting interest rates and managing interest rate differentials.
- Need for coordination with other central banks to manage global financial stability: Given the interconnectedness of global financial markets, the Fed needs to coordinate with other central banks to manage global financial stability and mitigate the risks associated with significant interest rate differentials.
Conclusion
The divergence in interest rate differentials between the Fed and other central banks is a complex issue driven by unique US economic conditions, differing monetary policy approaches, and global uncertainties. Understanding these interest rate differentials is vital for navigating the current economic climate. Staying informed about the Fed's actions and the broader global economic landscape is crucial for both investors and businesses. Keep abreast of developments concerning interest rate differentials and their impact on your financial strategies. Effective management of your investments requires a thorough understanding of these dynamics and their potential implications.

Featured Posts
-
 Victoire Du Psg Sur Dijon En Arkema Premiere Ligue Un Match Tendu
May 09, 2025
Victoire Du Psg Sur Dijon En Arkema Premiere Ligue Un Match Tendu
May 09, 2025 -
 Analysis Proposed Changes To Uk Visa Application Process For Specific Nationalities
May 09, 2025
Analysis Proposed Changes To Uk Visa Application Process For Specific Nationalities
May 09, 2025 -
 Montoya Doohans F1 Career Path Already Set
May 09, 2025
Montoya Doohans F1 Career Path Already Set
May 09, 2025 -
 Understanding Jeanine Pirro The Fox News Perspective
May 09, 2025
Understanding Jeanine Pirro The Fox News Perspective
May 09, 2025 -
 Live Tv Malfunction Exposes Colapintos F1 Sponsorship
May 09, 2025
Live Tv Malfunction Exposes Colapintos F1 Sponsorship
May 09, 2025
