Improving Driving Safety For Individuals With ADHD: Research Insights
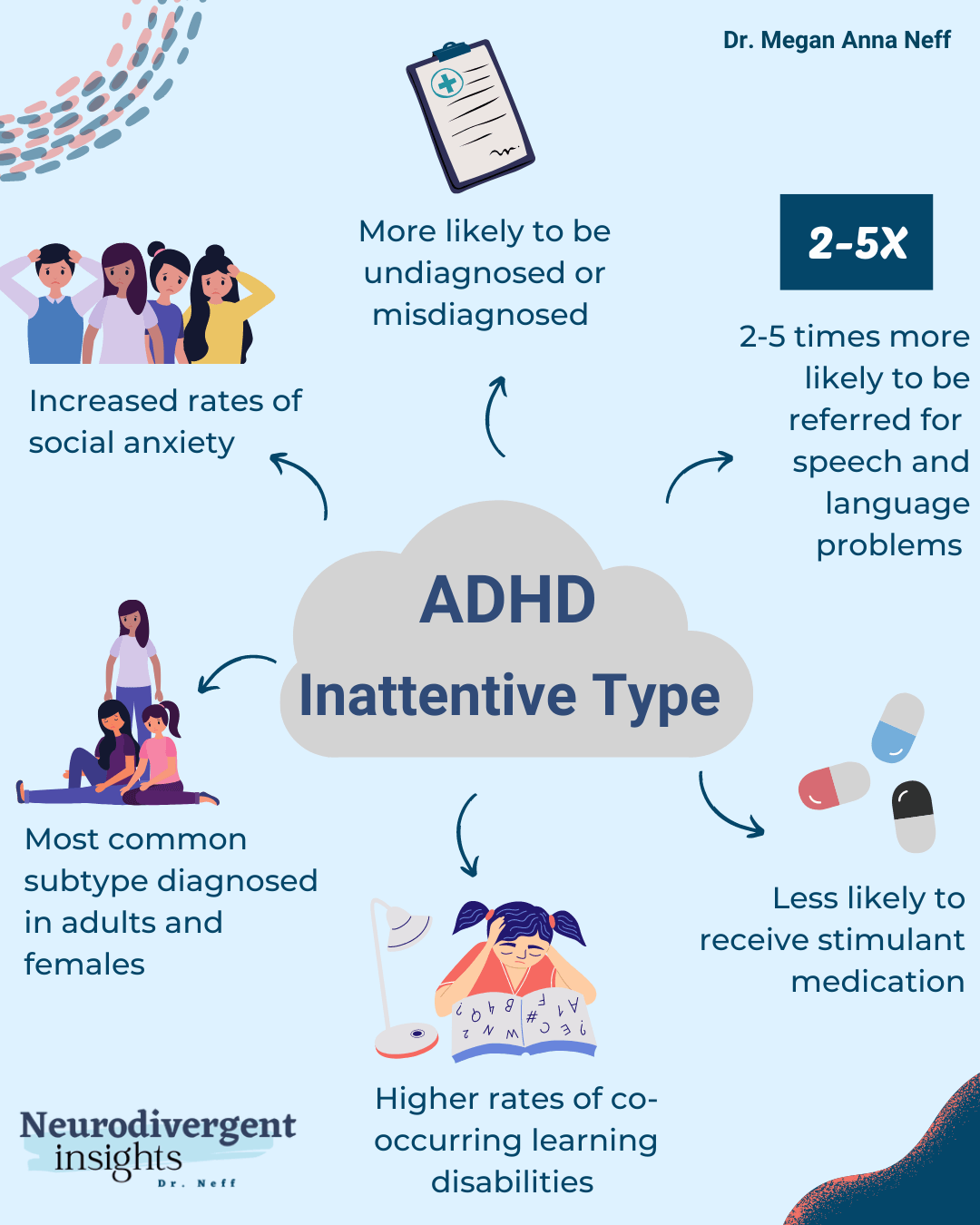
Table of Contents
Understanding the Challenges: ADHD and Driving Performance
Individuals with ADHD face several challenges behind the wheel, directly impacting their driving safety. Understanding these challenges is the first step towards developing effective strategies for improvement.
Increased Risk of Accidents
Research consistently demonstrates that individuals with ADHD are statistically more likely to be involved in motor vehicle accidents than their neurotypical counterparts. This increased risk is attributed to a higher frequency of risky driving behaviors.
- Speeding: Difficulty regulating speed and impulsive acceleration.
- Tailgating: Reduced ability to maintain safe following distances.
- Lane drifting: Inattention and difficulty maintaining lane position.
- Ignoring traffic signals: Impulsivity and inattention to traffic rules.
- Increased reaction time: Slower response to unexpected events on the road.
Studies using both observational methods and driving simulators have confirmed this heightened risk, highlighting the critical need for interventions to improve driving safety for individuals with ADHD.
Cognitive Difficulties and Driving
The cognitive challenges associated with ADHD directly affect driving ability. Executive function deficits, including difficulties with planning, working memory, and impulse control, significantly impact driving performance.
- Difficulty maintaining attention on the road: Mind wandering and distraction lead to lapses in concentration.
- Struggling with complex driving situations: Merging onto highways or navigating busy intersections can be particularly challenging.
- Poor decision-making in unpredictable circumstances: Difficulty responding appropriately to sudden changes or emergencies.
Driving simulators have proven invaluable in researching these cognitive challenges. These simulations allow researchers to objectively measure driving performance and identify specific areas of difficulty for individuals with ADHD.
Medication and Driving Safety
Medication plays a crucial role in managing ADHD symptoms and can positively impact driving safety. However, it's essential to understand both the benefits and potential side effects.
- Types of medication used: Stimulants and non-stimulants are commonly prescribed for ADHD, each with its own profile of effects.
- Potential side effects and their impact on driving: Some medications may cause drowsiness, dizziness, or reduced alertness, which can impair driving ability. Open communication with your physician is crucial.
- Importance of open communication with prescribing physicians: Discuss any concerns about driving safety with your doctor to ensure the medication dosage and type are appropriate.
While medication can significantly improve focus and impulse control, it's vital to follow your doctor's instructions carefully and be aware of potential side effects that might affect your driving.
Strategies for Improving Driving Safety
Improving driving safety for individuals with ADHD requires a multi-pronged approach combining adaptive driving techniques, therapeutic interventions, and technological aids.
Adaptive Driving Techniques
Implementing practical strategies can significantly improve driving skills and safety for individuals with ADHD.
- Practicing defensive driving techniques: Maintaining a wider following distance, scanning the road ahead, and anticipating potential hazards.
- Utilizing navigational aids (GPS): Reducing cognitive load by relying on GPS for route planning and navigation.
- Maintaining a safe following distance: Providing more reaction time in case of unexpected events.
- Planning routes in advance: Minimizing stress and unexpected situations during the drive.
These adaptive techniques help mitigate some of the challenges posed by ADHD symptoms.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Drivers
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a powerful approach to address impulsivity and improve attention in the context of driving.
- Techniques to enhance self-awareness and self-regulation: Identifying triggers for risky driving behaviors and developing strategies for managing them.
- Improving reaction time and decision-making skills behind the wheel: Practicing responding appropriately to various driving scenarios.
CBT equips individuals with the skills and tools to manage their ADHD symptoms and make safer driving choices.
Driving Assessments and Professional Guidance
Professional driving assessments provide valuable insights into specific driving weaknesses and allow for personalized recommendations.
- Identifying specific driving weaknesses: Pinpointing areas needing improvement, such as lane keeping or reaction time.
- Developing personalized strategies: Creating tailored interventions to address individual challenges.
- Accessing driving rehabilitation programs: Participating in structured programs designed to improve driving skills and safety.
Professional evaluations offer a structured approach to improving driving safety for individuals with ADHD.
Technological Aids
Technological advancements offer supplementary support to enhance driving safety for those with ADHD.
- Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS): Features like lane departure warnings, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control can provide additional safety measures.
- Smartphone apps for driver monitoring and feedback: Apps that track driving behavior and provide feedback on areas for improvement.
- GPS navigation systems: Simplifying route planning and reducing cognitive load.
These technological aids offer an extra layer of safety and support for individuals with ADHD.
Conclusion
Improving driving safety for individuals with ADHD requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the unique challenges posed by ADHD, implementing adaptive driving techniques, and utilizing available resources like CBT, professional assessments, and technological aids, individuals with ADHD can significantly enhance their driving safety. Remember to consult with your physician and consider seeking professional driving assessments. Proactive steps toward improving driving safety for individuals with ADHD are crucial for ensuring both personal well-being and public safety. Take control of your driving safety and explore the resources available to improve your skills and confidence behind the wheel. Don't hesitate to seek help—improving driving safety for individuals with ADHD is a journey worth taking.

Featured Posts
-
 Fck Gegen Bayern Champions League Duell Ohne Betzenberg Feuer
Apr 29, 2025
Fck Gegen Bayern Champions League Duell Ohne Betzenberg Feuer
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Reliance Shares Surge Biggest Gain In 10 Months
Apr 29, 2025
Reliance Shares Surge Biggest Gain In 10 Months
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Legendas F1 Technologia Porsche Koezuti Autoban
Apr 29, 2025
Legendas F1 Technologia Porsche Koezuti Autoban
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Antlaq Fealyat Fn Abwzby Dlyl Shaml 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025
Antlaq Fealyat Fn Abwzby Dlyl Shaml 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Kontsertt Na Dscheryata Na Iva Ekimova Sveti Valentin
Apr 29, 2025
Kontsertt Na Dscheryata Na Iva Ekimova Sveti Valentin
Apr 29, 2025
 50 Godini Praznuva Lyubimetst Na Milioni
50 Godini Praznuva Lyubimetst Na Milioni
