Impact Of Rosy Apple Aphid: 10-30% Decrease Predicted In Apple Production
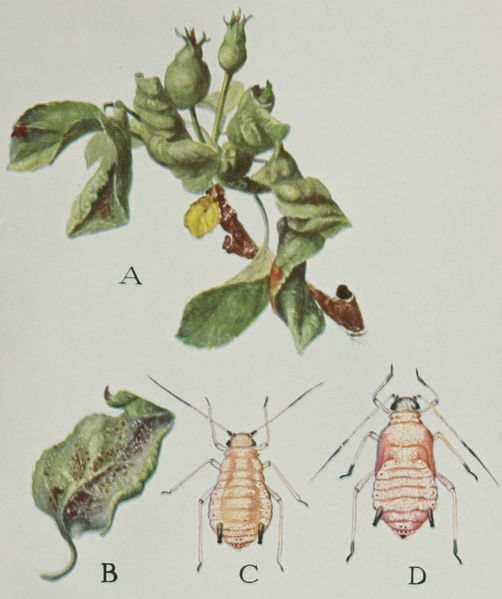
Table of Contents
Understanding the Rosy Apple Aphid and its Life Cycle
The Rosy Apple Aphid is easily identifiable by its characteristic pink or rosy hue. This small aphid primarily infests apple trees, feeding on their sap and causing significant damage. Its life cycle involves several stages:
- Eggs: Overwintering eggs are laid on apple twigs and branches.
- Nymphs: These wingless young aphids hatch in spring, feeding voraciously on new growth.
- Adults: Winged adults develop later in the season, allowing the aphid to spread to new trees and orchards.
The Rosy Apple Aphid utilizes piercing-sucking mouthparts to extract sap from apple leaves and buds. This feeding method leads to a variety of detrimental effects on the apple tree. Its preferred hosts are apple trees ( Malus domestica), making apple orchards particularly vulnerable.
Damage Caused by Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations
Rosy Apple Aphid infestations cause both direct and indirect damage to apple trees and their fruit:
-
Direct Damage: The aphids' feeding leads to leaf curling, distorted growth, and stunted development of shoots and leaves. Reduced photosynthesis significantly impacts the tree's overall health and vigor.
-
Indirect Damage: The aphids secrete honeydew, a sticky substance that attracts ants and promotes the growth of sooty mold. This sooty mold covers the leaves and fruit, affecting their appearance and marketability. The reduced fruit size and overall yield further exacerbate the economic losses.
-
Impact on Fruit Quality: Infested apples may be smaller, misshapen, and exhibit poor color development, rendering them unsuitable for sale. The overall impact on tree health can lead to decreased longevity and productivity over several seasons.
Predicting the Extent of Crop Losses Due to Rosy Apple Aphid
Research and field observations support the prediction of a 10-30% decrease in apple production due to Rosy Apple Aphid infestations. Several factors influence the severity of infestations:
-
Climate: Mild winters and warm, humid springs favor aphid reproduction and population growth.
-
Orchard Management: Poor orchard sanitation, inadequate pruning, and the absence of pest control measures can exacerbate infestations.
-
Geographical Areas: Regions with favorable climatic conditions and a high density of apple orchards experience more severe infestations. For example, certain areas in Europe and North America have reported significantly high levels of Rosy Apple Aphid presence. These areas are especially vulnerable to crop losses.
Effective Management Strategies for Rosy Apple Aphid Control
Effective Rosy Apple Aphid control relies on a multi-faceted approach, including Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies:
-
Biological Control: Introducing natural predators such as ladybugs and lacewings can help control aphid populations.
-
Chemical Control: Insecticides, when used judiciously and according to label instructions, provide effective control. Careful selection of insecticides is important to minimize harm to beneficial insects and the environment.
-
Cultural Practices: Proper pruning, sanitation (removal of infested leaves and twigs), and the use of resistant apple varieties can help to minimize infestations. Regular monitoring of the orchard is crucial for early detection and timely intervention.
Implementing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach is crucial. IPM balances the use of various methods to control pest populations while minimizing environmental impact and maintaining orchard health.
Conclusion: Protecting Apple Production from the Rosy Apple Aphid Threat
The Rosy Apple Aphid poses a significant threat to global apple production, with the potential for a 10-30% decrease in yields. Effective management strategies, including biological control, judicious use of insecticides, and the implementation of sound cultural practices are vital for mitigating the impact of this devastating pest. The adoption of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is essential for long-term sustainable apple production. To protect your apple crops, proactive rosy apple aphid control, managing rosy apple aphids effectively, and rosy apple aphid prevention are crucial. Learn more about integrated pest management strategies and begin implementing preventative measures today.

Featured Posts
-
 Fthina Kaysima Stin Kypro Poy Na Breite Tis Kalyteres Times
May 19, 2025
Fthina Kaysima Stin Kypro Poy Na Breite Tis Kalyteres Times
May 19, 2025 -
 Eurosong 2024 Marko Bosnjak Predstavlja Hrvatsku
May 19, 2025
Eurosong 2024 Marko Bosnjak Predstavlja Hrvatsku
May 19, 2025 -
 Eurovision Song Contest 2026 Oernskoeldsviks Intresseanmaelan
May 19, 2025
Eurovision Song Contest 2026 Oernskoeldsviks Intresseanmaelan
May 19, 2025 -
 Adios A Juan Aguilera Un Hito En El Tenis Masters 1000
May 19, 2025
Adios A Juan Aguilera Un Hito En El Tenis Masters 1000
May 19, 2025 -
 Luchtvaartverkeer Maastricht Minder Passagiers Verwacht In 2025
May 19, 2025
Luchtvaartverkeer Maastricht Minder Passagiers Verwacht In 2025
May 19, 2025
