Global Deforestation Surges: Wildfires Contribute To Unprecedented Loss
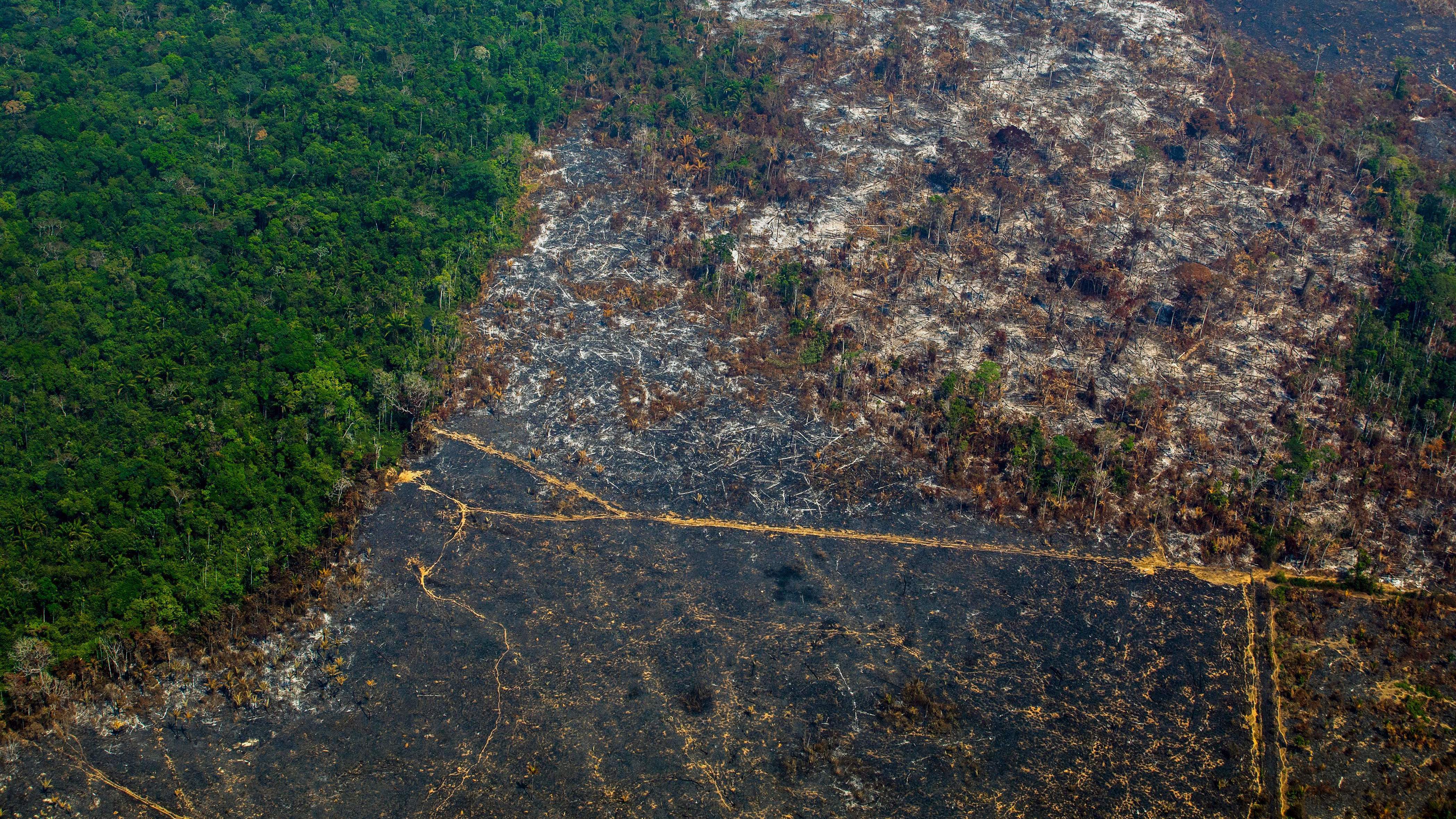

Table of Contents
The Extent of Global Deforestation and its Causes
Global deforestation refers to the clearing of forests on a global scale, transforming these vital ecosystems into other land uses. Currently, deforestation is occurring at an alarming rate, with millions of hectares of forest lost annually. This relentless destruction stems from a complex interplay of factors:
- Agriculture: The expansion of agricultural land for crops like soybeans, palm oil, and cattle ranching is a leading driver of deforestation, particularly in tropical regions.
- Logging: Illegal and unsustainable logging practices decimate forests for timber, contributing significantly to deforestation.
- Mining: Mining operations, especially for minerals and fossil fuels, clear vast tracts of forest for access to resources.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction of roads, dams, and other infrastructure projects often leads to forest clearing and fragmentation.
Wildfires as a Major Contributing Factor
Wildfires act as a devastating accelerant to global deforestation. Already weakened ecosystems, often due to the aforementioned drivers, become highly susceptible to fire, resulting in widespread and often irreversible damage.
- Major Wildfire Events: The Amazon rainforest fires of 2019 and the Australian bushfires of 2019-2020 are stark examples of the scale and devastating impact of wildfires on forest cover. These events resulted in the loss of millions of hectares of vital ecosystems.
- Acreage Lost Annually: Globally, millions of hectares of forest are consumed by wildfires each year, significantly contributing to the overall rate of deforestation. These statistics vary year to year depending on weather patterns and human activity, but the overall trend is upward.
- Climate Change's Role: Climate change is playing a crucial role in exacerbating the problem. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increased lightning strikes create conditions ripe for more frequent and intense wildfires, creating a dangerous feedback loop.
Environmental Consequences of Increased Deforestation
The consequences of rampant global deforestation, especially when combined with the devastation of wildfires, are far-reaching and devastating:
Biodiversity Loss
Habitat destruction and fragmentation due to deforestation are the primary drivers of biodiversity loss. Countless plant and animal species are losing their homes, leading to population declines and extinctions.
- Endangered Species: Orangutans in Borneo and Sumatra, jaguars in the Amazon, and numerous bird species are just a few examples of animals facing extinction due to habitat loss from deforestation and wildfires.
- Ecosystem Disruption: The loss of forests disrupts crucial ecosystem services, impacting nutrient cycles, pollination, and water regulation, creating a cascade effect throughout the entire ecosystem.
Climate Change Amplification
Deforestation and wildfires significantly contribute to climate change through increased greenhouse gas emissions. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere; their destruction releases this stored carbon, further fueling global warming.
- Carbon Emissions: Deforestation and wildfires are estimated to contribute significantly to annual global greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating climate change and increasing the likelihood of more frequent and intense wildfires.
- Impact on Global Carbon Sinks: The loss of forests reduces the Earth's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, weakening the planet's natural carbon sinks and accelerating the rate of climate change.
Soil Degradation and Water Cycle Disruption
Deforestation leads to soil erosion, desertification, and disruption of the water cycle. The loss of tree cover exposes the soil to the elements, leading to nutrient depletion and reduced water retention.
- Soil Erosion and Desertification: The loss of forest cover increases soil erosion, leading to desertification and reduced agricultural productivity in affected areas.
- Impact on Water Quality and Availability: Deforestation alters rainfall patterns, reduces water infiltration into the soil, and increases runoff, leading to decreased water availability and reduced water quality.
Economic and Social Impacts of Global Deforestation
The economic and social impacts of global deforestation are profound and far-reaching:
Loss of Livelihoods
Millions of people, particularly indigenous communities, rely on forests for their livelihoods. Deforestation and wildfires deprive these communities of their resources, leading to economic hardship and displacement.
- Affected Communities: Indigenous communities in the Amazon, local farmers dependent on forest products, and those working in sustainable forestry are disproportionately affected by deforestation and wildfires.
- Economic Consequences: The loss of forests can lead to reduced agricultural productivity, loss of income from forest products, and increased poverty in affected regions.
Increased Risk of Natural Disasters
Deforestation increases vulnerability to natural disasters. The loss of tree cover destabilizes slopes, increasing the risk of landslides, while the reduced water absorption capacity of deforested areas increases the risk of floods.
- Areas Affected: Regions experiencing significant deforestation are frequently hit harder by floods, landslides, and other natural disasters due to the loss of natural protection offered by forests.
- Economic and Human Costs: The economic and human costs of these disasters are often devastating, impacting infrastructure, livelihoods, and human lives.
Combating Global Deforestation: Solutions and Strategies
Addressing global deforestation requires a multifaceted approach involving various stakeholders and strategies:
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Sustainable logging techniques, responsible forest management, and reforestation efforts are crucial for mitigating deforestation.
- Successful Initiatives: Certification schemes like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) promote sustainable forest management practices and responsible sourcing of timber.
- Responsible Sourcing: Consumers can play a role by supporting companies that commit to sustainable forestry practices and avoid products derived from illegally logged timber.
Combating Wildfires
Effective wildfire prevention, early detection, and management strategies are essential to minimize the impact of wildfires on forests.
- Prevention Programs: Controlled burns, forest thinning, and improved firebreaks can help prevent the spread of wildfires.
- Technology and Community Involvement: Early warning systems, improved fire suppression techniques, and community involvement are vital for effective wildfire management.
Policy and Legislation
Strong national and international policies and regulations are crucial for protecting forests and combating deforestation.
- Effective Policies: Policies that protect forest areas, promote sustainable forestry, and punish illegal logging are essential.
- International Cooperation: International agreements and collaboration are vital for addressing the transnational nature of deforestation and its associated challenges.
Conclusion
Global deforestation, fueled by a complex interplay of factors including unsustainable agricultural practices, logging, mining, and increasingly, devastating wildfires, poses a significant threat to our planet. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting biodiversity, climate stability, and human well-being. The unprecedented loss of forest cover demands urgent and concerted global action. We must adopt sustainable forestry practices, improve wildfire prevention and management, and strengthen policies that protect forests. To combat deforestation, we need a collective commitment to responsible resource management, effective conservation strategies, and strong international cooperation. Learning about global deforestation, supporting organizations fighting to protect our forests, and advocating for policies that prevent deforestation and promote sustainable forestry are crucial steps towards securing a healthier future for our planet. Ignoring the escalating crisis of global deforestation is simply not an option; the future of our forests, and indeed our planet, depends on immediate and decisive action.

Featured Posts
-
 Analyzing The F1 Drivers Press Conference A Deep Dive
May 26, 2025
Analyzing The F1 Drivers Press Conference A Deep Dive
May 26, 2025 -
 Il Vient Cracher Dans La Soupe La Violente Attaque D Ardisson Contre Baffie
May 26, 2025
Il Vient Cracher Dans La Soupe La Violente Attaque D Ardisson Contre Baffie
May 26, 2025 -
 Understanding The Disappearance Case Studies And Analysis
May 26, 2025
Understanding The Disappearance Case Studies And Analysis
May 26, 2025 -
 Is Dr Terrors House Of Horrors Worth The Visit A Detailed Look
May 26, 2025
Is Dr Terrors House Of Horrors Worth The Visit A Detailed Look
May 26, 2025 -
 Enthoven Sur Le Pen Et Ramadan Morale Publique Et Purete Des M Urs
May 26, 2025
Enthoven Sur Le Pen Et Ramadan Morale Publique Et Purete Des M Urs
May 26, 2025
