Food Prices Rise Faster Than Inflation Again
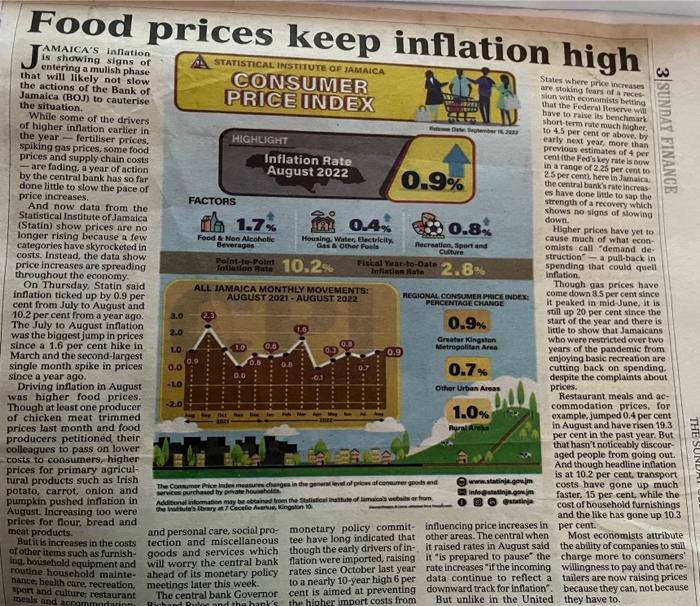
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to Soaring Food Prices
Several interconnected factors contribute to the current surge in food prices exceeding the overall inflation rate. Understanding these elements is key to mitigating the impact on consumers and the economy.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chains, already strained by the pandemic, continue to grapple with significant disruptions. This directly impacts the production and distribution of food products, leading to increased prices.
- Increased transportation costs: Fuel prices have soared, making the transportation of food from farms to processing plants and ultimately to consumers significantly more expensive. Logistics bottlenecks are further driving up costs.
- Labor shortages: A shortage of workers across the agricultural and food processing sectors hampers production and efficiency, pushing prices higher.
- Port congestion: Delays in unloading cargo at ports worldwide create significant backlogs, delaying the delivery of essential food items and increasing costs.
- Geopolitical instability: Conflicts and political instability in key agricultural regions disrupt harvests and exports, limiting supply and driving up prices. The ongoing war in Ukraine, for instance, has significantly impacted global grain supplies.
The impact is substantial. Recent reports show transportation costs alone account for a significant percentage of the increase in food prices, particularly for perishable goods.
Increased Energy Costs
The energy sector plays a crucial role in the entire food system, from farming to transportation and storage. Rising energy prices have a direct and significant impact on the cost of food production.
- Fuel costs for farming equipment: Farmers rely heavily on machinery powered by fossil fuels. Increased fuel costs directly translate to higher production expenses.
- Electricity for processing plants: Food processing plants require substantial energy to operate, and rising electricity prices directly inflate production costs.
- Refrigeration costs: Maintaining cold storage for perishable goods is energy-intensive. Higher energy prices translate to increased costs for storing and transporting temperature-sensitive foods.
Data clearly shows a strong correlation between energy price fluctuations and subsequent increases in food prices, especially for products with longer and more complex supply chains.
Climate Change Impacts
Extreme weather events, a direct consequence of climate change, are wreaking havoc on agricultural production worldwide.
- Droughts: Prolonged periods of drought severely impact crop yields, reducing the availability of essential food staples and increasing prices. Recent droughts in major agricultural regions have led to significant food shortages.
- Floods: Excessive rainfall and flooding damage crops and disrupt farming operations, leading to reduced harvests and price increases.
- Heatwaves: Extreme heat can devastate crops, particularly those sensitive to high temperatures, resulting in lower yields and higher prices.
The impact of climate change on food production is becoming increasingly apparent, with extreme weather events leading to significant price spikes in vulnerable regions.
Geopolitical Instability
International conflicts and political tensions significantly impact global food security and prices.
- Disruptions in grain exports: Conflicts often disrupt the flow of essential food commodities, such as wheat and corn, leading to scarcity and price increases.
- Sanctions and trade wars: Trade restrictions and sanctions can limit access to food supplies, driving up prices in affected regions.
- Resource allocation shifts: Conflicts often lead to the reallocation of resources, diverting funds and attention away from agricultural production and increasing the cost of food.
The ongoing war in Ukraine exemplifies the dramatic impact of geopolitical instability on global food prices, with substantial disruptions to grain exports leading to worldwide shortages and price hikes.
Increased Demand
Rising global population and shifting dietary preferences are also contributing to higher food prices.
- Rising global population: A growing global population increases demand for food, putting pressure on supply chains and leading to price increases.
- Shifting consumer preferences: Increased demand for specific foods, such as meat and processed foods, can lead to imbalances in the market and drive up prices.
Impact of Rising Food Prices on Consumers
The surge in food prices is having a devastating effect on consumers worldwide.
Reduced Purchasing Power
Higher food costs significantly reduce household purchasing power, forcing families to make difficult choices.
- Increased food insecurity: Many households are struggling to afford enough food, leading to increased food insecurity and malnutrition.
- Trade-offs in spending on other necessities: Rising food costs necessitate cuts in spending on other essential goods and services, impacting overall well-being.
Statistics consistently show that a larger percentage of household income is now being allocated to food, leaving less for other needs.
Changes in Consumer Behavior
Consumers are adapting to higher food prices through various strategies.
- Switching to cheaper alternatives: Many consumers are switching to cheaper, often less nutritious, food options to manage their budgets.
- Reducing food waste: Consumers are becoming more conscious of food waste, aiming to minimize spoilage and maximize the value of their food purchases.
- Eating out less: Dining out is becoming increasingly unaffordable for many, leading to a reduction in restaurant spending.
Government Responses and Potential Solutions
Addressing the escalating food price crisis requires a multi-pronged approach involving government interventions and long-term sustainable strategies.
Government Interventions
Governments are implementing various measures to mitigate the impact of rising food prices.
- Subsidies for farmers: Government subsidies can help farmers offset rising production costs and maintain food production.
- Price controls: While controversial, price controls can temporarily curb inflation, but they may also lead to shortages.
- Food assistance programs: Expanding access to food assistance programs can provide vital support for vulnerable populations struggling to afford food.
Long-Term Strategies
Sustainable solutions are essential for ensuring long-term food security.
- Investing in resilient farming techniques: Promoting drought-resistant crops and sustainable agricultural practices can enhance food production in the face of climate change.
- Improving infrastructure: Investing in better transportation and storage infrastructure can improve efficiency and reduce costs throughout the food supply chain.
- Promoting food diversification: Encouraging a more diverse range of crops and food sources can reduce reliance on vulnerable crops and increase resilience to price shocks.
Conclusion
The rise in food prices exceeding inflation is a complex issue driven by a confluence of factors, including supply chain disruptions, increased energy costs, climate change impacts, geopolitical instability, and increased demand. This has profound consequences for consumers, reducing purchasing power and forcing difficult choices. Governments must implement both short-term interventions and invest in long-term strategies to bolster food security and ensure affordable access to nutritious food for all. Stay informed about the issue of rising food costs, exploring resources on ways to combat food inflation, reducing food costs, and finding sustainable food solutions. The urgency of addressing this critical challenge cannot be overstated. We must act decisively to mitigate the effects of food prices rising faster than inflation and build a more resilient and equitable food system.

Featured Posts
-
 Blake Lively Iced Out Sisters Rally Around Amidst A List Falling Out
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively Iced Out Sisters Rally Around Amidst A List Falling Out
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou Benoemen Karin Polman Tot Directeur Hypotheken
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou Benoemen Karin Polman Tot Directeur Hypotheken
May 22, 2025 -
 Avoiding Conflict G 7 And Us Trade Relations In Focus For Finance Ministers
May 22, 2025
Avoiding Conflict G 7 And Us Trade Relations In Focus For Finance Ministers
May 22, 2025 -
 Echo Valley Images Reveal Tense Atmosphere Of New Thriller Starring Sydney Sweeney And Julianne Moore
May 22, 2025
Echo Valley Images Reveal Tense Atmosphere Of New Thriller Starring Sydney Sweeney And Julianne Moore
May 22, 2025 -
 Testing Googles Ai Smart Glasses Features And Functionality
May 22, 2025
Testing Googles Ai Smart Glasses Features And Functionality
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Route 581 Traffic Stopped Following Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Traffic Stopped Following Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025 -
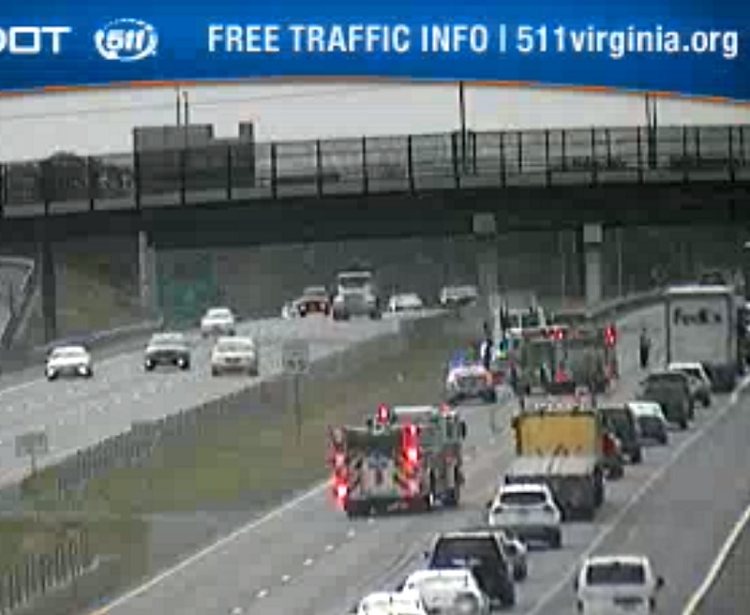 Box Truck Accident Shuts Down Part Of Route 581
May 22, 2025
Box Truck Accident Shuts Down Part Of Route 581
May 22, 2025 -
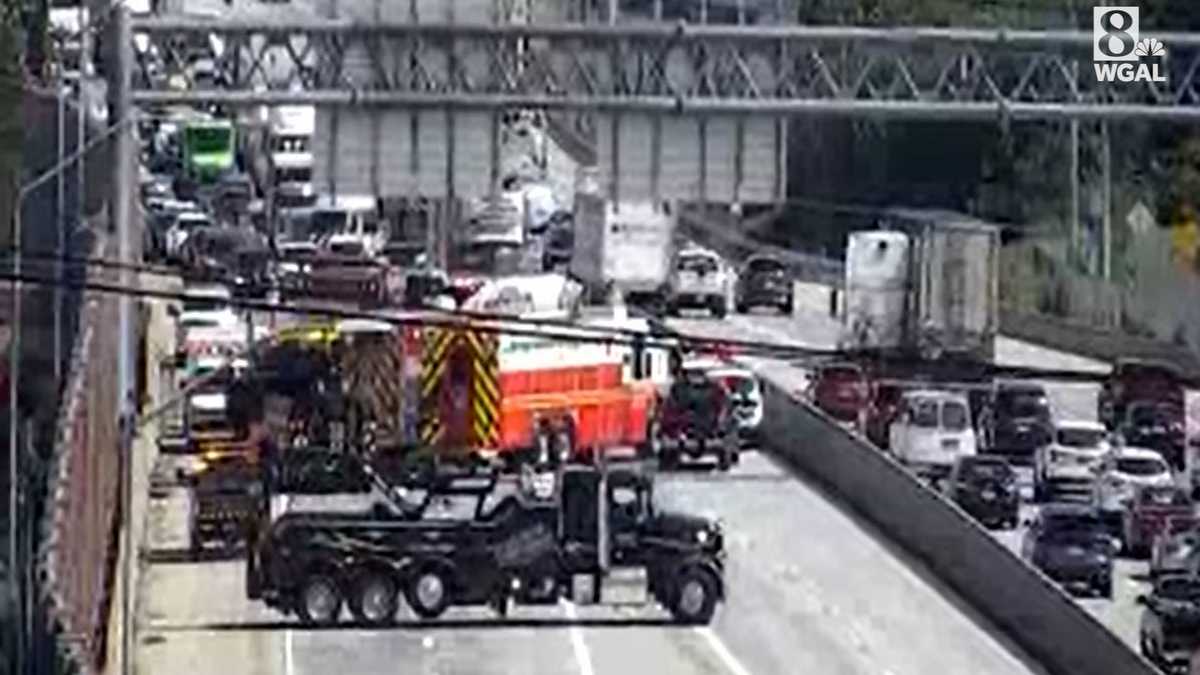 Route 581 Closure Box Truck Crash Causes Major Delays
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Closure Box Truck Crash Causes Major Delays
May 22, 2025 -
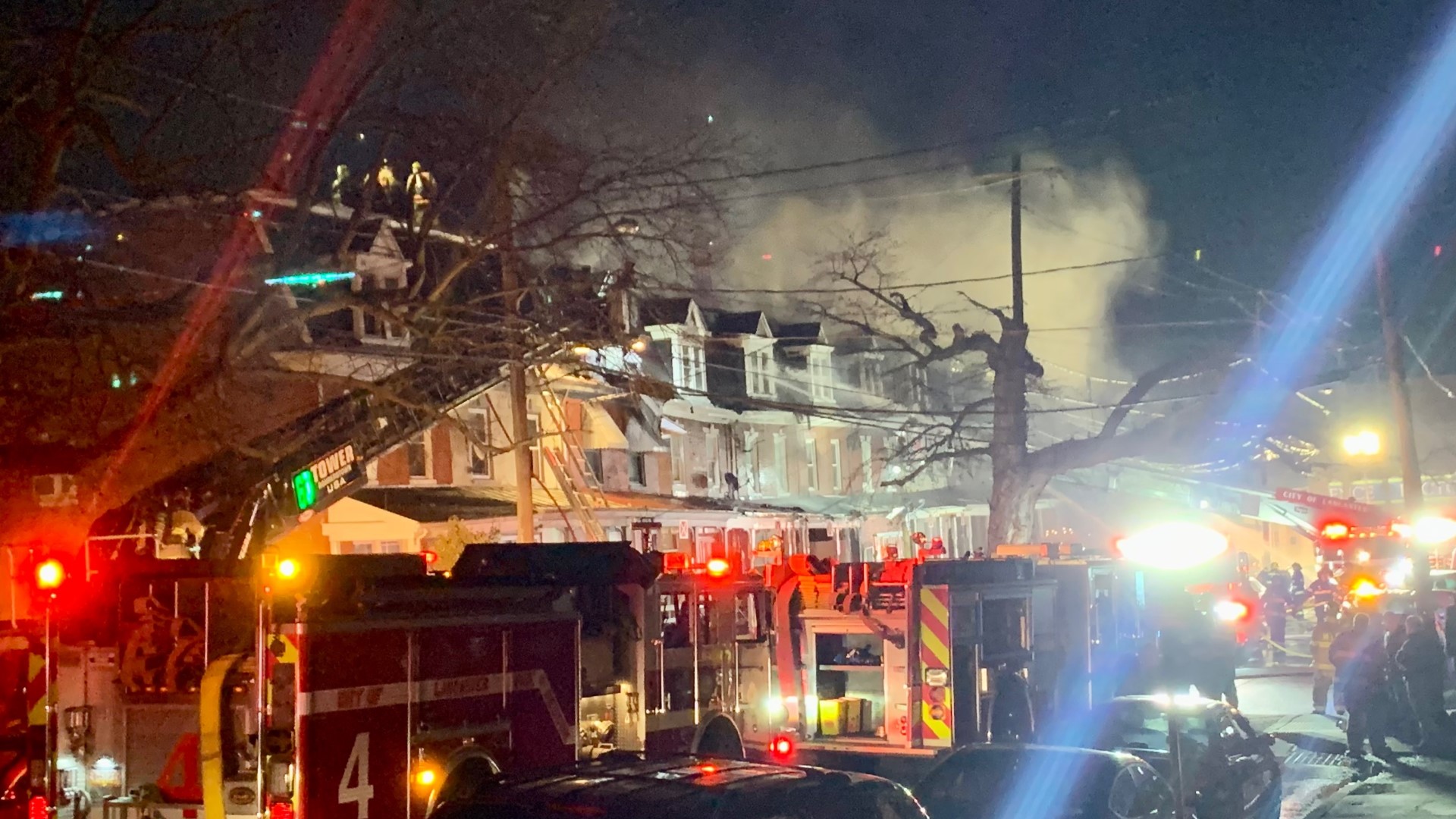 Lancaster County Emergency Response To Fed Ex Truck Fire On Route 283
May 22, 2025
Lancaster County Emergency Response To Fed Ex Truck Fire On Route 283
May 22, 2025 -
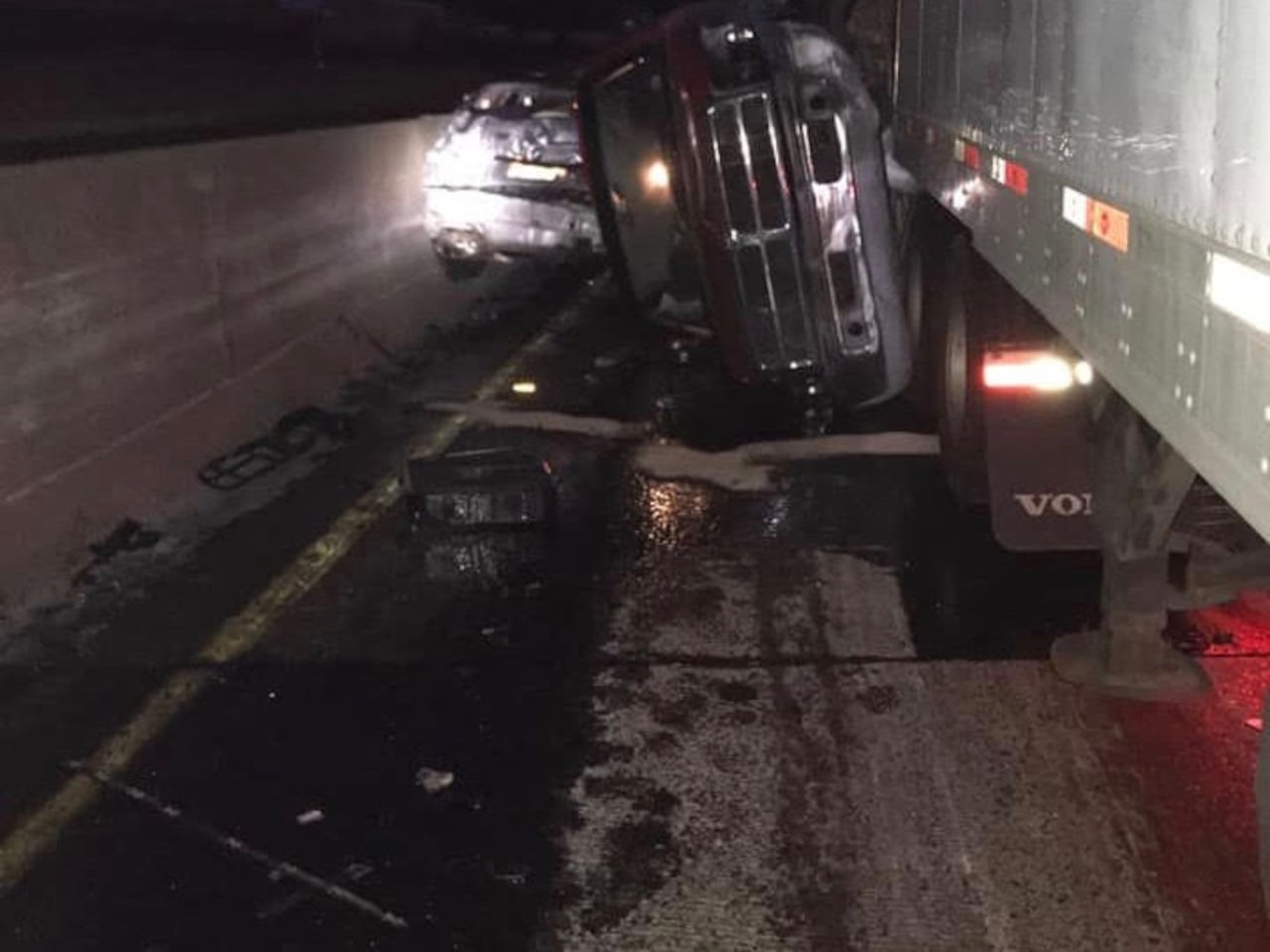 I 83 Tractor Trailer Crash Involving Produce Shipment
May 22, 2025
I 83 Tractor Trailer Crash Involving Produce Shipment
May 22, 2025
