Femicide: Understanding The Rise In Cases And Its Underlying Causes
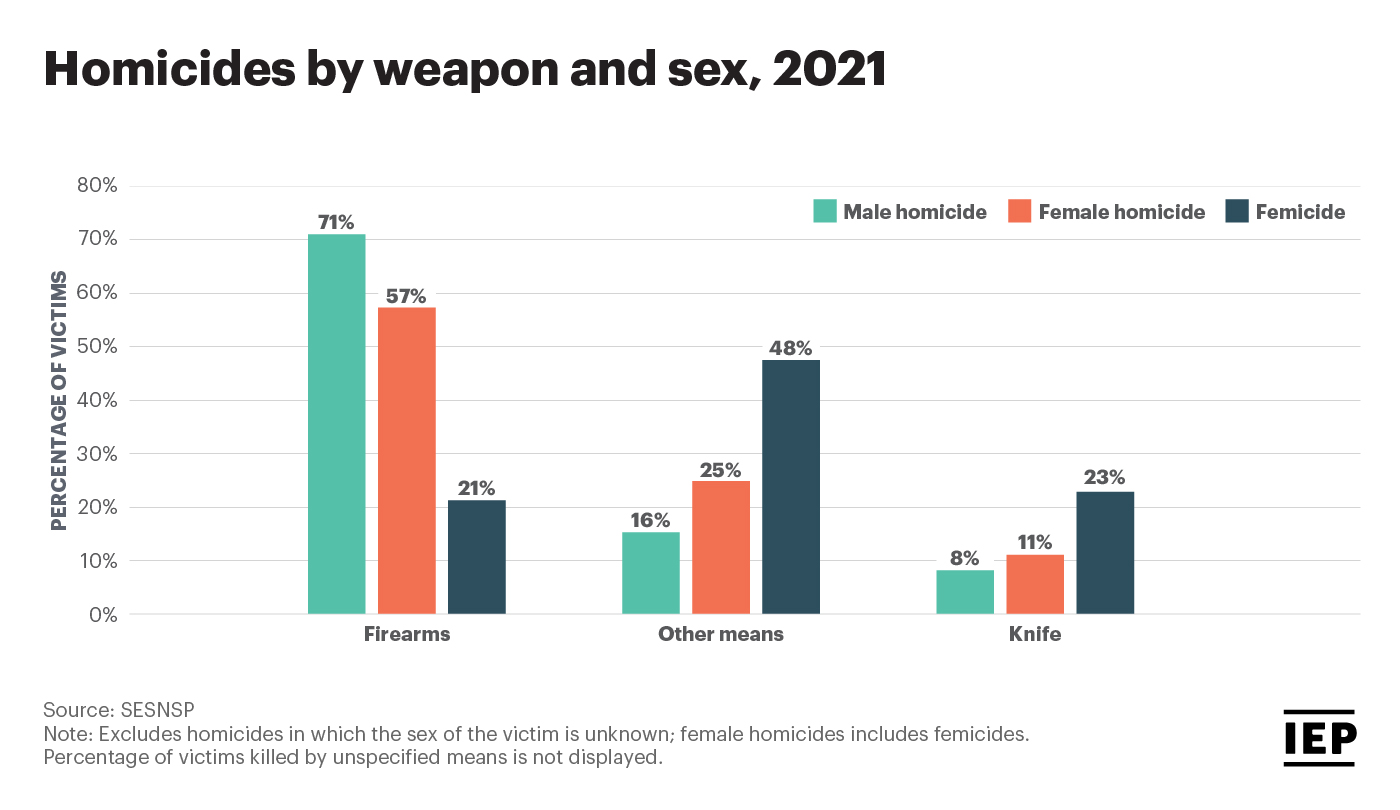
Table of Contents
H2: Defining Femicide and its Scope
Femicide, distinct from other forms of violence against women, specifically targets women due to their gender. It encompasses a range of acts, from intimate partner femicide—the killing of a woman by a current or former partner—to honor killings, where women are murdered for perceived violations of family or community norms. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports significant regional variations in femicide rates, with some areas experiencing far higher occurrences than others. These differences often reflect variations in cultural norms, legal systems, and socioeconomic factors.
- Examples of Femicide: A recent case in Mexico highlighted the vulnerability of women in conflict zones, while statistics from several African nations reveal the disproportionate impact of intimate partner violence leading to femicide.
- Statistics and Sources: [Insert links to reputable sources like UN Women, WHO, and relevant national statistics bureaus providing femicide data.] These sources offer a crucial understanding of the global scale of this issue.
H2: Underlying Causes of Femicide: A Multifaceted Issue
Femicide isn't a singular issue with a simple solution; it's a complex problem born from the intersection of societal, economic, political, and psychological factors.
H3: Societal and Cultural Factors
Deep-rooted gender inequality lies at the heart of femicide. Patriarchal norms and cultural traditions often normalize violence against women, creating an environment where such acts are tolerated or even condoned. Harmful gender stereotypes, portraying women as submissive and men as dominant, contribute to a sense of entitlement and control among perpetrators.
- Cultural Practices Contributing to Femicide: Certain cultural practices, like honor killings or dowry-related violence, directly contribute to femicide rates.
- Misogyny and Violence: The link between misogynistic attitudes and violence against women is undeniable, creating a climate where the dehumanization of women is prevalent.
H3: Economic and Political Factors
Poverty and lack of economic opportunities for women often increase their vulnerability to abuse and femicide. Women facing economic hardship may be more reliant on abusive partners, lacking the resources to escape violent situations. Furthermore, weak legal systems and lack of enforcement of laws designed to protect women create an environment of impunity for perpetrators.
- Poverty and Femicide Rates: Studies consistently show a correlation between poverty and higher rates of femicide.
- Weak Legal Frameworks: Countries with weak legal frameworks and ineffective law enforcement often have significantly higher femicide rates.
H3: Psychological Factors
The psychological profiles of femicide perpetrators often reveal traits like jealousy, possessiveness, and a sense of ownership over women. Substance abuse and mental health issues can further exacerbate these tendencies. Understanding these psychological factors is crucial in developing effective prevention strategies.
- Research on Perpetrator Psychology: Research indicates a common thread of control and a belief in the perpetrator's right to dominate and punish the victim.
- Relevant Psychological Disorders: Conditions like narcissistic personality disorder and antisocial personality disorder have been linked to violent behavior, including femicide.
H2: Combating Femicide: Strategies and Solutions
Addressing femicide requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing legal reforms, educational initiatives, and robust support systems for survivors.
H3: Legal and Policy Reforms
Strengthening legal frameworks to ensure harsher penalties for femicide perpetrators is paramount. This includes improving law enforcement responsiveness to reports of gender-based violence and ensuring access to justice for survivors. Successful examples of legislation include those implementing protective orders and providing legal aid to victims.
- Protective Orders and Legal Avenues: Effective protective orders and accessible legal channels are crucial for ensuring the safety of at-risk women.
- Harsher Penalties for Perpetrators: Implementing stricter penalties, including life sentences or the death penalty in certain jurisdictions, acts as a strong deterrent.
H3: Educational and Social Interventions
Education plays a vital role in challenging harmful gender norms and promoting gender equality. Public awareness campaigns and community initiatives can effectively raise awareness and foster a societal shift away from accepting violence against women.
- Successful Awareness Campaigns: [Insert links to examples of successful campaigns and initiatives.]
- Challenging Patriarchal Attitudes: Educational programs focusing on healthy relationships, consent, and challenging patriarchal attitudes are vital.
H3: Support Systems for Survivors
Providing comprehensive support services for survivors of femicide attempts or related violence is crucial. This includes shelters, counseling, legal assistance, and long-term support to ensure their safety and well-being.
- Support Organizations: [Insert links to relevant organizations providing support to survivors.]
- Importance of Psychological Support: Addressing the psychological trauma experienced by survivors through therapy and support groups is essential.
3. Conclusion
The rise in femicide is a devastating consequence of intersecting societal, economic, political, and psychological factors. Combating this global crisis requires a comprehensive strategy that strengthens legal frameworks, promotes gender equality through education, and provides vital support to survivors. We must all actively participate in preventing femicide by supporting organizations working to end gender-based violence, advocating for stronger legal protections, and challenging the harmful societal norms that perpetuate this violence. Let's work together to create a safer world where women are valued, respected, and free from the threat of femicide. Learn more and get involved by visiting [Insert links to relevant organizations and resources].

Featured Posts
-
 The Countrys Evolving Business Landscape Key Growth Areas
May 20, 2025
The Countrys Evolving Business Landscape Key Growth Areas
May 20, 2025 -
 Pechalnye Novosti Sostoyanie Mikhaelya Shumakhera Vyzyvaet Bespokoystvo
May 20, 2025
Pechalnye Novosti Sostoyanie Mikhaelya Shumakhera Vyzyvaet Bespokoystvo
May 20, 2025 -
 Is A Logitech Forever Mouse Finally Possible
May 20, 2025
Is A Logitech Forever Mouse Finally Possible
May 20, 2025 -
 Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News Jan 6th Falsehoods
May 20, 2025
Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News Jan 6th Falsehoods
May 20, 2025 -
 Milica Milsa Na Sahrani Andelke Milivojevic Tadic Tuga I Secanje
May 20, 2025
Milica Milsa Na Sahrani Andelke Milivojevic Tadic Tuga I Secanje
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Corruption Conviction Rocks Us Navy Retired Four Star Admirals Case
May 20, 2025
Corruption Conviction Rocks Us Navy Retired Four Star Admirals Case
May 20, 2025 -
 Us Four Star Admiral Found Guilty The Corruption Case Explained
May 20, 2025
Us Four Star Admiral Found Guilty The Corruption Case Explained
May 20, 2025 -
 Four Star Admirals Corruption Conviction A Detailed Analysis
May 20, 2025
Four Star Admirals Corruption Conviction A Detailed Analysis
May 20, 2025 -
 High Ranking Admirals Fall From Grace Corruption Case Analysis
May 20, 2025
High Ranking Admirals Fall From Grace Corruption Case Analysis
May 20, 2025 -
 Admirals Bribery Case Examining The Systemic Issues Within The Navy
May 20, 2025
Admirals Bribery Case Examining The Systemic Issues Within The Navy
May 20, 2025
