Falling Retail Sales: A Harbinger Of Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts?
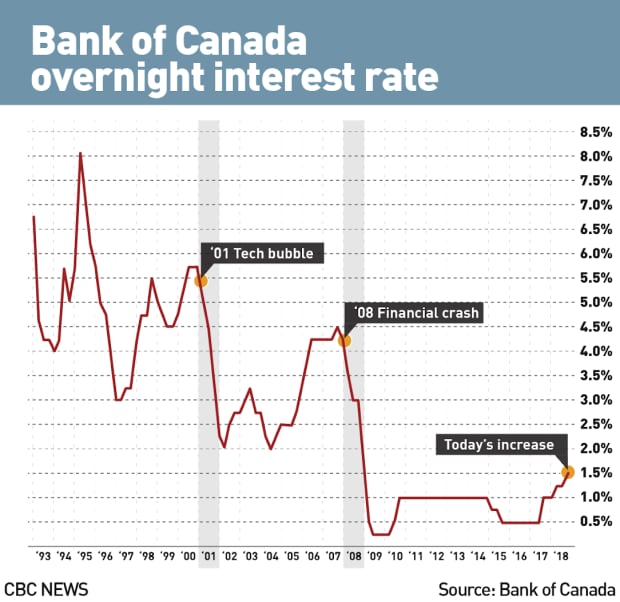
Table of Contents
The Impact of Falling Retail Sales on the Canadian Economy
H3: Consumer Spending as a Key Economic Driver
Consumer spending is the engine of the Canadian economy, representing a substantial portion of the nation's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Understanding its fluctuations is crucial for predicting economic trends.
- Consumer spending accounts for approximately 55% of Canada's GDP (hypothetical data). A decline in consumer spending directly impacts economic growth.
- Reduced consumer spending creates a ripple effect across various sectors. Manufacturing industries experience lower demand for their goods, leading to potential production cuts and job losses. The service sector, heavily reliant on consumer activity, also faces reduced revenue and potential downsizing.
H3: Analyzing the Causes of Declining Retail Sales
Several factors contribute to the recent decline in retail sales. Understanding these causes is vital for predicting future trends and the Bank of Canada's response.
- High Inflation: Persistent inflation erodes purchasing power, forcing consumers to cut back on non-essential spending.
- Rising Interest Rates: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for consumers, impacting affordability for big-ticket items like homes and vehicles, leading to decreased demand.
- Decreased Consumer Confidence: Negative economic news and uncertainty about the future can dampen consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Geopolitical instability and global economic slowdowns can negatively impact the Canadian economy and consumer spending.
- Specific sectors like automobile sales and furniture retail have reported particularly sharp declines, reflecting the impact of higher interest rates on major purchases.
Bank of Canada's Current Monetary Policy and Rate Decisions
H3: Recent Interest Rate Hikes and Their Impact
The Bank of Canada has implemented several interest rate hikes in recent months to combat inflation.
- The rationale behind these rate hikes was to cool down the overheated economy and curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive.
- While the rate hikes have had some success in slowing inflation, their full impact is yet to be fully realized, and the lagged effect on the economy needs to be carefully observed.
H3: Indicators the Bank of Canada Monitors
The Bank of Canada considers various economic indicators when making monetary policy decisions.
- Inflation: The primary focus is controlling inflation and bringing it back to the 2% target. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is closely monitored.
- Unemployment: A rising unemployment rate could signal a weakening economy, potentially prompting rate cuts.
- GDP Growth: GDP growth provides a broad measure of the overall health of the economy. Slower-than-expected growth might indicate a need for rate adjustments.
- Current data on inflation remains stubbornly high (hypothetical data: 4.5%), while unemployment is relatively low (hypothetical data: 5.2%). This mixed data presents a challenge for the Bank of Canada.
Predicting Future Bank of Canada Rate Cuts Based on Retail Sales Data
H3: Correlation vs. Causation
It's important to differentiate between correlation and causation when analyzing the relationship between falling retail sales and interest rate decisions.
- Falling retail sales are a significant indicator of weakening consumer demand and overall economic slowdown, and a factor the Bank of Canada will consider.
- However, it's not the sole determinant. Other factors, such as inflation rates, employment figures, and global economic conditions, also play crucial roles.
H3: Expert Opinions and Market Forecasts
Economists and financial analysts offer varying perspectives on the likelihood of future rate cuts.
- Some believe the persistent weakness in retail sales, coupled with signs of slowing economic growth, increases the probability of a rate cut in the near future.
- Others argue that inflation remains a significant concern and that the Bank of Canada might hold off on rate cuts until inflation shows clearer signs of easing.
- For example, [Cite a reputable source here, e.g., a financial news article from the Globe and Mail] predicts a 25 basis point rate cut by the end of the year.
Conclusion
Falling retail sales signal a potential weakening in the Canadian economy and are a significant factor the Bank of Canada will consider when deciding on future interest rate adjustments. However, it's crucial to remember that this is just one piece of the puzzle. Inflation levels, unemployment rates, and global economic conditions also heavily influence monetary policy decisions. Understanding the complex interplay of these factors is key to predicting future interest rate movements. Stay tuned for updates on falling retail sales and their potential impact on Bank of Canada rate cuts. Follow our blog for further analysis on Canadian economic trends. Understanding the implications of falling retail sales for future Bank of Canada decisions is crucial.

Featured Posts
-
 Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Receives Green Light For Hong Kong Share Offering
Apr 29, 2025
Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Receives Green Light For Hong Kong Share Offering
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Mwedna Me Fn Abwzby 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025
Mwedna Me Fn Abwzby 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trump To Issue Full Pardon For Rose
Apr 29, 2025
Trump To Issue Full Pardon For Rose
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Analisis Del Rendimiento Goleador De Alberto Ardila Olivares
Apr 29, 2025
Analisis Del Rendimiento Goleador De Alberto Ardila Olivares
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Fck Gegen Bayern Champions League Duell Ohne Betzenberg Feuer
Apr 29, 2025
Fck Gegen Bayern Champions League Duell Ohne Betzenberg Feuer
Apr 29, 2025
 50 Godini Praznuva Lyubimetst Na Milioni
50 Godini Praznuva Lyubimetst Na Milioni
