England Records 311 Deaths Due To Extreme Heat: Examining The Causes And Consequences
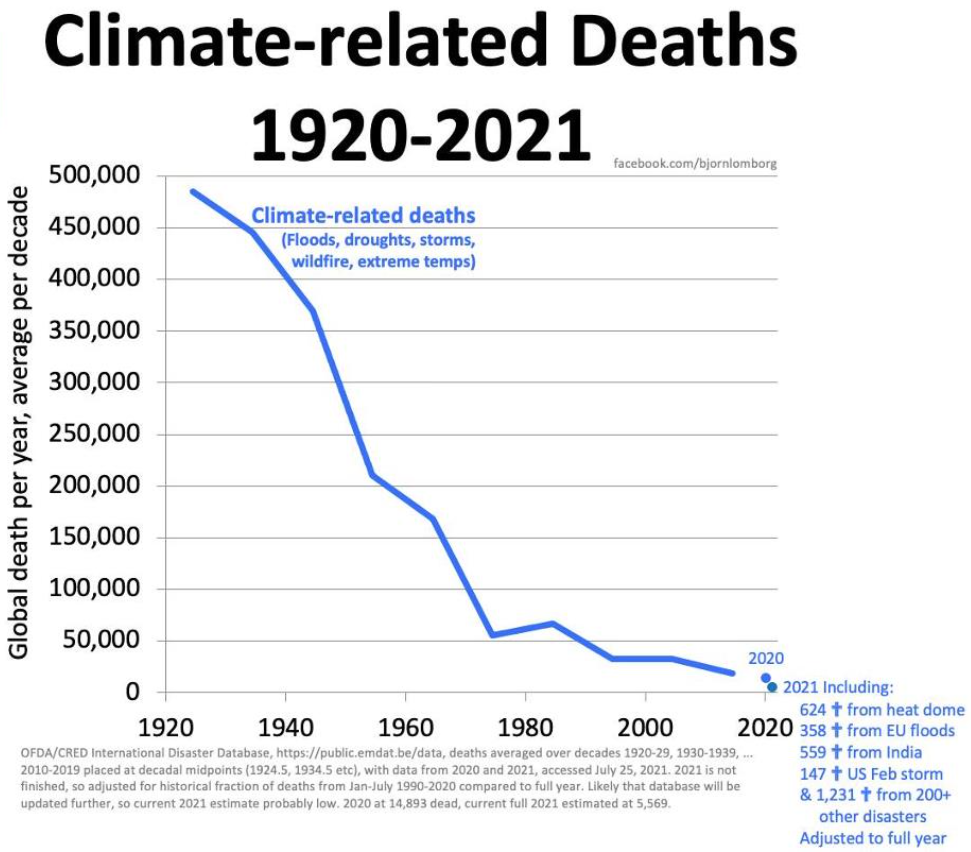
Table of Contents
Underlying Causes of Extreme Heat Deaths in England
The high number of extreme heat deaths in England in 2023 wasn't a random occurrence; it stemmed from a confluence of factors. Understanding these causes is crucial to developing effective preventative measures.
The Impact of the Heatwave
The 2023 heatwave in England was characterized by its intensity, duration, and widespread geographical impact.
- Temperature Highs: Many areas experienced temperatures exceeding 35°C (95°F) for several consecutive days, with some locations reaching even higher temperatures.
- Duration of Extreme Temperatures: The prolonged period of extreme heat, lasting over a week in many regions, significantly increased the risk of heat-related illnesses and deaths.
- Affected Regions: While the impact was felt nationwide, certain urban areas with limited green spaces and poor ventilation experienced particularly high mortality rates. The South East and London were particularly hard hit.
- Demographic Disparities: Analysis revealed a disproportionate impact on specific demographics: older individuals (over 65), those with pre-existing health conditions, and people in lower socioeconomic groups suffered higher mortality rates. This highlights existing inequalities within the healthcare system and access to resources.
- Exacerbating Health Conditions: Pre-existing conditions like cardiovascular diseases, respiratory illnesses, and kidney disease were significantly exacerbated by the extreme heat, leading to increased hospital admissions and fatalities.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups were disproportionately affected by the extreme heat, highlighting societal vulnerabilities.
- Elderly Population: The elderly, with their often decreased thermoregulation capacity, were particularly vulnerable. Statistics showed a significantly higher death rate among this age group compared to younger populations. Heat stroke was a common cause of death.
- Individuals with Pre-existing Health Conditions: People with chronic illnesses, especially those affecting the cardiovascular or respiratory systems, experienced severe complications. The heat stress added an extra burden on already compromised systems.
- Socially Disadvantaged Communities: Individuals living in poverty often lack access to adequate cooling, such as air conditioning, and may reside in poorly insulated housing. Furthermore, limited access to healthcare further increases their vulnerability.
Inadequate Infrastructure and Preparedness
England's preparedness for extreme heat events faced significant shortcomings, contributing to the high death toll.
- Lack of Cooling Centers and Awareness: The availability of public cooling centers was insufficient to meet the demand during the heatwave. Furthermore, public awareness campaigns regarding heat-related risks and preventative measures were inadequate.
- Ineffective Communication Strategies: Communication during the heatwave could have been more effective, reaching vulnerable populations earlier and more clearly with heat health warnings and safety advice.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Many public spaces and housing lacked sufficient air conditioning or effective ventilation systems, making them dangerous during extreme heat. This infrastructure deficiency proved fatal for many vulnerable individuals.
Consequences of Extreme Heat Deaths
The consequences of the extreme heat deaths in England extend far beyond the immediate loss of life, impacting multiple sectors.
Strain on Healthcare System
The heatwave placed an enormous strain on the National Health Service (NHS).
- Increased Hospital Admissions: Hospitals experienced a surge in admissions for heatstroke, dehydration, and other heat-related illnesses, overwhelming resources.
- Delays in Providing Care: The high demand for care led to delays in treatment for many patients, impacting their prognosis and potentially contributing to fatalities.
- Financial Implications: The increased demand for healthcare services resulted in significant financial strain on the NHS, requiring additional resources and staff.
Social and Economic Impacts
The repercussions of the heatwave extended beyond the healthcare system, impacting society and the economy.
- Lost Productivity: High rates of sickness and reduced work capacity due to heat-related illnesses led to significant losses in productivity across various sectors.
- Increased Mortality Rates Affecting Workforce: The deaths directly impacted the workforce, leading to shortages and economic disruption in some industries.
- Potential for Long-Term Health Problems: Survivors of severe heat-related illnesses may experience long-term health complications, adding to the overall burden on the healthcare system.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Preventing future tragedies requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on both immediate preparedness and long-term climate change mitigation.
Improving Public Health Preparedness
The UK needs to significantly improve its response to extreme heat events.
- Comprehensive Heatwave Action Plans: Developing and implementing comprehensive heatwave action plans that involve clear communication strategies and proactive measures to protect vulnerable populations.
- Expanded Public Awareness Campaigns: Investing in sustained, targeted public awareness campaigns that educate the public about heat-related risks, prevention, and early warning signs.
- Increased Investment in Cooling Infrastructure: Significant investments in cooling infrastructure, particularly in public buildings and homes in vulnerable communities, are crucial.
Long-Term Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing climate change is essential in reducing the frequency and intensity of extreme heat events.
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Implementing policies to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions is paramount to limiting global warming.
- Investing in Renewable Energy Sources: Transitioning to renewable energy sources reduces reliance on fossil fuels, a major contributor to climate change.
- Strengthening International Cooperation: International cooperation on climate change is vital to achieving global emission reduction targets and protecting vulnerable communities worldwide.
Conclusion
The 311 deaths attributed to extreme heat in England serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for improved preparedness and mitigation strategies. The consequences extend far beyond the immediate loss of life, impacting the healthcare system, the economy, and society as a whole. Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing better public health initiatives, improved infrastructure, and a commitment to tackling climate change. We must learn from this tragedy and take proactive steps to prevent future extreme heat deaths in England. Understanding the causes and consequences of these extreme heat deaths in England is crucial for building resilience and protecting vulnerable populations. We need a national conversation about how to better prepare for and mitigate the effects of future heatwaves to prevent further loss of life. Investing in better infrastructure, improving public awareness, and addressing climate change are crucial steps in reducing future extreme heat deaths in England.

Featured Posts
-
 Ouverture Du Tunnel De Tende En Juin Confirmation Du Ministre Tabarot
May 30, 2025
Ouverture Du Tunnel De Tende En Juin Confirmation Du Ministre Tabarot
May 30, 2025 -
 Replay Loeil De Philippe Caveriviere Du 24 Avril 2025 Face A Philippe Tabarot Video
May 30, 2025
Replay Loeil De Philippe Caveriviere Du 24 Avril 2025 Face A Philippe Tabarot Video
May 30, 2025 -
 Plires Programma Tileoptikon Metadoseon 19 4 M Savvato
May 30, 2025
Plires Programma Tileoptikon Metadoseon 19 4 M Savvato
May 30, 2025 -
 Katastrofa Ekologiczna Na Odrze Jaka Jest Szansa Na Powtorzenie Tragedi
May 30, 2025
Katastrofa Ekologiczna Na Odrze Jaka Jest Szansa Na Powtorzenie Tragedi
May 30, 2025 -
 Alastqlal Msdr Ilham Llajyal
May 30, 2025
Alastqlal Msdr Ilham Llajyal
May 30, 2025
