End Of School Desegregation Order: Implications And Future Of School Diversity
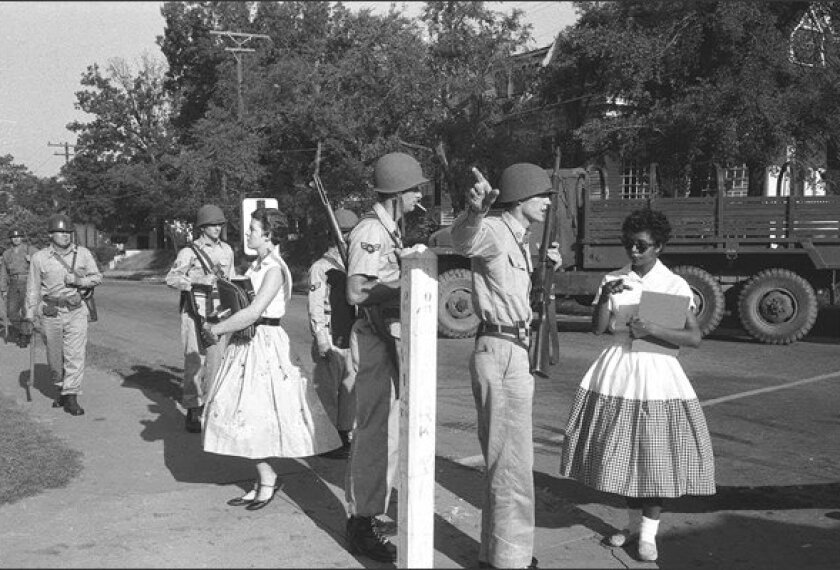

Table of Contents
Legal Implications of Ending School Desegregation Orders
The legal landscape surrounding school desegregation is complex and constantly evolving. Understanding the legal ramifications of ending these orders is crucial.
Supreme Court Rulings and their Impact
Supreme Court decisions have significantly shaped the course of school desegregation. Landmark cases have both advanced and, at times, hindered progress.
- Brown v. Board of Education (1954): This landmark case declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, implementation proved challenging.
- Milliken v. Bradley (1974): This case limited the power of federal courts to impose desegregation plans across multiple school districts, effectively hindering efforts to address widespread segregation patterns.
- Parents Involved in Community Schools v. Seattle School District No. 1 (2007): This ruling further restricted the use of race as a primary factor in assigning students to schools, impacting the effectiveness of some integration strategies.
These rulings, and the resulting legal precedent, significantly influence how school districts approach desegregation. The potential end of a desegregation order will inevitably lead to legal challenges and interpretations of existing legislation.
State and Local Level Responses
The response to the potential end of a desegregation order will vary significantly across states and localities. Some states might actively seek to maintain diversity through alternative policies, while others may allow for greater school district autonomy, potentially leading to increased segregation.
- Legislative Changes: States might revise their laws regarding school assignment, transportation, or funding mechanisms.
- Challenges to Existing Policies: Legal challenges to existing desegregation plans are anticipated.
- Variations in Enforcement: The level of enforcement of remaining desegregation mandates will differ across districts, leading to inconsistencies in school demographics.
The autonomy granted to individual school districts will be a key factor determining the impact of an end to desegregation orders at the local level.
Socioeconomic Implications of School Segregation
The socioeconomic consequences of school segregation extend far beyond academic performance.
Impact on Academic Achievement
School segregation significantly impacts academic achievement, creating and perpetuating the achievement gap.
- Resource Allocation: Segregated schools often face disparities in resource allocation, with schools serving predominantly minority and low-income students receiving less funding and fewer resources than those in wealthier, predominantly white districts.
- Teacher Quality: Segregated schools may struggle to attract and retain high-quality teachers, leading to further disparities in educational outcomes.
- Statistics on Achievement Gaps: Numerous studies show a consistent correlation between school segregation and lower academic achievement among students from marginalized communities.
This disparity in educational resources directly contributes to the achievement gap, perpetuating a cycle of inequality.
Consequences for Social Integration and Cohesion
Segregated schools can have detrimental effects on social integration and community cohesion.
- Limited Interracial Interaction: Lack of diversity limits opportunities for students from different backgrounds to interact, fostering misunderstandings and prejudices.
- Perpetuation of Inequality: Segregation reinforces existing social and economic inequalities, impacting students’ social networks and future opportunities.
- Social Biases: Segregated environments can exacerbate existing social biases and limit exposure to diverse perspectives, hindering the development of empathy and understanding.
Addressing these social consequences requires proactive interventions aimed at fostering positive intergroup relationships and breaking down societal barriers.
Strategies for Promoting School Diversity in a Post-Desegregation Era
Even with the potential end of some desegregation orders, strategies to promote school diversity remain crucial.
Innovative Approaches to School Choice and Integration
Several innovative approaches can contribute to creating more diverse student populations:
- Magnet Schools: Specialized schools offering unique programs can attract students from different neighborhoods and backgrounds.
- Open Enrollment Policies: Allowing students to attend schools outside their assigned district can promote diversity.
- Controlled Choice Plans: These plans use lotteries or weighted systems to ensure a more balanced student population in schools.
- Inter-district Transfers: Facilitating transfers between districts can help address segregation across wider geographical areas.
These strategies, while not without challenges, offer alternative pathways to achieving greater school integration.
Addressing Underlying Socioeconomic Factors
Addressing school segregation requires confronting underlying socioeconomic factors that contribute to residential segregation and, consequently, school segregation.
- Affordable Housing Initiatives: Promoting affordable housing options in diverse neighborhoods can help break down residential segregation.
- Economic Inequality: Tackling income inequality is crucial to ensure equitable access to quality education regardless of zip code.
- Socioeconomic Integration Strategies: Policies aiming to integrate communities economically can have a positive impact on school diversity.
Conclusion
The potential end of school desegregation orders presents significant challenges to the ongoing pursuit of educational equity. The legal implications are complex, and the socioeconomic consequences, particularly regarding the achievement gap and social integration, are substantial. However, the future of school diversity is not predetermined. By implementing innovative approaches to school choice, actively addressing underlying socioeconomic factors, and engaging in open dialogue, we can work towards a more equitable and integrated educational system. We urge you to contact your local representatives, support organizations dedicated to educational equity, and participate in community initiatives promoting school integration. The future of school desegregation – and the future of our children’s education – depends on our collective action and commitment to ending school segregation orders and building a more diverse and inclusive learning environment for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Le Couple Macron Regards Sur Leur Intimite Apres Plusieurs Annees De Mariage
May 03, 2025
Le Couple Macron Regards Sur Leur Intimite Apres Plusieurs Annees De Mariage
May 03, 2025 -
 Ukraina Makron Dobilsya Ot S Sh A Uzhestocheniya Pozitsii Protiv Rossii
May 03, 2025
Ukraina Makron Dobilsya Ot S Sh A Uzhestocheniya Pozitsii Protiv Rossii
May 03, 2025 -
 Cassidy Hutchinsons Fall Memoir A First Hand Account Of The January 6th Hearings
May 03, 2025
Cassidy Hutchinsons Fall Memoir A First Hand Account Of The January 6th Hearings
May 03, 2025 -
 When Will Trust Care Health Offer Mental Health Treatment A Comprehensive Overview
May 03, 2025
When Will Trust Care Health Offer Mental Health Treatment A Comprehensive Overview
May 03, 2025 -
 Finding Newsround A Bbc Two Hd Tv Schedule
May 03, 2025
Finding Newsround A Bbc Two Hd Tv Schedule
May 03, 2025
