Easing Regulations For Bond Forwards: A Plea From Indian Insurers
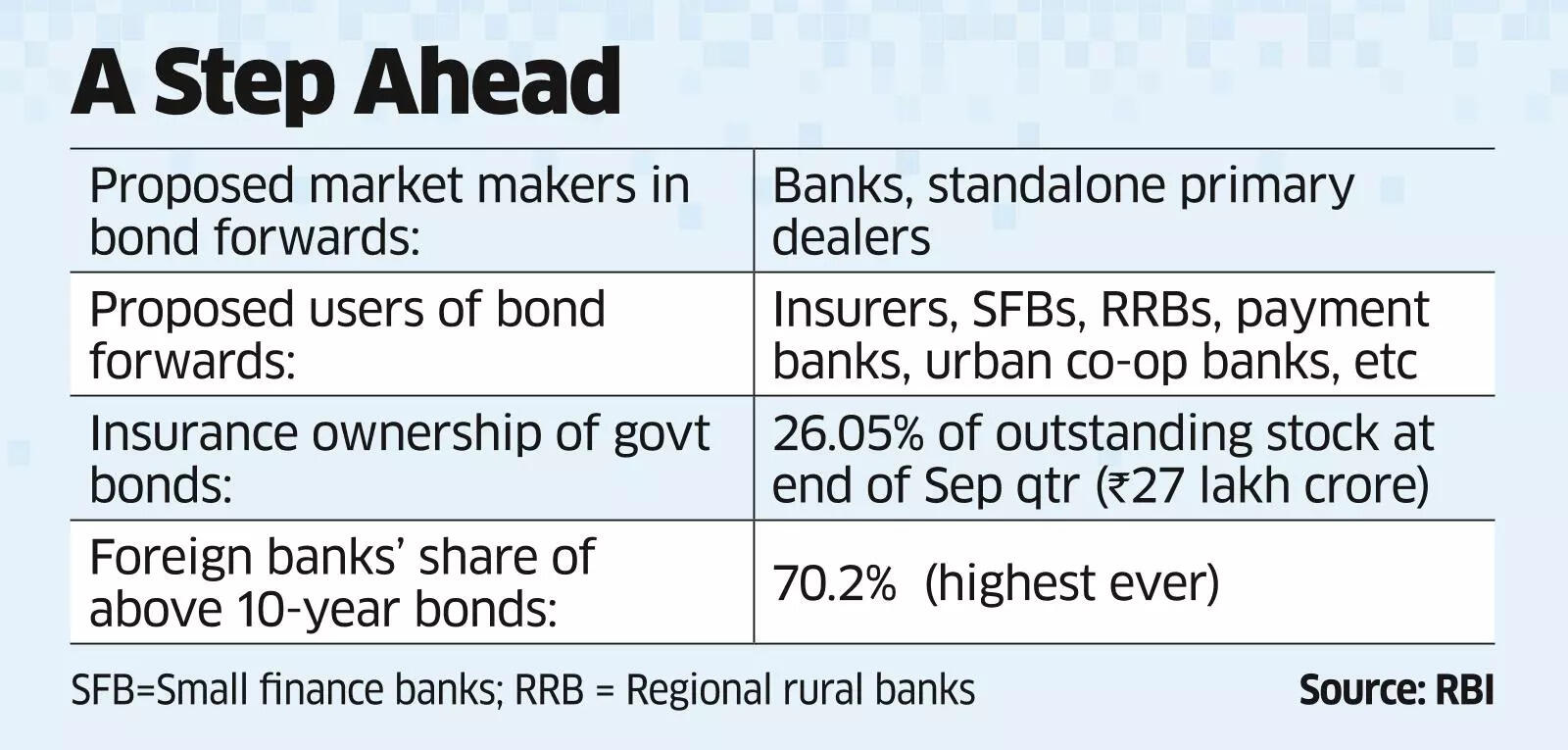
Table of Contents
The Stifling Impact of Current Regulations on Bond Forwards
India's existing regulatory framework for bond forwards places significant constraints on insurers. These limitations stem from concerns about systemic risk and the potential for excessive leverage. However, the current approach is overly cautious, resulting in several negative consequences.
-
Limited Investment Options: The restricted range of permissible bond forwards limits portfolio diversification strategies for insurers. This over-reliance on specific asset classes increases vulnerability to market fluctuations. For example, the current regulations may prohibit insurers from hedging against specific interest rate scenarios, forcing them to rely on less effective, potentially more expensive, alternative strategies.
-
Ineffective Interest Rate Risk Management: Bond forwards are crucial tools for managing interest rate risk, a significant concern for insurers with long-term liabilities. The restrictive regulations hamper their ability to effectively hedge against these risks, leading to potential losses and reduced profitability. Specific regulations like [mention specific regulation and its effect, e.g., IRDAI circular X on permissible investments] directly impact an insurer’s ability to employ sophisticated hedging techniques.
-
Reduced Profitability and Competitiveness: The inability to fully utilize bond forwards directly impacts profitability. Compared to their global counterparts, Indian insurers operate at a disadvantage, lacking the flexibility to optimize their investment portfolios and achieve higher returns. This reduced profitability diminishes their competitiveness in attracting both domestic and foreign investors.
-
Increased Reliance on Less Efficient Hedging Strategies: The limitations on bond forward usage force insurers to rely on alternative, often less efficient, hedging strategies. This may include increased reliance on derivatives with higher transaction costs or less precise hedging capabilities, ultimately reducing overall returns. Data from [cite a relevant source if available] shows that the cost of hedging for Indian insurers is significantly higher than in countries with more liberal regulations on bond forwards.
Benefits of Easing Regulations for Bond Forwards: A Catalyst for Growth
Easing regulations on bond forwards offers significant potential benefits for the Indian insurance sector:
-
Enhanced Risk Management and Investment Opportunities: Relaxed regulations would unlock a wider array of investment options and sophisticated risk management tools. Insurers could better tailor their portfolios to specific risk profiles and market conditions, leading to increased efficiency and returns.
-
Improved Profitability and Competitiveness: By allowing insurers to employ more effective hedging and investment strategies, deregulation would contribute directly to higher profitability. This increased profitability would attract foreign investment and boost the sector’s overall competitiveness on a global scale.
-
Attracting Foreign Investment: A more favorable regulatory environment would make India a more attractive destination for foreign insurance companies, boosting investment and fostering competition, which ultimately benefits policyholders.
-
Financial Innovation and Deeper Bond Markets: Greater access to bond forwards would stimulate innovation within the Indian insurance sector and contribute to the development of a deeper, more liquid bond market. This would create a virtuous cycle of growth and stability. The experience of [mention a country with successful deregulation, e.g., the UK] demonstrates the positive impact of allowing increased access to bond forwards for insurers.
Addressing Concerns: Mitigating Risks Through Prudent Regulation
While easing regulations offers significant advantages, potential risks must be addressed. The key is to implement a balanced regulatory approach that fosters growth without compromising financial stability.
-
Strengthened Regulatory Oversight: Enhanced monitoring and surveillance are crucial. This includes robust reporting requirements and regular audits to ensure compliance with risk management guidelines.
-
Robust Risk Management Frameworks: Insurers must adopt sophisticated risk management frameworks tailored to the increased use of bond forwards. This includes stress testing and scenario analysis to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
-
Increased Transparency and Disclosure: Clear and detailed disclosure requirements would enhance transparency, allowing regulators and investors to assess the risk profile of insurers effectively.
-
Stricter Capital Adequacy Requirements: Adjusting capital adequacy ratios to reflect the increased risk associated with greater utilization of bond forwards is vital. This would ensure that insurers have sufficient capital buffers to absorb potential losses.
Recommendations for Policymakers: A Roadmap for Reform
Policymakers should consider a phased approach to deregulation, incorporating the following recommendations:
-
Relax Restrictions on Permitted Bond Forwards: Gradually expand the range of permissible bond forwards, starting with those considered less risky.
-
Increase Permitted Leverage Levels: Allow for higher leverage levels for bond forward positions, but within carefully defined limits and subject to strict risk management oversight.
-
Simplify Regulatory Reporting: Streamline reporting requirements to reduce the administrative burden on insurers, allowing them to focus on core business activities.
-
Create a Clear Regulatory Framework: Develop a transparent and easily understood regulatory framework that clearly defines the permissible activities and reporting obligations related to bond forwards.
Conclusion
Easing regulations for bond forwards is not merely a matter of removing restrictions; it’s about creating a regulatory environment that promotes growth, innovation, and stability within the Indian insurance sector. The potential benefits – increased investment opportunities, improved risk management, and enhanced competitiveness – significantly outweigh the risks, provided appropriate safeguards are in place. We urge policymakers to consider the recommendations outlined above and take decisive action towards liberalizing regulations for bond forwards and improving the regulatory environment for bond forwards. This decisive move will empower Indian insurers to thrive in the increasingly competitive global insurance market.

Featured Posts
-
 Renewed Hope In Madeleine Mc Cann Case Following 108 000 Funding
May 09, 2025
Renewed Hope In Madeleine Mc Cann Case Following 108 000 Funding
May 09, 2025 -
 Understanding The Epstein Client List Controversy Pam Bondis Perspective
May 09, 2025
Understanding The Epstein Client List Controversy Pam Bondis Perspective
May 09, 2025 -
 Data Breach Exposes Millions In Losses Office365 Executive Accounts Targeted
May 09, 2025
Data Breach Exposes Millions In Losses Office365 Executive Accounts Targeted
May 09, 2025 -
 Nyt Strands Hints And Answers Sunday February 23 Game 357
May 09, 2025
Nyt Strands Hints And Answers Sunday February 23 Game 357
May 09, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnsons Stunning White Dress At Materialists Premiere
May 09, 2025
Dakota Johnsons Stunning White Dress At Materialists Premiere
May 09, 2025
