CNN's Misinformation Experts: Why Facts Don't Always Change Minds
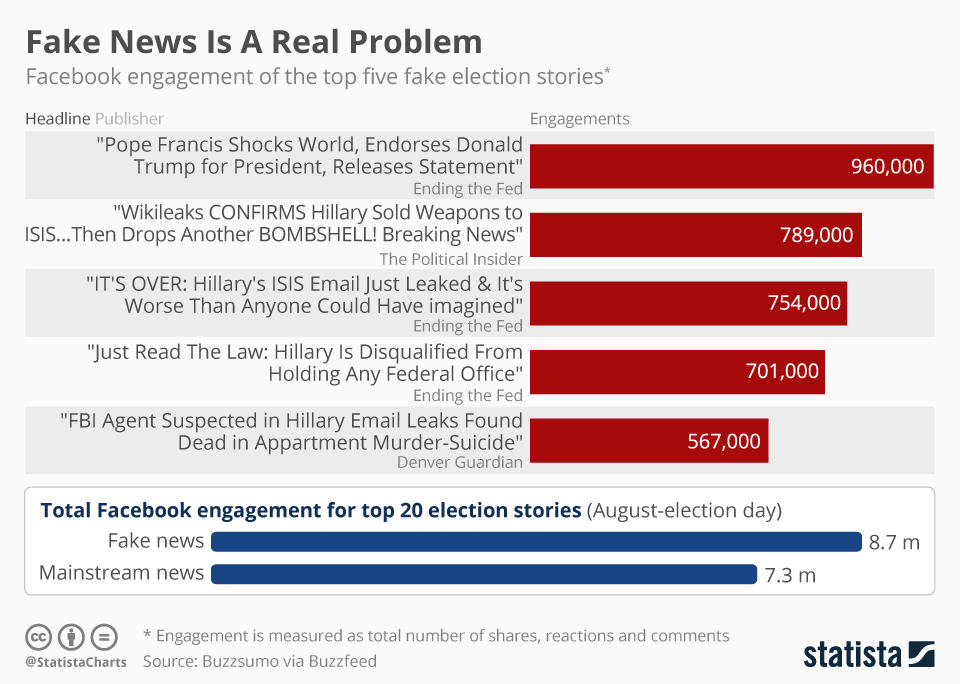
Table of Contents
The Psychology of Misinformation
Understanding why people resist facts is crucial to developing effective countermeasures. The spread of misinformation is fueled by several psychological factors.
Cognitive Biases and Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias, the tendency to favor information confirming pre-existing beliefs, is a major obstacle. People selectively seek out and interpret information aligning with their worldview, dismissing contradictory evidence.
- Examples: A climate change skeptic might dismiss scientific reports while readily accepting anecdotal evidence that supports their views. Similarly, a supporter of a particular political candidate might ignore negative news stories about them.
- Impact on Fact-Checking: Fact-checks often fail to sway those with strong pre-existing beliefs because the information is filtered through the lens of confirmation bias.
- Emotional Reinforcement: Emotions play a crucial role. Fear, anger, or excitement linked to a false belief can make it more resistant to correction.
The Backfire Effect
Sometimes, correcting misinformation can paradoxically strengthen the false belief. This "backfire effect" occurs when individuals feel their intelligence or identity is challenged by the correction.
- Examples: Directly confronting someone about a false belief can trigger defensiveness, leading them to double down on their inaccurate claim.
- Mitigation Strategies: Instead of directly challenging a belief, try framing the correction within a broader narrative that respects the individual's perspective.
- Understanding the Audience: Empathy and understanding are key. Approaching the conversation with a focus on shared values and common ground can improve receptiveness.
The Role of Trust and Source Credibility
Trust is paramount. People are more likely to accept information from sources they perceive as credible and trustworthy.
- CNN's Credibility: While CNN is a major news organization, its credibility is debated, particularly among certain segments of the population. Perceived media bias plays a significant role in how viewers assess information.
- Partisan Media: The rise of partisan media outlets further complicates the issue, reinforcing pre-existing biases and eroding trust in neutral sources.
- Impact of Perceived Bias: If viewers perceive CNN (or any source) as biased, they are more likely to discount its information, even if factually accurate.
CNN's Approach to Misinformation
CNN, like other major news organizations, actively combats misinformation. However, it faces significant challenges.
CNN's Fact-Checking Initiatives
CNN employs various fact-checking methods, including dedicated fact-checking teams and on-air corrections. They leverage social media to flag and debunk false narratives.
- Examples: CNN's fact-checks are often published on their website and promoted on social media platforms. They also incorporate fact-checking segments into their news broadcasts.
- Reach and Impact: The effectiveness of these initiatives is debatable. While they reach a large audience, their impact on changing entrenched beliefs remains limited.
- Strengths and Weaknesses: CNN’s strengths lie in its resources and journalistic expertise. However, the speed of misinformation spread and the fragmentation of the media landscape pose significant challenges.
Challenges Faced by CNN Fact-Checkers
Combating misinformation is a relentless battle.
- Speed of Misinformation Spread: False narratives can spread rapidly across social media, making real-time fact-checking incredibly difficult.
- Volume of Misinformation: The sheer volume of misinformation makes it impossible to address every instance.
- Reaching Target Audiences: Fact-checks often fail to reach the individuals who need them most – those who are already entrenched in their beliefs.
- Limitations in a Rapidly Evolving Digital Landscape: New platforms and technological advancements constantly challenge fact-checking efforts.
The Impact of Media Fragmentation
The media landscape is increasingly fragmented.
- Echo Chambers and Social Media: Algorithms on social media platforms often reinforce pre-existing biases by creating echo chambers, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives.
- Spread Through Curated Algorithms: Misinformation spreads efficiently through curated algorithms, reaching vast audiences with minimal effort.
- Combating Misinformation Across Platforms: The challenge of combating misinformation effectively across numerous platforms is enormous, requiring coordinated efforts and cross-platform strategies.
Effective Strategies for Combating Misinformation
Addressing misinformation requires a more nuanced approach than simply presenting facts.
Beyond Fact-Checking: Narrative and Framing
Effective communication requires appealing to emotions and values.
- Audience Focus: Tailoring the message to resonate with the audience's values and concerns is crucial.
- Storytelling Techniques: Employing storytelling techniques can make information more engaging and memorable.
- Emotional Appeals: Appealing to emotions, such as hope or empathy, can be more effective than solely relying on logic and reason.
The Role of Community and Dialogue
Fostering dialogue and community engagement is essential.
- Respectful Discussions: Creating spaces for respectful discussions, where individuals can express their views without fear of judgment, is crucial.
- Constructive Conversations: Promoting constructive conversations focused on finding common ground can be more effective than confrontational approaches.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Educating individuals about critical thinking and media literacy helps them to better evaluate information.
Utilizing Technology and Social Media
Leveraging technology and social media is crucial.
- Algorithms to Identify Misinformation: Employing algorithms to identify and flag misinformation can help limit its spread.
- Disseminating Accurate Information: Utilizing social media to actively disseminate accurate information can counter false narratives.
- Fact-Checking Bots and AI: Fact-checking bots and AI technologies can assist in identifying and addressing misinformation more efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding why facts alone don't always change minds is crucial. The psychology of misinformation, coupled with the challenges faced by organizations like CNN, highlights the need for a more comprehensive approach. We must move beyond simply presenting facts and embrace strategies that focus on narrative, dialogue, and technology. Engaging critically with information sources, being mindful of our own biases, and participating in constructive discussions are essential steps in combating misinformation. Understanding the limitations of even CNN's misinformation experts highlights the need for a multi-faceted approach to effectively tackle this growing problem.

Featured Posts
-
 Tragic Loss 10 Year Old Dies On Rugby Pitch Leaving Behind A Legacy
May 02, 2025
Tragic Loss 10 Year Old Dies On Rugby Pitch Leaving Behind A Legacy
May 02, 2025 -
 Nikki Burdine Departs Wkrn News 2 Morning Show After Seven Years
May 02, 2025
Nikki Burdine Departs Wkrn News 2 Morning Show After Seven Years
May 02, 2025 -
 Lotto 6aus49 Zahlen Und Gewinnklassen Vom 12 April 2025
May 02, 2025
Lotto 6aus49 Zahlen Und Gewinnklassen Vom 12 April 2025
May 02, 2025 -
 Nea Ethniki Stratigiki P Syxikis Ygeias 2025 2028 Stoxoi Kai Draseis
May 02, 2025
Nea Ethniki Stratigiki P Syxikis Ygeias 2025 2028 Stoxoi Kai Draseis
May 02, 2025 -
 Is Fortnite Offline Current Server Status And Chapter 6 Season 3 Galactic Battle Updates
May 02, 2025
Is Fortnite Offline Current Server Status And Chapter 6 Season 3 Galactic Battle Updates
May 02, 2025
