Climate Change's Impact On Rainfall In Western Massachusetts
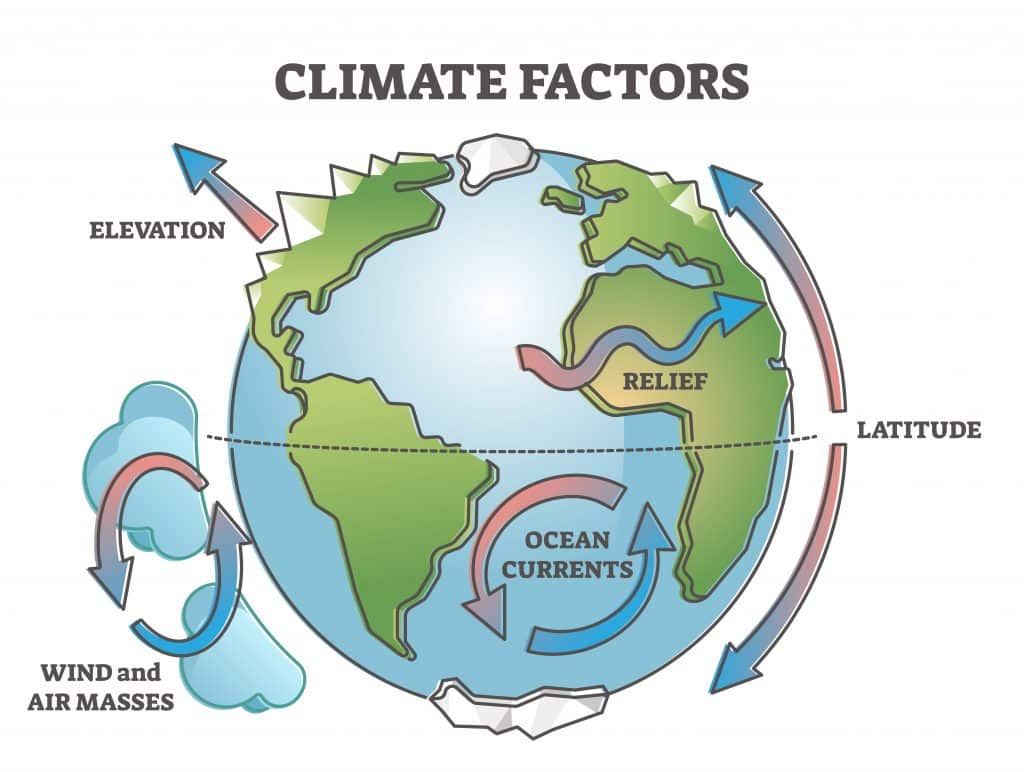
Table of Contents
Western Massachusetts, like many regions globally, is experiencing the undeniable effects of climate change. One of the most significant and readily observable impacts is the alteration of rainfall patterns. These shifts pose substantial challenges to the region's agriculture, water resources, and overall infrastructure. This article explores the observed and projected changes in rainfall in Western Massachusetts, examining the consequences and potential adaptation measures. We will delve into the implications for various sectors, offering insights into how Western Massachusetts can build resilience in the face of a changing climate.
Observed Changes in Rainfall Patterns
Western Massachusetts has witnessed noticeable changes in its rainfall patterns in recent decades. These changes are not subtle; they are impacting the daily lives of residents and the long-term sustainability of the region.
Increased Frequency of Intense Rainfall Events
The region is experiencing a concerning increase in the frequency and intensity of heavy rainfall events. This leads to several detrimental consequences:
- Increased risk of flash floods and soil erosion: Intense downpours overwhelm drainage systems, causing flash floods that damage property and erode valuable topsoil, impacting agricultural lands.
- Damage to infrastructure (roads, bridges, buildings): The force of rapidly rising water can severely damage roads, bridges, and buildings, leading to costly repairs and disruptions. This is particularly true for older infrastructure not designed to withstand such extreme events.
- Negative impacts on water quality due to runoff: Heavy rainfall washes pollutants and sediment from surfaces into rivers and streams, degrading water quality and harming aquatic ecosystems.
- Examples of recent extreme rainfall events in Western MA: Specific examples, such as the [insert date and location of a significant rainfall event], highlight the increasing severity of these events. Data from the National Weather Service can be referenced to support these claims.
Changes in Seasonal Rainfall Distribution
The timing and amount of rainfall throughout the year are also shifting. This altered seasonal distribution presents unique challenges:
- Shifts in the timing and amount of rainfall throughout the year: We're seeing instances of both prolonged dry spells and periods of excessive precipitation, disrupting the established seasonal patterns.
- Potential for longer periods of drought or excessive precipitation: This unpredictability makes it difficult for farmers and water managers to plan effectively. Longer droughts stress water resources, while excessive precipitation leads to flooding and erosion.
- Impacts on agriculture and water resource management: These shifts directly impact agricultural yields and water resource management strategies. Farmers face challenges in planting and harvesting, while water managers must adapt to fluctuating water levels.
- Data illustrating shifts in seasonal precipitation patterns: Data from sources like the [mention relevant local or state environmental agency] can be used to illustrate the observed shifts in seasonal precipitation.
Decreased Snowpack
A noticeable decline in snowpack is another consequence of climate change in Western Massachusetts:
- Reduced snow accumulation in winter months: Warmer temperatures are resulting in less snowfall and quicker snowmelt.
- Implications for water supply during spring and summer: Reduced snowpack diminishes the natural spring runoff that replenishes rivers and reservoirs, potentially leading to water shortages during drier months.
- Impact on winter tourism and recreational activities: Less snow negatively affects the winter tourism industry and recreational activities such as skiing and snowboarding.
- Comparison of historical snowpack data with recent trends: Analyzing historical snowpack data from reliable sources will vividly illustrate the downward trend.
Projected Future Changes in Rainfall
Understanding projected future changes is crucial for effective planning and mitigation.
Climate Models and Projections for Western Massachusetts
Various climate models predict significant changes in rainfall patterns for Western Massachusetts:
- Discussion of different climate models and their predictions: While there are variations between different models, a common theme emerges – an increase in the intensity of rainfall events and a shift in seasonal distribution.
- Projected changes in average annual rainfall: While total annual rainfall may not change drastically, the distribution will be highly uneven.
- Projected changes in the intensity and frequency of extreme rainfall events: Models consistently project a considerable increase in the frequency and intensity of heavy rainfall events.
- Uncertainty in climate projections and limitations of models: It's crucial to acknowledge the inherent uncertainties in climate projections and the limitations of the models. However, the general trends are clear and warrant proactive action.
Impacts on Water Resources
Changes in rainfall will significantly strain water resources:
- Increased strain on water resources during droughts: Longer and more severe droughts will put increasing pressure on water supplies.
- Increased risk of water shortages and conflicts over water allocation: Competition for limited water resources may lead to conflicts among different users.
- Potential for increased flooding and water contamination: Extreme rainfall events can cause widespread flooding, contaminating water sources and posing risks to public health.
- Strategies for improving water resource management: Implementing water conservation measures, improving water storage capacity, and exploring alternative water sources are crucial steps.
Impacts on Agriculture
Farmers will face significant challenges:
- Challenges for farmers due to unpredictable rainfall patterns: Farmers struggle to adapt to unpredictable rainfall, affecting planting schedules, crop yields, and overall farm profitability.
- Increased risk of crop failure and reduced yields: Unpredictable rainfall and extreme weather events significantly increase the risk of crop failure.
- Need for adaptation strategies such as drought-resistant crops: Adopting drought-resistant crops and implementing water-efficient irrigation techniques are crucial adaptations.
- Opportunities for climate-smart agriculture: Climate-smart agriculture practices can improve resilience and sustainability.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Proactive strategies are essential to mitigate the negative impacts and adapt to changing rainfall patterns.
Infrastructure Improvements
Investing in resilient infrastructure is paramount:
- Investing in improved drainage systems and flood defenses: Upgrading drainage systems and constructing flood defenses are crucial to protect communities from the increased risk of flooding.
- Strengthening infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events: Building more resilient roads, bridges, and buildings is vital to reduce damage from heavy rainfall and flooding.
- Examples of successful adaptation projects in other regions: Learning from successful adaptation projects in other regions can inform strategies for Western Massachusetts.
Water Resource Management
Effective water management is critical:
- Implementing water conservation measures: Promoting water-efficient practices in agriculture, industry, and households is crucial.
- Developing strategies for managing water supply during droughts: Developing strategies for managing water allocation and ensuring equitable access during droughts is critical.
- Improving water storage and distribution infrastructure: Investing in improved water storage and distribution infrastructure can ensure water availability during dry periods.
Agricultural Practices
Farmers need to adopt adaptive strategies:
- Promoting drought-resistant crops and farming techniques: Encouraging the use of drought-resistant crops and water-efficient farming techniques is essential.
- Improving soil health to enhance water retention: Healthy soils absorb and retain more water, reducing the impact of droughts.
- Diversifying agricultural practices to reduce risk: Diversification can help mitigate the risks associated with unpredictable rainfall.
Conclusion
Climate change is profoundly altering rainfall patterns in Western Massachusetts, leading to more intense rainfall events, shifts in seasonal distribution, and decreased snowpack. These changes have far-reaching implications for agriculture, water resources, and infrastructure, demanding proactive mitigation and adaptation strategies. Understanding the impact of climate change on rainfall in Western Massachusetts is crucial for effective planning and resource management. By implementing the adaptation and mitigation strategies discussed, we can build a more resilient future and protect our communities from the effects of changing rainfall patterns. Learn more about how you can contribute to addressing the challenges of climate change and its impact on rainfall in Western Massachusetts. Your actions today will help shape a more sustainable tomorrow.

Featured Posts
-
 Thompsons Struggle In Monte Carlo A Detailed Look
May 31, 2025
Thompsons Struggle In Monte Carlo A Detailed Look
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguia Denies Doping Claims After Positive Test Result
May 31, 2025
Munguia Denies Doping Claims After Positive Test Result
May 31, 2025 -
 Building The Good Life A Step By Step Approach
May 31, 2025
Building The Good Life A Step By Step Approach
May 31, 2025 -
 Cycle News Magazine 2025 Issue 17 Features And Articles On Cycling Technology And Performance
May 31, 2025
Cycle News Magazine 2025 Issue 17 Features And Articles On Cycling Technology And Performance
May 31, 2025 -
 Miley Cyrus Unveils New Visuals For End Of The World Single
May 31, 2025
Miley Cyrus Unveils New Visuals For End Of The World Single
May 31, 2025
