Cities Face Increasing Risks From Dangerous Climate Whiplash

Table of Contents
Understanding Climate Whiplash and its Urban Impact
Climate whiplash refers to rapid and unpredictable transitions between extreme weather events. Instead of a gradual shift in climate patterns, we see jarring juxtapositions like intense heatwaves immediately followed by torrential downpours or prolonged droughts suddenly giving way to devastating storms. These rapid shifts overwhelm city infrastructure and emergency services, creating cascading effects that disrupt daily life and threaten public safety.
For example, a city experiencing a prolonged heatwave might see its water resources severely strained, putting pressure on the water supply and increasing the risk of wildfires. Then, a sudden deluge of rainfall can overload aging sewage systems, leading to widespread flooding and contamination. This back-to-back onslaught of extreme weather is far more challenging to manage than a single, isolated event.
- Increased strain on water resources: Heatwaves increase demand, while floods can contaminate supplies.
- Damage to transportation networks: Roads, bridges, and public transport are vulnerable to both heat damage and flooding.
- Overwhelmed healthcare systems: Heat-related illnesses and injuries from extreme weather events surge, straining hospital capacity.
- Widespread power outages: Storms and floods frequently damage power lines and disrupt electricity supply.
- Increased risk of disease outbreaks: Standing water after floods creates breeding grounds for disease vectors.
Vulnerable Urban Infrastructure and Populations
Certain urban infrastructures are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate whiplash. Aging sewage systems, inadequate drainage networks, and coastal areas are particularly at risk of catastrophic damage from floods and storms. Furthermore, the consequences of climate whiplash are not felt equally. Vulnerable populations – including low-income communities, the elderly, and people with disabilities – are disproportionately affected. Existing inequalities exacerbate these risks, creating a vicious cycle of vulnerability.
- Limited access to resources during emergencies: Vulnerable populations often lack access to essential resources like clean water, food, and shelter during and after extreme weather events.
- Higher rates of heat-related illness: The elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions are especially susceptible to heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses during heatwaves.
- Increased risk of displacement and homelessness: Extreme weather events can damage homes and displace residents, especially those living in precarious housing situations.
- Difficulty in accessing emergency services: Vulnerable populations may face greater challenges in accessing emergency services during and after extreme weather events.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Cities
Combating the threat of climate whiplash requires a two-pronged approach: mitigation and adaptation. Mitigation focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow the pace of climate change and lessen the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Adaptation, on the other hand, involves implementing strategies to build city resilience and minimize the impacts of climate whiplash.
- Investing in green infrastructure: Parks, green roofs, and urban forests can help regulate temperatures, reduce stormwater runoff, and improve air quality.
- Implementing water management strategies: Improved drainage systems, water storage solutions, and drought-resistant landscaping can enhance a city's ability to withstand extreme rainfall and prolonged dry spells.
- Developing robust emergency response plans: Cities need well-rehearsed and well-resourced emergency response plans to effectively manage the consequences of climate whiplash events.
- Improving building codes: Strengthening building codes to withstand extreme weather conditions is crucial for protecting lives and property.
- Promoting community-based adaptation initiatives: Engaging local communities in developing and implementing adaptation strategies can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility.
The Economic Costs of Climate Whiplash
The economic toll of climate whiplash on cities is substantial and escalating. Repair and reconstruction costs after extreme weather events are astronomical, not to mention the losses from business disruption and decreased productivity. The cost of inaction far outweighs the investment required in mitigation and adaptation strategies. Ignoring these risks will lead to a cycle of expensive emergency responses, while proactively building resilience will yield long-term economic benefits.
- Repair and reconstruction costs: The financial burden of repairing damaged infrastructure and rebuilding after extreme weather events is immense.
- Loss of productivity and business disruption: Extreme weather events disrupt businesses, leading to lost revenue and decreased productivity.
- Increased insurance premiums: The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events lead to higher insurance premiums for cities and businesses.
- Healthcare costs related to extreme weather events: The rise in heat-related illnesses and injuries puts a strain on healthcare systems, increasing costs.
Conclusion:
Cities face a growing threat from climate whiplash, experiencing increasingly frequent and intense cycles of extreme weather events. This poses significant risks to urban infrastructure, vulnerable populations, and the economy. Addressing this challenge requires a concerted effort to both mitigate climate change and adapt to its unavoidable consequences. Investing in resilient infrastructure, developing robust emergency response plans, and fostering community-based adaptation initiatives are crucial for building resilient cities that can withstand the impacts of climate whiplash. Don't wait for the next climate whiplash event to devastate your city. Take action today by supporting policies and initiatives that promote urban resilience and adaptation strategies to mitigate the dangers of climate whiplash, ensuring a safer and more sustainable future for all.

Featured Posts
-
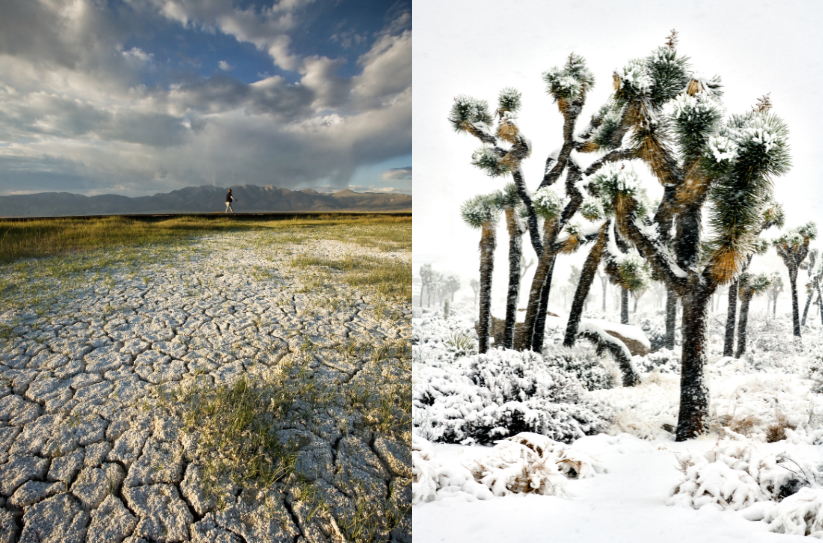 New Report Details Dangerous Climate Whiplash In Cities
May 28, 2025
New Report Details Dangerous Climate Whiplash In Cities
May 28, 2025 -
 Mathurins Ejection Details On The Game 4 Incident With Hunter
May 28, 2025
Mathurins Ejection Details On The Game 4 Incident With Hunter
May 28, 2025 -
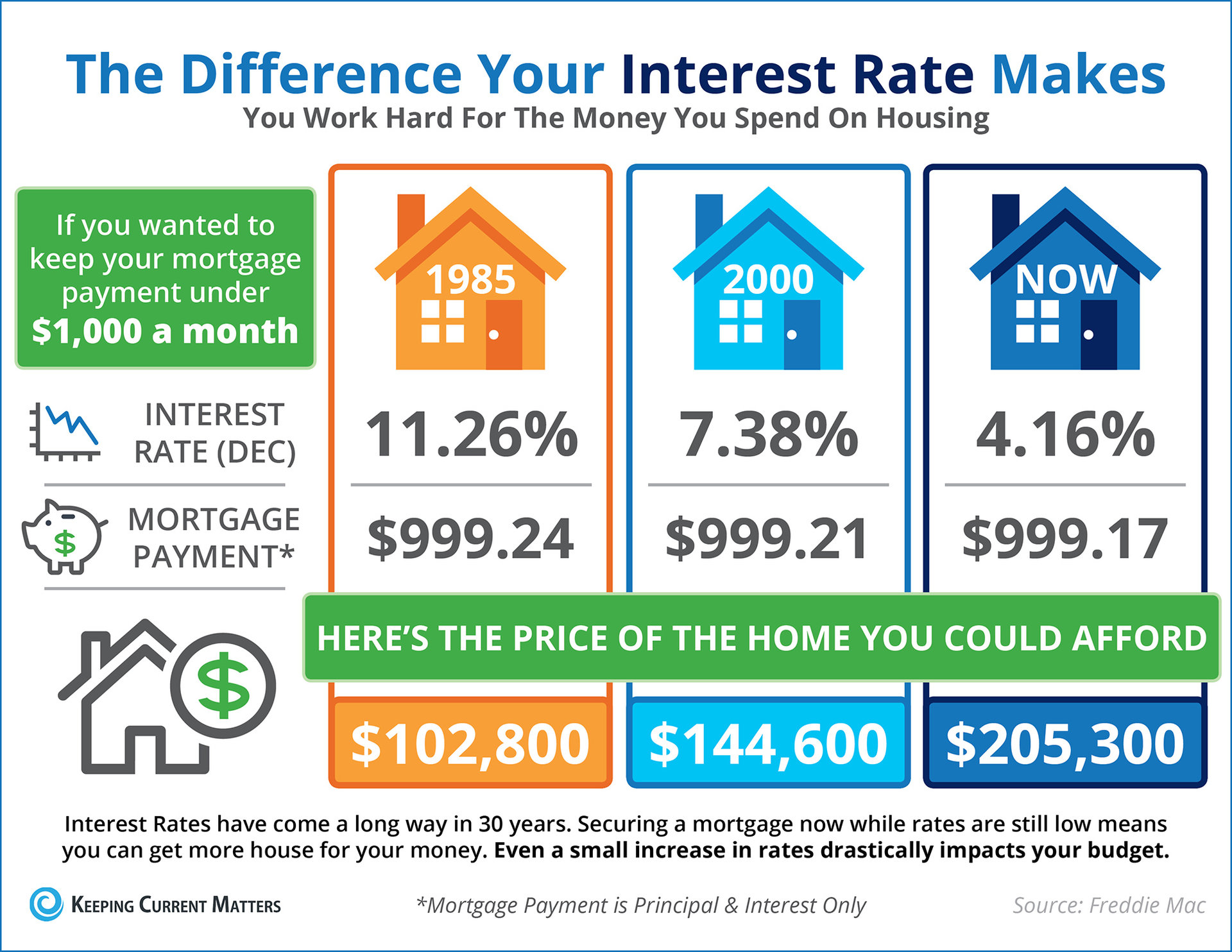 Find The Best Personal Loan Interest Rates Today Simple Comparison
May 28, 2025
Find The Best Personal Loan Interest Rates Today Simple Comparison
May 28, 2025 -
 Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Tengah 24 April 2024 Antisipasi Hujan
May 28, 2025
Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Tengah 24 April 2024 Antisipasi Hujan
May 28, 2025 -
 Program Pembangunan Taman Kota Wawali Bagus Susetyo Di Balikpapan
May 28, 2025
Program Pembangunan Taman Kota Wawali Bagus Susetyo Di Balikpapan
May 28, 2025
