Choosing The Right Bus: Hydrogen Vs. Battery Power In European Cities
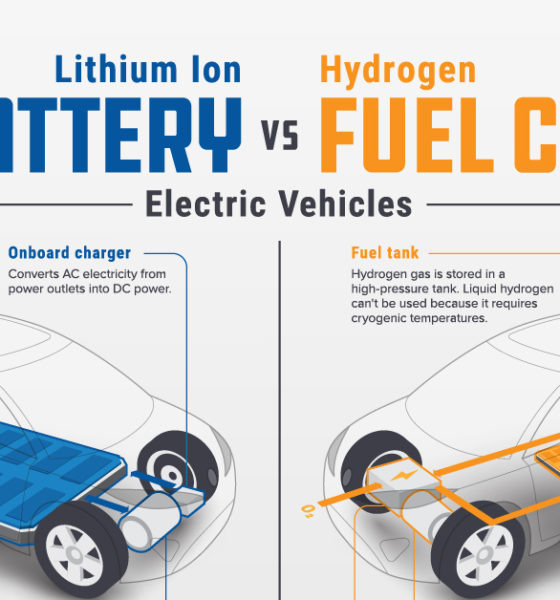
Table of Contents
- Environmental Impact: A Comparison of Emissions
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Air Pollution
- Operational Considerations: Range, Refueling Infrastructure, and Cost
- Range and Refueling Time
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Technological Maturity and Future Prospects for Hydrogen vs Battery Buses in Europe
- Current Market Share and Deployment
- Scalability and Future Developments
- Conclusion
European cities are facing increasing pressure to decarbonize their public transport systems. A key element of this transition is the choice between hydrogen and battery-electric buses. This article will explore the advantages and disadvantages of each technology, helping city planners and transport authorities make informed decisions about which type of bus best suits their specific needs and contributes to a sustainable future. The debate surrounding Hydrogen vs Battery Buses Europe is crucial for shaping the future of urban mobility.
Environmental Impact: A Comparison of Emissions
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The lifecycle emissions of hydrogen and battery buses differ significantly. For hydrogen buses, the production method of hydrogen heavily influences the overall carbon footprint. "Grey hydrogen," produced from natural gas, carries a substantial carbon footprint, while "green hydrogen," produced via electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources, offers significantly lower emissions. Battery buses, on the other hand, depend on the electricity source used for charging. Charging from a grid heavily reliant on fossil fuels results in higher emissions, while renewable energy sources drastically reduce the carbon footprint.
- Hydrogen buses (green hydrogen): Offer zero tailpipe emissions and significantly reduced lifecycle emissions compared to grey hydrogen.
- Hydrogen buses (grey hydrogen): Have higher lifecycle emissions due to the carbon-intensive production of hydrogen.
- Battery buses (renewable energy): Have low to zero lifecycle emissions depending on the renewable energy mix of the electricity grid.
- Battery buses (fossil fuel electricity): Have higher lifecycle emissions due to the reliance on fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
Air Pollution
Air quality is a critical concern in European cities. Both hydrogen and battery buses offer significant advantages over diesel buses, but their impacts differ.
- Hydrogen buses: Produce only water vapor as tailpipe emissions, significantly improving local air quality.
- Battery buses: Have no direct tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner urban air. However, the electricity generation process may still impact air quality depending on the energy source.
- Diesel buses: Emit significant levels of particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other harmful pollutants, contributing to respiratory illnesses and other health problems.
The reduction in NOx and PM from both hydrogen and battery buses translates to improved public health and a better quality of life for urban residents.
Operational Considerations: Range, Refueling Infrastructure, and Cost
Range and Refueling Time
Range and refueling time are crucial operational aspects to consider when choosing between hydrogen and battery buses.
- Hydrogen buses: Generally offer longer ranges, making them suitable for longer routes and less frequent refueling. Refueling time is comparable to diesel buses, typically taking just a few minutes.
- Battery buses: Have shorter ranges, requiring more frequent charging stops, particularly on longer routes. Charging times can range from several hours for overnight charging to shorter periods using fast-charging technology.
The required refueling/charging infrastructure is a major investment consideration for both technologies. The existing charging infrastructure for electric buses is more widespread in Europe than hydrogen refueling stations.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is a significant factor in the decision-making process. While battery electric bus technology has a lower initial investment cost, long-term operational costs need careful consideration.
- Initial Investment: Hydrogen buses currently have higher upfront costs due to the limited economies of scale in production and the need for specialized refueling infrastructure.
- Operational Costs: The cost of hydrogen fuel and the maintenance of hydrogen fuel cell technology needs to be compared with the electricity costs and maintenance of battery electric buses. This varies considerably depending on energy prices and maintenance contracts.
- Long-term Cost-effectiveness: The long-term cost-effectiveness depends on several factors, including the price of hydrogen, the price of electricity, the lifespan of the fuel cells and batteries, and the cost of maintenance.
Technological Maturity and Future Prospects for Hydrogen vs Battery Buses in Europe
Current Market Share and Deployment
Currently, battery-electric buses have a significant market share in Europe due to the more established charging infrastructure and lower initial investment costs. However, hydrogen bus technology is rapidly developing, supported by increasing investments and government incentives.
- Battery Electric Buses: Dominate the current market in Europe.
- Hydrogen Buses: Demonstrating rapid technological progress and increasing deployment in pilot projects across various European cities.
- Government Policies: Various European Union and national government policies and subsidies are supporting the development and deployment of both technologies.
Scalability and Future Developments
Both hydrogen and battery technologies are expected to experience significant advancements in the coming years, impacting their scalability and market competitiveness.
- Green Hydrogen Production: Costs are decreasing, making hydrogen a more viable and environmentally friendly fuel source.
- Battery Technology: Continuous improvements in energy density, lifespan, and fast-charging capabilities are enhancing the practicality of battery-electric buses.
- Research and Development: Significant investment in research and development is driving innovation in both battery and hydrogen technologies.
Conclusion
The choice between hydrogen and battery-electric buses for European cities is a complex decision. While battery-electric buses currently lead the market due to established infrastructure and lower initial costs, hydrogen buses offer compelling advantages in terms of range and refueling time, particularly for longer routes. The optimal choice depends heavily on specific city needs, existing infrastructure, energy mix, and budget constraints. Careful consideration of all factors—environmental impact, operational aspects, and technological advancements—is essential. Continued research into Hydrogen vs Battery Buses Europe will be crucial for ensuring the most sustainable and efficient public transport systems in European cities. Choose the right bus for your city – weigh the pros and cons of hydrogen vs battery buses in Europe carefully!
 Warrior Steve Kerrs Optimism Stephen Currys Injury Update And Return
Warrior Steve Kerrs Optimism Stephen Currys Injury Update And Return
 El Futuro De Simone Biles Los Angeles 2028 En La Balanza
El Futuro De Simone Biles Los Angeles 2028 En La Balanza
 The Trae Young Travel Debate Were The Refs Too Lenient
The Trae Young Travel Debate Were The Refs Too Lenient
 White Lotus A Surprise Cameo From An Oscar Winner
White Lotus A Surprise Cameo From An Oscar Winner
 Laura And Jason Kennys Joy A Daughter Arrives
Laura And Jason Kennys Joy A Daughter Arrives
