Canadian Regulatory Pause: Examining The Controversy Surrounding ESG Reporting
Table of Contents
The Genesis of the Pause: Understanding the Government's Rationale
The Canadian government's stated reasons for pausing the implementation of mandatory ESG reporting stem from a confluence of concerns. While proponents of mandatory ESG disclosure highlight its benefits, the government has cited several key challenges:
-
Lack of internationally harmonized ESG reporting standards: The absence of globally consistent metrics makes comparison difficult and could lead to inconsistencies in reporting across different sectors and jurisdictions. This lack of standardization complicates the process of enforcement and evaluation. The diversity in ESG frameworks globally creates difficulties for Canadian companies operating internationally.
-
Concerns about the potential for increased regulatory burden on businesses: The government acknowledges concerns that mandatory ESG reporting could place a significant administrative and financial burden on Canadian businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This added cost could hinder their growth and competitiveness. The complexities involved in data collection, verification, and reporting could prove particularly challenging for smaller entities.
-
Need for further consultation with stakeholders: The government emphasizes the importance of broad consultation with various stakeholders – including businesses, investors, civil society organizations, and Indigenous communities – to ensure that any future ESG reporting framework is well-designed and effective. This comprehensive stakeholder engagement is vital for creating a sustainable and widely accepted regulatory structure.
-
Uncertainty about the effectiveness of current ESG frameworks in driving meaningful change: There is ongoing debate regarding the actual effectiveness of ESG disclosures in fostering genuine improvements in environmental and social performance. The government has expressed a need for further research and evidence to demonstrate a direct correlation between ESG reporting and tangible improvements.
Arguments For and Against Mandatory ESG Reporting in Canada
The debate surrounding mandatory ESG reporting in Canada is sharply divided. Proponents and opponents present compelling arguments.
Proponents' Viewpoint:
Arguments in favor of mandatory ESG reporting center around:
-
Increased transparency and accountability for Canadian companies: Mandatory reporting would shed light on corporate practices and improve corporate accountability, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions. This transparency helps identify companies that engage in greenwashing.
-
Attracting responsible investments and improving corporate reputation: Companies with strong ESG performance are increasingly attracting responsible investments, leading to better access to capital and improved corporate reputation. Mandatory ESG reporting facilitates this trend.
-
Alignment with global ESG trends and international best practices: Many countries are adopting mandatory ESG reporting, and Canada aligning itself with global standards ensures competitiveness in international markets. Harmonization of reporting frameworks is crucial for investor confidence and effective global action on sustainability.
-
Driving sustainable business practices and positive environmental impact: Mandatory disclosure encourages companies to prioritize sustainable practices to improve their ESG ratings. This promotes a wider adoption of sustainable business models.
-
Protecting investors from greenwashing: Mandatory reporting with robust verification mechanisms would reduce the risk of greenwashing – instances where companies make misleading or exaggerated claims about their ESG performance.
Opponents' Viewpoint:
Counterarguments against mandatory ESG reporting highlight:
-
Concerns about the cost and administrative burden on businesses, particularly SMEs: The cost of compliance with mandatory reporting requirements could be prohibitive for smaller businesses, potentially hindering their growth and competitiveness. Tailored approaches that account for size and sector are often proposed as solutions.
-
Potential for inconsistencies and complexities in reporting frameworks: A lack of standardized metrics could lead to inconsistencies in reporting and make it difficult to compare companies' ESG performance accurately. Streamlining and harmonizing reporting requirements are essential to avoid confusion.
-
Fear of unintended consequences and potential for stifling economic growth: Opponents argue that excessive regulation could stifle economic growth by discouraging investment and innovation. Finding a balance between regulation and economic growth is a key challenge.
-
Debate over the effectiveness of ESG disclosures in actually improving ESG performance: There's a lack of conclusive evidence that ESG disclosures directly translate to improved ESG performance. Further research and robust verification mechanisms are essential to bridge this gap.
-
Concerns about the potential for politicization of ESG standards: Some worry that ESG standards could become politicized, with governments imposing subjective interpretations that favor certain industries or ideologies. Transparency and evidence-based approaches are vital to avoid such politicization.
The International Context: Comparing Canadian ESG Regulations to Other Jurisdictions
Canada's approach to ESG reporting differs from other jurisdictions. The EU, for example, has implemented comprehensive and mandatory ESG disclosure requirements for many sectors, leading the charge in setting global standards. The US, while having a less centralized approach, is seeing increased state-level activity and growing pressure for federal regulation. The UK also has robust guidelines and regulations encouraging ESG reporting. Comparing these various approaches reveals that a balanced approach is crucial – one that considers the specific context and industry specifics without sacrificing essential transparency and accountability. International cooperation and the harmonization of ESG reporting standards are crucial steps to ensure consistency and effectiveness.
The Future of ESG Reporting in Canada: Potential Outcomes and Implications
The regulatory pause leaves several potential scenarios:
-
Potential for a revised or modified mandatory ESG reporting framework: The government might introduce a revised framework, addressing the concerns raised regarding standardization, cost, and effectiveness. A phased approach, beginning with larger companies and gradually expanding to SMEs, is possible.
-
Increased focus on voluntary ESG reporting and industry initiatives: While mandatory reporting remains paused, voluntary initiatives and industry-led standards could gain prominence. This approach might lack the uniformity of mandatory reporting but could foster innovation and collaboration.
-
The impact on Canadian businesses' investment strategies and global competitiveness: The uncertainty created by the pause could affect Canadian businesses' investment strategies and potentially impact their global competitiveness. Clarity is needed to ensure continued foreign direct investment and business confidence.
-
The role of investor pressure and stakeholder engagement in shaping future regulations: Investor pressure and active stakeholder engagement are crucial in shaping future ESG reporting regulations. Active participation in consultations and dialogue is vital.
Conclusion:
The Canadian government's pause on mandatory ESG reporting in Canada is a significant development. While concerns about regulatory burden and standardization are valid, the potential benefits of transparency, improved sustainability, and enhanced investor confidence remain compelling. The outcome will profoundly impact Canadian businesses and Canada's position on the global ESG stage. It is essential to stay informed on developments regarding ESG reporting in Canada and to participate in the ongoing conversation to help shape a balanced approach that fosters both sustainable business practices and economic competitiveness. Engage with stakeholders, participate in consultations, and advocate for clear, effective, and internationally harmonized standards for ESG reporting in Canada.

Featured Posts
-
 Ryujinx Emulators Development Ceases After Nintendo Intervention
Apr 25, 2025
Ryujinx Emulators Development Ceases After Nintendo Intervention
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Eurovision 2024 Uks Surprising Reveal Ahead Of Competition
Apr 25, 2025
Eurovision 2024 Uks Surprising Reveal Ahead Of Competition
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Your Spring 2025 Country Music Festival Guide Top Picks And Essential Info
Apr 25, 2025
Your Spring 2025 Country Music Festival Guide Top Picks And Essential Info
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Apple Tv S Rise As A Crime Thriller Powerhouse Is Its Next Series The Best Yet
Apr 25, 2025
Apple Tv S Rise As A Crime Thriller Powerhouse Is Its Next Series The Best Yet
Apr 25, 2025 -
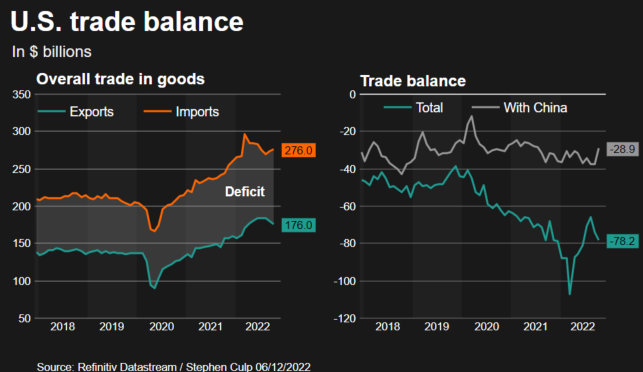 Chinas Increased Pain Tolerance Implications For The Us China Trade War
Apr 25, 2025
Chinas Increased Pain Tolerance Implications For The Us China Trade War
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ashhr Njwm Krt Alqdm Almdkhnyn Hqayq Sadmt
May 10, 2025
Ashhr Njwm Krt Alqdm Almdkhnyn Hqayq Sadmt
May 10, 2025 -
 Large Scale Music Festival With Olly Murs At Picturesque Castle Near Manchester
May 10, 2025
Large Scale Music Festival With Olly Murs At Picturesque Castle Near Manchester
May 10, 2025 -
 Paris Saint Germains Triumph Luis Enriques Strategic Masterclass
May 10, 2025
Paris Saint Germains Triumph Luis Enriques Strategic Masterclass
May 10, 2025 -
 How Luis Enrique Reshaped Paris Saint Germain A Winning Formula
May 10, 2025
How Luis Enrique Reshaped Paris Saint Germain A Winning Formula
May 10, 2025 -
 Beautiful Castle Near Manchester The Venue For Olly Murs Music Festival
May 10, 2025
Beautiful Castle Near Manchester The Venue For Olly Murs Music Festival
May 10, 2025
