Building Privacy-Compliant Mobile Apps: A CNIL Perspective

Table of Contents
Understanding the CNIL's Guidelines for Mobile Apps
The CNIL, France's data protection authority, provides comprehensive guidelines for ensuring the privacy of personal data processed by mobile applications. Adherence to these guidelines is crucial for any app developer targeting the French market or handling data of French citizens.
Key Principles of the CNIL
The CNIL emphasizes several core principles when it comes to data protection in mobile applications. These principles form the foundation of a privacy-compliant app:
-
Data Minimization: Collect only the data strictly necessary for the app's functionality. Avoid collecting excessive or irrelevant personal information. For example, if your app only needs a user's email for login, don't ask for their home address or phone number.
-
Purpose Limitation: Clearly define the purpose for collecting each piece of data and ensure that you only use it for that specified purpose. Avoid repurposing data without obtaining fresh consent. For instance, if you collect email addresses for newsletter subscriptions, don’t use them for targeted advertising without explicit permission.
-
Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access, loss, or alteration. This includes encryption, secure storage, access controls, and regular security audits. The CNIL provides detailed recommendations on appropriate security measures for mobile apps on their website.
-
User Consent: Obtain freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous consent before collecting and processing any personal data. Consent must be easily withdrawable. This means clear, concise language and granular control over what data is shared.
The CNIL provides detailed recommendations and publications on their website (www.cnil.fr) that delve deeper into these principles and offer practical guidance for developers.
Data Protection by Design and Default
Integrating privacy considerations from the very beginning of the app's development lifecycle is essential. This "privacy by design" approach ensures privacy is not an afterthought but a fundamental aspect of the app's architecture.
-
Anonymization Techniques: Employ techniques like data masking or pseudonymization to reduce the identifiability of users wherever possible.
-
Differential Privacy: Consider incorporating differential privacy methods to protect individual user data while still allowing for data analysis.
-
Federated Learning: Explore the use of federated learning models to train machine learning algorithms without directly accessing sensitive user data.
Privacy by default means configuring the app to offer the highest level of privacy protection from the start. This means minimizing data collection and processing unless the user actively chooses to share more information.
Managing User Consent and Data Collection
Obtaining valid consent and adhering to data minimization and purpose limitation are critical for CNIL compliance.
Obtaining Meaningful Consent
The CNIL strictly regulates how consent is obtained. It must be:
-
Freely Given: Users shouldn't feel pressured or coerced into providing consent.
-
Specific: Consent must be given for each specific purpose of data processing. A blanket consent statement is insufficient.
-
Informed: Users must be fully informed about what data is collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it.
-
Unambiguous: Consent should be clearly expressed, either through a checkbox or other explicit action.
Examples of appropriate consent mechanisms include clear, concise checkboxes within the app's settings, allowing users to opt-in or opt-out of specific data collection practices. Conversely, pre-checked boxes or unclear consent language are considered insufficient and violate CNIL guidelines.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Only collect the minimum necessary data to achieve the app's functionality. This reduces the risk of data breaches and strengthens user privacy.
-
Pseudonymization: Replace identifying information with pseudonyms whenever possible.
-
Clear Communication: Explicitly state the purpose for collecting each piece of data in your privacy policy and within the app itself.
For example, if your app requires location data for a specific feature, explain this clearly to the user and only collect location data when that feature is actively used.
Data Security and Breach Notification
Protecting user data is paramount, and reacting appropriately to incidents is critical.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
The CNIL expects robust security measures to protect user data throughout its lifecycle. This includes:
-
Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
-
Secure Storage: Utilize secure storage solutions compliant with CNIL guidelines.
-
Access Control: Implement strong access controls to limit access to user data only to authorized personnel.
-
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities.
-
Vulnerability Assessments: Proactively scan your app for known vulnerabilities and patch them promptly.
The CNIL offers detailed recommendations on appropriate security standards for mobile apps, which developers should consult.
Responding to Data Breaches
In the event of a data breach, the CNIL requires prompt reporting and remediation:
-
Incident Response Plan: Have a well-defined incident response plan in place to guide actions in case of a breach.
-
Notification Procedures: Know your obligations regarding notifying users and the CNIL of a data breach.
-
Remediation Strategies: Take swift action to contain the breach, mitigate its impact, and prevent future occurrences.
Failing to comply with breach notification requirements can lead to significant penalties.
Transparency and User Rights
Transparency and respecting user rights are crucial aspects of CNIL compliance.
Providing a Clear Privacy Policy
A comprehensive and easily understandable privacy policy is essential. It should include:
-
Data Collected: A detailed list of all data collected by the app.
-
Purpose of Collection: Clearly stated purposes for collecting each piece of data.
-
Data Retention Periods: Explain how long data is stored and the criteria for deletion.
-
User Rights: Clearly explain users' rights under GDPR and French data protection law (access, rectification, erasure, etc.).
-
Contact Information: Provide contact details for users to exercise their rights or ask questions.
Facilitating User Rights
Your app should enable users to easily exercise their rights:
-
Data Access: Provide a simple mechanism for users to access their data.
-
Data Rectification: Allow users to correct any inaccurate information.
-
Data Erasure (“Right to be Forgotten”): Implement a process for users to request deletion of their data.
-
Data Portability: Allow users to receive their data in a machine-readable format.
User-friendly interfaces for managing privacy settings within the app are crucial for demonstrating commitment to user rights.
Conclusion
Building privacy-compliant mobile apps is not merely a regulatory requirement; it's a crucial step in building trust with users and avoiding significant legal penalties. By adhering to the CNIL's guidelines and prioritizing data protection from the design phase, developers can create secure and trustworthy applications. This involves understanding key principles like data minimization, obtaining meaningful consent, implementing robust security measures, and providing users with clear transparency regarding their data. Remember, consistently integrating privacy considerations throughout the development lifecycle is essential for creating truly privacy-compliant mobile apps. Start prioritizing building privacy-compliant mobile apps today!

Featured Posts
-
 Seb S A Document Amf Cp 2025 E1021792 Analyse Du Rapport Du 24 Fevrier 2025
Apr 30, 2025
Seb S A Document Amf Cp 2025 E1021792 Analyse Du Rapport Du 24 Fevrier 2025
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Mdynt Martyny Tshhd Rqma Qyasya Jdyda Fy Asthlak Alraklyt
Apr 30, 2025
Mdynt Martyny Tshhd Rqma Qyasya Jdyda Fy Asthlak Alraklyt
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Princeton Donates Laptops To New Jersey Correctional Facilities For Education
Apr 30, 2025
Princeton Donates Laptops To New Jersey Correctional Facilities For Education
Apr 30, 2025 -
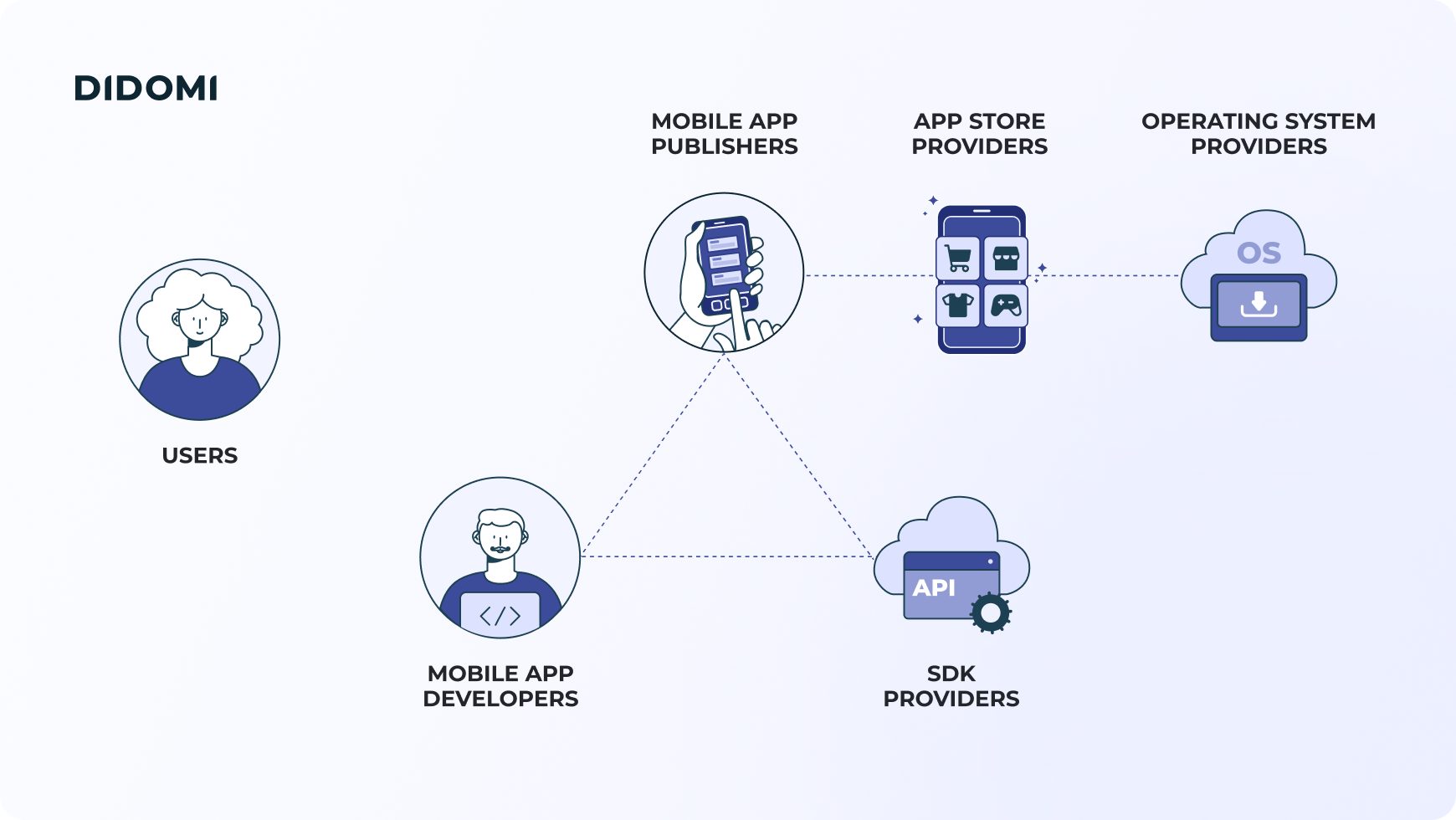 Cnil Recommendations For Mobile App Privacy A Practical Guide
Apr 30, 2025
Cnil Recommendations For Mobile App Privacy A Practical Guide
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Blue Ivy And Rumis Stylish Super Bowl Appearance Beyonces Absence Explained
Apr 30, 2025
Blue Ivy And Rumis Stylish Super Bowl Appearance Beyonces Absence Explained
Apr 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Climate Smart Villages In Africa Schneider Electrics Innovative Approach
Apr 30, 2025
Climate Smart Villages In Africa Schneider Electrics Innovative Approach
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Schneider Electric Brings Climate Smart Villages To Africa
Apr 30, 2025
Schneider Electric Brings Climate Smart Villages To Africa
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Channing Tatum Confirms Relationship With Inka Williams Following Zoe Kravitz Split
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatum Confirms Relationship With Inka Williams Following Zoe Kravitz Split
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Channing Tatums New Girlfriend Inka Williams And Their Public Display Of Affection
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatums New Girlfriend Inka Williams And Their Public Display Of Affection
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Channing Tatum And Inka Williams Rumoured F1 Appearance In Melbourne
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatum And Inka Williams Rumoured F1 Appearance In Melbourne
Apr 30, 2025
