Bilateral Anophthalmia: Understanding The Rare Condition Of Babies Born Without Eyes
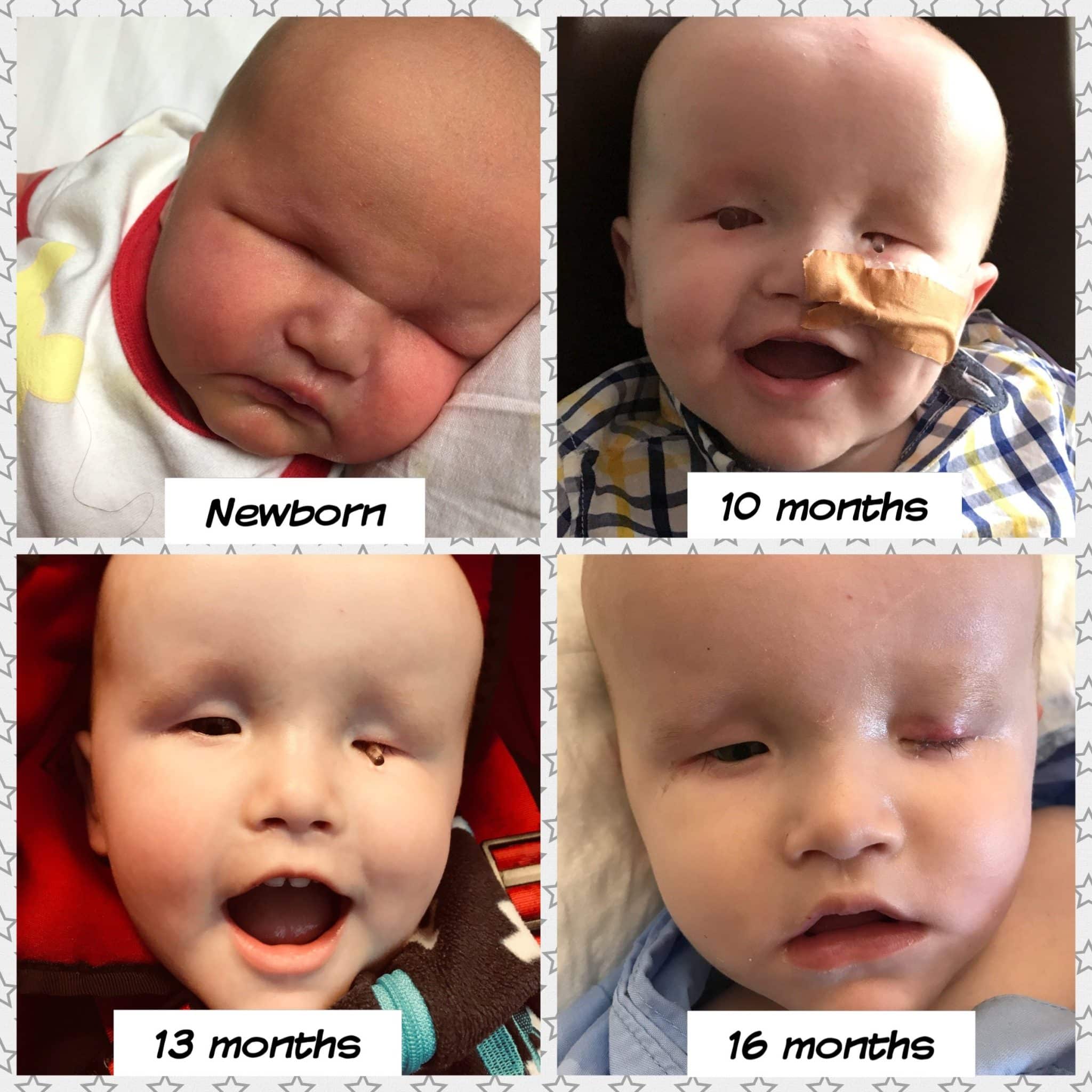
Table of Contents
Causes of Bilateral Anophthalmia
The absence of eyes at birth, known as bilateral anophthalmia, results from a complex interplay of genetic and potentially environmental factors. While research continues to unravel the complexities of this condition, several key areas have been identified.
Genetic Factors
Genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities play a significant role in many cases of bilateral anophthalmia. Several genes have been implicated, although the exact mechanisms are still being investigated.
- Known Genetic Associations: Research has identified links between bilateral anophthalmia and mutations in genes such as PAX6, OTX2, and SOX2, which are crucial for eye development during fetal stages. These genes regulate the expression of other genes involved in the intricate process of eye formation.
- Inheritance Patterns: Inheritance patterns can vary. Some cases are linked to autosomal recessive inheritance, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene for the child to be affected. Other instances may involve autosomal dominant inheritance or more complex genetic interactions.
- Ongoing Research: The genetic landscape of bilateral anophthalmia is complex. Ongoing research using advanced genomic techniques is crucial to identifying further genetic contributors and clarifying inheritance patterns. This understanding will improve genetic counseling for families affected by this condition.
Environmental Factors
While genetic factors are predominantly implicated, the possibility of environmental influences cannot be entirely ruled out. However, research in this area is significantly limited.
- Limitations of Current Research: The role of environmental factors in bilateral anophthalmia remains largely unknown. Establishing a definitive link between environmental exposures and the condition is challenging due to the rarity of the condition and the difficulties in identifying specific causal factors.
- Potential Teratogens: Some studies cautiously suggest a potential association with certain teratogens – substances that can cause birth defects – during pregnancy. However, more research is needed to confirm any causal relationship and to identify specific teratogenic agents involved. It's crucial to note that correlation does not equal causation.
Diagnosis and Screening
Early diagnosis of bilateral anophthalmia is essential for enabling parents to prepare and for facilitating access to appropriate support and intervention services. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of prenatal and postnatal methods.
Prenatal Diagnosis
Prenatal diagnosis allows for early parental preparation and facilitates access to support services.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound scans during pregnancy can sometimes detect the absence of eyes. However, the accuracy of prenatal ultrasound in diagnosing bilateral anophthalmia may be limited, particularly in early stages of pregnancy.
- Other Imaging Techniques: More sophisticated imaging techniques, such as fetal MRI, might provide a more detailed assessment, but these are not routinely used for this specific condition due to its rarity.
- Limitations of Prenatal Diagnosis: Prenatal diagnosis is not always definitive, and some cases may only be confirmed after birth.
Postnatal Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination immediately after birth will confirm the diagnosis of bilateral anophthalmia.
- Physical Examination: The absence of eyes is readily apparent upon visual inspection by healthcare professionals.
- Ophthalmologist and Specialists: A pediatric ophthalmologist will confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of associated anomalies, as bilateral anophthalmia can sometimes be accompanied by other health conditions.
Treatment and Management of Bilateral Anophthalmia
The management of bilateral anophthalmia focuses on supporting development, improving quality of life, and addressing the various challenges this condition presents.
Prosthetic Eyes (Ocular Prostheses)
The use of prosthetic eyes plays a crucial role, both cosmetically and developmentally.
- Cosmetic Benefits: Prosthetic eyes improve the child's appearance, potentially reducing the likelihood of social stigma and enhancing self-esteem.
- Developmental Benefits: Prosthetic eyes can help with the development of the eye sockets and surrounding facial structures.
- Different Types and Fitting Procedures: Different types of prosthetic eyes are available, customized to fit each child’s unique needs. Regular fitting and adjustments are necessary as the child grows.
Sensory Integration Therapy
This type of therapy helps compensate for the lack of visual input.
- Sensory Integration Therapy: Specialized therapies can help children develop their other senses (hearing, touch, etc.) to navigate their environment more effectively.
Social and Emotional Support
Early and comprehensive support is crucial for the child and their family.
- Importance of Early Intervention: Early intervention programs can assist with developmental milestones and provide essential support to parents.
- Support Groups and Resources: Connecting with support groups and accessing resources for families facing similar challenges is vital for emotional well-being and practical guidance.
Living with Bilateral Anophthalmia
Individuals with bilateral anophthalmia can lead fulfilling lives with appropriate support and adaptation.
Educational Considerations
Education is adapted to meet the needs of the child.
- Adapted Learning Strategies: Educational strategies are tailored to support learning using auditory, tactile, and other sensory modalities.
- Educational Support Systems: Specialized educational support services are essential to ensure successful academic progress.
Assistive Technology
Various assistive technologies improve independence.
- Assistive Technology: Assistive technology, such as mobility aids and adaptive devices, contributes to greater independence.
Social Adaptation
Social integration requires strategies and support.
- Social Integration Challenges: Social integration may present challenges; early intervention can help in developing social skills and coping mechanisms.
- Strategies to Overcome Challenges: Appropriate support and social skills training can help children navigate social situations successfully.
Conclusion
Bilateral anophthalmia presents unique challenges for children and their families. However, with early diagnosis, appropriate treatment such as prosthetic eyes and sensory integration therapy, comprehensive support, and access to valuable resources, children can thrive and lead fulfilling lives. Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and management options for bilateral anophthalmia is crucial for families and healthcare professionals. If you suspect bilateral anophthalmia in a child or require more information on this rare condition, consult with a specialist immediately. Learning more about bilateral anophthalmia empowers families to provide the best possible care and support for their children. Seek resources and connect with support groups to navigate this journey effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Zavershennya Viyni Kritika Dzhonsonom Mirnogo Planu Trampa
May 11, 2025
Zavershennya Viyni Kritika Dzhonsonom Mirnogo Planu Trampa
May 11, 2025 -
 Intriguing Matchup Cissokho Meets Kavaliauskas For Wbc Title Shot
May 11, 2025
Intriguing Matchup Cissokho Meets Kavaliauskas For Wbc Title Shot
May 11, 2025 -
 Ufc 313 Mauricio Ruffys Ko Clinching Spinning Kick Revealed
May 11, 2025
Ufc 313 Mauricio Ruffys Ko Clinching Spinning Kick Revealed
May 11, 2025 -
 Resi Awards 2025 A Look At The Winning Projects
May 11, 2025
Resi Awards 2025 A Look At The Winning Projects
May 11, 2025 -
 Exposition D Art La Visite Surprise De Sylvester Stallone
May 11, 2025
Exposition D Art La Visite Surprise De Sylvester Stallone
May 11, 2025
