Are School Suspensions More Harmful Than Helpful? A Critical Analysis
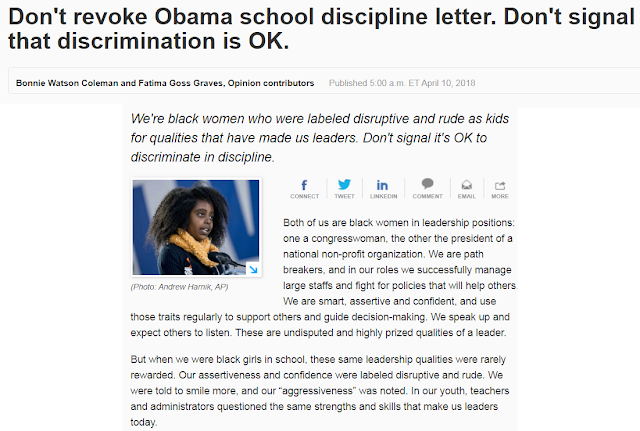
Table of Contents
The Negative Impact of School Suspensions on Academic Performance
School suspensions significantly impact students' academic progress and overall well-being. The consequences extend far beyond the immediate days missed from class.
Increased Absenteeism and Lower Graduation Rates
A strong correlation exists between school suspensions and decreased school attendance, ultimately leading to lower graduation rates and reduced academic achievement.
- Statistics show that students with multiple suspensions are significantly more likely to drop out of high school than their peers. For example, a study by the [Insert credible source and statistic here] found that students suspended even once are [Insert percentage]% more likely to drop out.
- The cumulative effect of missed classes, coupled with the disruption to learning routines, contributes to significant academic setbacks. Missed tests, assignments, and crucial classroom instruction create a substantial learning gap that is difficult to overcome.
- Furthermore, suspensions negatively impact standardized test scores, potentially limiting future educational and career opportunities. The lost instructional time directly translates to lower performance on standardized assessments.
The Disruption of Learning and Social-Emotional Development
Beyond the academic impact, school suspensions disrupt a student's learning trajectory and negatively impact their social and emotional well-being.
- Suspended students experience social isolation, impacting their sense of belonging and connection to the school community. This isolation can exacerbate feelings of alienation and increase the risk of future behavioral problems.
- The stress and anxiety associated with suspension can negatively affect mental health, potentially leading to increased rates of depression and anxiety among suspended students. The lack of consistent support during this period only compounds these challenges.
- Reintegrating into the school environment after a suspension can be particularly challenging, often requiring significant effort from both the student and school staff. The stigma associated with suspension can further hinder their ability to re-engage successfully in learning.
Alternative Disciplinary Approaches and Their Effectiveness
Instead of relying heavily on school suspensions, schools should explore and implement alternative disciplinary approaches that focus on rehabilitation and positive behavior change.
Restorative Justice Practices
Restorative justice practices prioritize repairing harm and fostering reconciliation between students and the school community. This approach moves away from punitive measures and focuses on dialogue, understanding, and accountability.
- Successful restorative justice programs empower students to take ownership of their actions and contribute to solutions. These programs often involve collaborative circles and facilitated discussions to address the harm caused by a student's behavior.
- Conflict resolution skills are taught and practiced, fostering a more positive and collaborative school climate. Restorative approaches have been shown to significantly reduce suspension rates while improving student-teacher relationships.
- By focusing on repairing the harm caused and facilitating understanding, restorative justice can lead to improved behavior and a stronger sense of community within the school.
Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS) employ proactive strategies to prevent disruptive behavior through positive reinforcement and individualized student support.
- PBIS programs emphasize teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors, creating a school culture that supports respectful interactions and academic success. This preventative approach minimizes the need for punitive measures like suspension.
- A positive school climate reduces the likelihood of disruptive behavior. By fostering a sense of belonging and providing students with the support they need, schools can create environments conducive to positive behavior.
- Early intervention is a critical component of PBIS. By addressing behavioral challenges early on, schools can prevent escalation and minimize the need for more serious disciplinary actions, including suspensions.
The Disproportionate Impact of Suspensions on Marginalized Students
School suspensions disproportionately affect marginalized students, highlighting systemic biases and inequities within the school disciplinary system.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in School Discipline
Data consistently reveals the overrepresentation of minority students in suspension data, reflecting inherent biases within school disciplinary practices.
- Statistics reveal significant disparities in suspension rates based on race and ethnicity. [Insert credible source and statistics here] These disparities cannot be attributed solely to differences in student behavior.
- Implicit bias plays a significant role in disciplinary decisions, leading to harsher punishments for students of color who may exhibit similar behaviors to their white peers. Unconscious biases influence teacher perceptions and disciplinary actions.
- Addressing racial and ethnic disparities requires systematic reform of school discipline policies and practices. This includes training for school staff on implicit bias and cultural competency.
Socioeconomic Factors and Suspension Rates
Socioeconomic status is strongly linked to suspension rates. Students from low-income families often face greater challenges that contribute to disciplinary issues.
- Poverty, lack of resources, and limited community support can negatively impact student behavior and increase the likelihood of suspension. Students facing these challenges may lack the support systems needed to thrive academically and socially.
- Strengthening community partnerships and ensuring equitable resource allocation are crucial in addressing the disproportionate impact of socioeconomic factors on school discipline. This includes providing support services such as counseling and after-school programs.
- Equitable resource allocation ensures all students have access to the resources and support they need to succeed, regardless of their socioeconomic background. Investing in these resources can significantly reduce disciplinary issues and improve student outcomes.
Conclusion
The evidence overwhelmingly suggests that school suspensions are more harmful than helpful. They negatively impact academic performance, disrupt social-emotional development, and disproportionately affect marginalized students. Instead of relying on suspensions, schools should embrace evidence-based alternative disciplinary approaches like restorative justice and PBIS. By focusing on prevention, positive behavior reinforcement, and addressing systemic inequities, we can create safer, more supportive learning environments for all students. By advocating for evidence-based practices like restorative justice and PBIS, and by addressing the systemic issues that disproportionately affect marginalized students, we can create safer, more supportive learning environments that foster academic success for all. Let's work together to move beyond the harmful effects of school suspensions and embrace more effective, equitable approaches to school discipline.

Featured Posts
-
 Fortnite Update 34 20 Server Downtime And Whats New
May 03, 2025
Fortnite Update 34 20 Server Downtime And Whats New
May 03, 2025 -
 A Deep Dive Into The Fierce Row Splitting Reform Uk
May 03, 2025
A Deep Dive Into The Fierce Row Splitting Reform Uk
May 03, 2025 -
 Loyle Carner Dublin 3 Arena Concert Announced
May 03, 2025
Loyle Carner Dublin 3 Arena Concert Announced
May 03, 2025 -
 A Qui Est Dedie Les Tuche 5 Devoilement Du Destinataire
May 03, 2025
A Qui Est Dedie Les Tuche 5 Devoilement Du Destinataire
May 03, 2025 -
 I Was In The Room My Nigel Farage Press Conference Experience
May 03, 2025
I Was In The Room My Nigel Farage Press Conference Experience
May 03, 2025
