Apple Harvest Losses: Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation To Reduce Yields By 10-30%
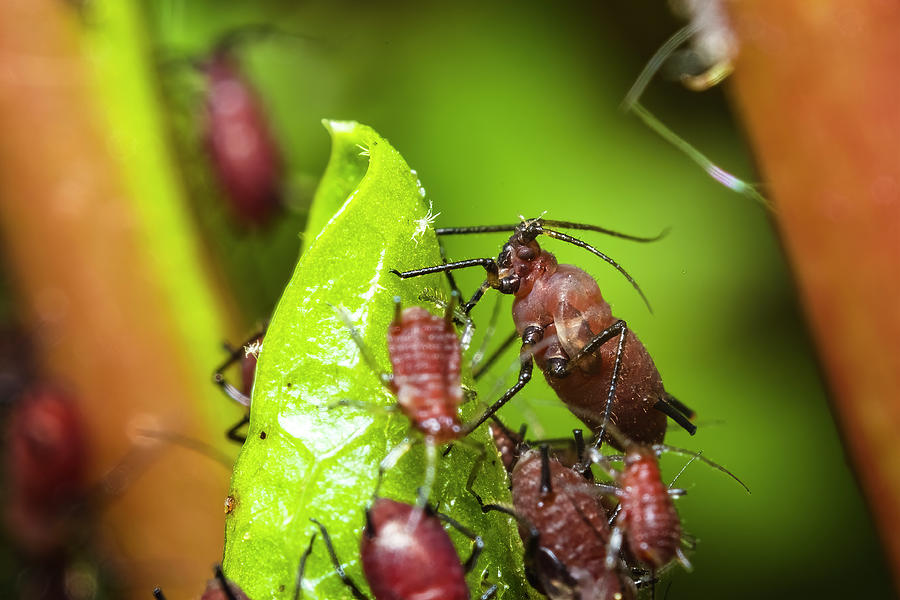

Table of Contents
Understanding Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations and Their Impact on Apple Yields
Identifying Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations
The rosy apple aphid ( Dysaphis plantaginea ) is a small, pink aphid, making "rosy apple aphid identification" crucial for early intervention. These "pink aphids" are typically found clustered on the undersides of leaves, buds, and shoots. Signs of infestation include:
- Leaf curling: Infested leaves often curl upwards, creating a protective environment for the aphids.
- Honeydew: Aphids excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which coats the leaves and attracts sooty mold. Searching for "honeydew" and "sooty mold" are key signs of an infestation.
- Sooty mold: This black, fungal growth thrives on the honeydew, further damaging the leaves and reducing photosynthesis. This is a significant factor in "apple tree damage."
<br>(Insert images here showing close-ups of rosy apple aphids and infested apple leaves with leaf curling, honeydew, and sooty mold.)
- Common Aphid Locations:
- Undersides of leaves, especially young, tender leaves.
- Tips of new shoots and branches.
- Around buds and blossoms.
The Mechanisms of Yield Reduction
Rosy apple aphids directly impact apple production through their sap-sucking activity. This "sap-sucking insect" feeds on the plant's sap, stunting the growth of the fruit and reducing its overall size. This leads to "fruit damage" and "stunted growth". The indirect effects are equally damaging:
- Secondary Infections: Honeydew creates a favorable environment for fungal diseases, increasing the apple's susceptibility to secondary infections and further impacting "apple disease."
- Reduced Fruit Quality: The affected apples may be smaller, misshapen, and less marketable, leading to significant losses in terms of "fruit quality."
Studies have shown that untreated infestations can result in yield reductions ranging from 10% to 30%, representing substantial "apple harvest losses" for growers. (Cite relevant studies or reports here).
- Specific Impacts on Fruit:
- Reduced fruit size and weight.
- Poor fruit shape and color.
- Increased susceptibility to bruising and blemishes.
- Lower sugar content and overall fruit quality, making them less desirable for sale.
Factors Influencing Aphid Infestation Severity
Several factors influence the severity of rosy apple aphid infestations:
-
Climate Conditions: Warmer temperatures and moderate humidity favor aphid reproduction and survival. Understanding the "aphids life cycle" and "environmental factors" is crucial for predicting infestations.
-
Natural Enemies: Predatory insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and certain parasitoids help control aphid populations. Encouraging these "natural enemies" through biodiversity promotion is a key component of "biological control."
-
Orchard Management Practices: Proper pruning improves air circulation, reducing humidity and hindering aphid development. Furthermore, balanced fertilization strengthens the trees, making them more resistant to infestation. This ties into "sustainable apple farming" and "integrated pest management".
-
Factors Increasing Infestation:
- High temperatures and humidity.
- Lack of natural predators.
- Poor orchard sanitation.
- Overcrowded trees.
-
Factors Decreasing Infestation:
- Regular pruning and thinning.
- Healthy, well-fertilized trees.
- Presence of beneficial insects.
- Proper irrigation practices.
Management Strategies for Minimizing Apple Harvest Losses due to Rosy Apple Aphids
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
IPM is a cornerstone of sustainable pest control, emphasizing prevention and minimizing pesticide use. "Integrated pest management," or "sustainable pest control," aims for environmentally friendly solutions. Key IPM techniques include:
-
Monitoring Aphid Populations: Regular visual inspections, coupled with sticky traps, allow for early detection of infestations and timely intervention. This "pest monitoring" and "aphids detection" is vital.
-
Biological Control: Introducing natural enemies like ladybugs and lacewings into the orchard can significantly reduce aphid numbers.
-
Cultural Practices: Proper pruning, thinning, and fertilization strengthen the trees and make them less susceptible to infestation. "Orchard sanitation" and "proper pruning" are crucial parts of this strategy.
-
Specific IPM Steps:
- Regularly inspect trees for signs of infestation.
- Introduce beneficial insects into the orchard.
- Practice proper pruning and fertilization.
- Remove infested leaves and branches.
- Use horticultural oils to suffocate aphids.
Chemical Control Options (When Necessary)
Chemical control should be employed only as a last resort when IPM strategies are insufficient. "Insecticide application" and "chemical control" should be precise. Always choose environmentally friendly "organic insecticides" and "biopesticides" that minimize environmental impact. "Safe insecticide application" and "targeted spraying" are essential to prevent harm to beneficial insects and the environment.
- Insecticide Types:
- Specific insecticides targeting rosy apple aphids (consult local agricultural extension office for recommendations).
- Note: Always follow label instructions carefully and consider the potential impact on beneficial insects and pollinators.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Apple Harvest from Rosy Apple Aphid Damage
Rosy apple aphid infestations pose a serious threat to apple production, potentially resulting in significant apple harvest losses of 10-30%. Early detection and proactive management are crucial to minimize damage. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including monitoring, biological control, and cultural practices, is the most effective approach. Chemical control should be considered only as a last resort, with careful selection and application of environmentally friendly insecticides.
Learn more about effective rosy apple aphid management and protect your apple harvest today! Research integrated pest management (IPM) techniques and contact your local agricultural extension office for further assistance in minimizing apple harvest losses.

Featured Posts
-
 Ramazan Bayrami Gazze De Anadolu Ajansi Nin Raporlari
May 19, 2025
Ramazan Bayrami Gazze De Anadolu Ajansi Nin Raporlari
May 19, 2025 -
 Postage Stamp Price Increase First Class To 1 70
May 19, 2025
Postage Stamp Price Increase First Class To 1 70
May 19, 2025 -
 Rs 44 Crore Bugatti Details On Haalands New Supercar
May 19, 2025
Rs 44 Crore Bugatti Details On Haalands New Supercar
May 19, 2025 -
 Jyoti Malhotra You Tubers Pahalgam Trip And Alleged Links To Pakistani Agents Before Terror Attack
May 19, 2025
Jyoti Malhotra You Tubers Pahalgam Trip And Alleged Links To Pakistani Agents Before Terror Attack
May 19, 2025 -
 Oi Protes Eortes Toy Maioy Stin Kastoria Ethima Kai Ekdiloseis
May 19, 2025
Oi Protes Eortes Toy Maioy Stin Kastoria Ethima Kai Ekdiloseis
May 19, 2025
