Analyzing Thailand's Negative Inflation And Its Impact On Interest Rates
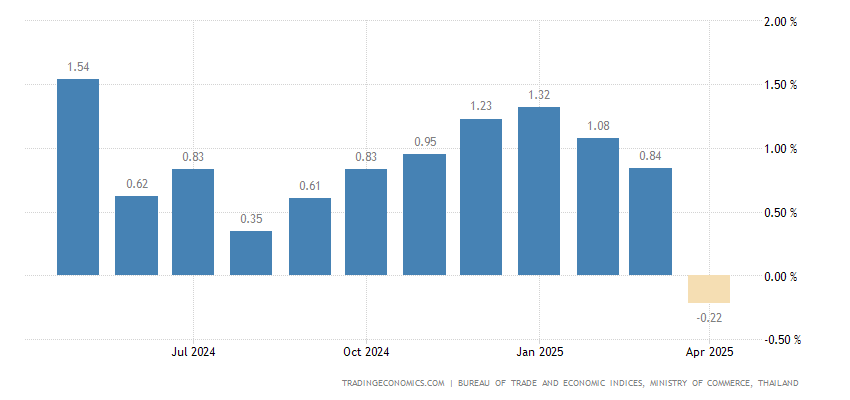
Table of Contents
Understanding Thailand's Negative Inflation
Defining Negative Inflation (Deflation):
Deflation, unlike disinflation (a slowing rate of inflation), represents a sustained decline in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. This seemingly positive development carries significant risks. Falling prices, while initially attractive to consumers, can lead to a dangerous downward spiral.
- Falling prices: Decreased prices may seem beneficial, but they often signal weakening demand and economic trouble.
- Decreased consumer spending: Consumers may delay purchases expecting further price drops, leading to reduced aggregate demand.
- Increased debt burden: The real value of debt increases as prices fall, making it harder for borrowers to repay loans.
- Deflationary spiral risk: A deflationary spiral can occur when falling prices lead to decreased investment and employment, further depressing demand and accelerating the price decline.
Thailand's recent negative inflation was primarily driven by lower energy prices and decreased overall demand. The specific contribution of these and other factors will be discussed in the following sections.
Causes of Negative Inflation in Thailand:
Several interconnected factors contributed to deflationary pressure in Thailand:
- Global economic slowdown: The global economic slowdown, impacting both exports and imports, reduced overall demand for Thai goods and services.
- Reduced tourism: The decline in international tourism, particularly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, significantly affected Thailand's service sector and overall economic activity. Data from the Tourism Authority of Thailand illustrates this dramatic decrease.
- Decreased domestic consumption: Reduced consumer confidence and uncertainty about the future led to decreased spending by Thai households.
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: The pandemic significantly disrupted supply chains and led to lockdowns, negatively impacting production and consumption across various sectors.
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain disruptions contributed to shortages and increased production costs in certain sectors, although this effect was counteracted by overall weak demand in many cases.
Measuring Negative Inflation in Thailand:
The primary measure of inflation in Thailand is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI tracks the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of goods and services. The Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC) collects and publishes this data monthly.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): The CPI is calculated using a weighted average of prices for a wide range of consumer goods and services.
- Methodology: The NESDC employs a detailed methodology that considers various factors like seasonal variations and changes in consumer preferences.
- Data sources: Data is collected from various sources, including retail outlets, wholesalers, and producers.
- Reliability of the data: While the data is generally considered reliable, limitations exist, such as potential biases and challenges in accurately capturing price changes for all goods and services.
Impact of Negative Inflation on Interest Rates
The Bank of Thailand's Response:
The Bank of Thailand (BOT) responded to negative inflation through various monetary policy measures aimed at stimulating economic activity.
- Interest rate cuts: The BOT reduced its policy interest rate to historically low levels, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers.
- Quantitative easing (QE): While not implemented on the scale seen in other countries, the BOT explored and implemented limited QE programs.
- Other stimulative measures: Other measures included initiatives to support specific sectors and liquidity injections into the financial system.
- Rationale: The BOT aimed to increase aggregate demand by lowering borrowing costs and making credit more accessible.
Challenges in Setting Interest Rates during Deflation:
Central banks face significant challenges in managing deflation, primarily because of the zero lower bound.
- Limited room for interest rate cuts: Interest rates cannot be lowered below zero, restricting the central bank's ability to stimulate demand through conventional monetary policy.
- Effectiveness of monetary policy in deflationary environments: The effectiveness of monetary policy is reduced during deflation, as consumers may delay purchases expecting further price declines.
- Potential for unintended consequences: Aggressive monetary easing can lead to asset bubbles or increased inflation in other sectors.
The Relationship between Negative Inflation and Investment:
Negative inflation creates uncertainty and can significantly influence investment decisions.
- Delayed investment: Businesses may delay investment projects due to expectations of further price drops, impacting their ROI.
- Impact on return on investment (ROI): Falling prices can reduce profitability and make investment less attractive.
- Potential for increased corporate debt: Businesses may take on more debt to maintain production levels during a period of falling prices, increasing their financial risk.
Economic Consequences of Thailand's Negative Inflation
Impact on Consumers:
Negative inflation affects consumer behavior and spending patterns.
- Delayed purchases: Consumers tend to postpone purchases, expecting lower prices in the future.
- Impact on consumer confidence: Deflation can erode consumer confidence and lead to reduced spending.
- Potential for decreased aggregate demand: Reduced consumer spending contributes to a further decline in aggregate demand, potentially worsening deflation.
Impact on Businesses:
Negative inflation presents significant challenges for businesses.
- Reduced profits: Falling prices squeeze profit margins, forcing businesses to cut costs or accept lower returns.
- Difficulties in pricing strategies: Businesses face difficulties setting prices that cover costs and maintain profitability in a deflationary environment.
- Challenges related to debt servicing: The real value of debt increases during deflation, making it more difficult for businesses to service their loans.
Overall Economic Implications:
Sustained negative inflation poses significant risks to Thailand's economy.
- GDP growth impact: Deflation can significantly reduce GDP growth, as decreased demand leads to lower production and investment.
- Employment implications: Reduced economic activity can lead to job losses and increased unemployment.
- Potential for economic stagnation: Prolonged deflation can lead to a period of economic stagnation, hindering economic development.
- Long-term economic risks: Deflation can damage long-term economic prospects by undermining investment, innovation, and economic growth.
Conclusion:
Thailand's recent experience with negative inflation highlights the significant challenges associated with managing deflation and its impact on interest rates. The Bank of Thailand's response, though necessary, faced limitations due to the zero lower bound. The consequences of this period of deflation are far-reaching, impacting consumer behavior, business profitability, and the overall economic outlook. Further research into the complexities of Thailand's negative inflation and its implications for future economic policy is crucial. Understanding Thailand's negative inflation is essential for investors, businesses, and policymakers to make informed decisions and navigate the economic challenges ahead. Stay informed about developments concerning Thailand's negative inflation and its evolving impact on interest rates.

Featured Posts
-
 Unexpected Guest Lewis Capaldi Joins Tom Walker On Stage For Charity
May 07, 2025
Unexpected Guest Lewis Capaldi Joins Tom Walker On Stage For Charity
May 07, 2025 -
 Dont Worry Warriors Fans History And Blowout Losses
May 07, 2025
Dont Worry Warriors Fans History And Blowout Losses
May 07, 2025 -
 Simone Biles Seeks Police Action After Receiving Threatening Texts
May 07, 2025
Simone Biles Seeks Police Action After Receiving Threatening Texts
May 07, 2025 -
 Hurwitzs Original Cobra Kai Pitch A Look At The Unaired Trailer
May 07, 2025
Hurwitzs Original Cobra Kai Pitch A Look At The Unaired Trailer
May 07, 2025 -
 Report Negotiations Sour George Pickens May Leave Steelers Before 2026
May 07, 2025
Report Negotiations Sour George Pickens May Leave Steelers Before 2026
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Heat Vs Cavaliers Expert Predictions And Best Bets For Game 1 Playoffs
May 07, 2025
Heat Vs Cavaliers Expert Predictions And Best Bets For Game 1 Playoffs
May 07, 2025 -
 Nba Playoffs Cavaliers Vs Heat Game 2 Live Stream Tv Channel And Start Time
May 07, 2025
Nba Playoffs Cavaliers Vs Heat Game 2 Live Stream Tv Channel And Start Time
May 07, 2025 -
 Game 1 Nba Playoffs Heat Vs Cavaliers Predictions And Betting Picks
May 07, 2025
Game 1 Nba Playoffs Heat Vs Cavaliers Predictions And Betting Picks
May 07, 2025 -
 Nba Playoffs Heat Vs Cavaliers Prediction Best Bets For Game 1
May 07, 2025
Nba Playoffs Heat Vs Cavaliers Prediction Best Bets For Game 1
May 07, 2025 -
 Cavaliers Vs Heat Game 2 Live Stream Tv Channel And Game Time
May 07, 2025
Cavaliers Vs Heat Game 2 Live Stream Tv Channel And Game Time
May 07, 2025
