Analysis Of April's U.S. Jobs Report: 177,000 Jobs Created, Unemployment At 4.2%
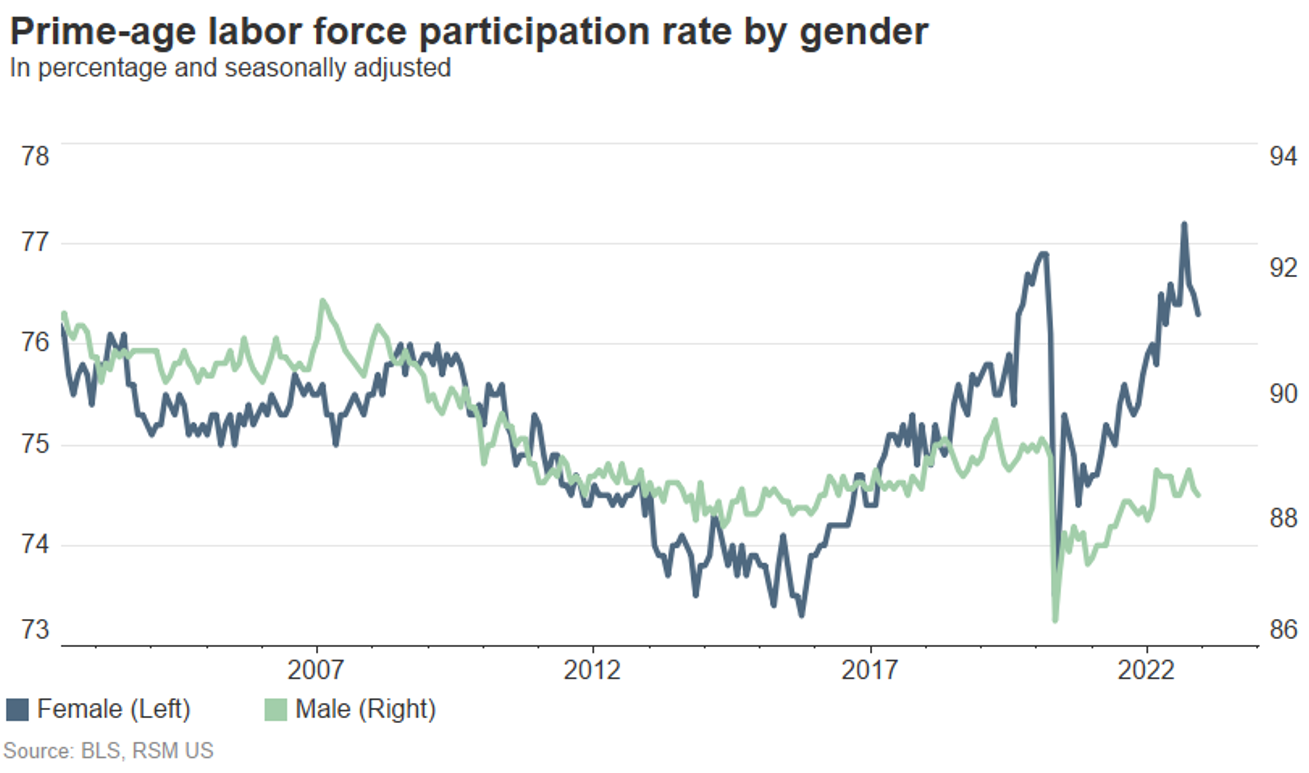
Table of Contents
Detailed Breakdown of Job Creation in April's Report
Job Growth by Sector: A Sectoral Analysis of Employment Trends
The April jobs report reveals a varied picture of sectoral job growth. While some sectors experienced robust expansion, others saw slower or even negative growth. Let's examine the key areas:
- Leisure and Hospitality: This sector added [insert number] jobs, a [insert percentage]% increase. This continues a trend of recovery in this area, though growth is slowing compared to previous months' figures. The ongoing easing of pandemic restrictions likely contributes to this growth.
- Professional and Business Services: This sector added [insert number] jobs, a [insert percentage]% increase. The continued growth suggests strong demand for professional services in the current economic climate. This sector often reflects the overall health of the economy.
- Manufacturing: This sector showed [insert number] jobs added/lost, a [insert percentage]% [increase/decrease]. This reflects [insert reason for growth or decline, e.g., supply chain challenges, increased automation]. This is [compare to previous months and the average].
Analyzing this sectoral job growth allows us to better understand the nuances of the overall employment picture. Understanding industry employment trends is crucial for effective economic policy. The variation in job creation by sector highlights the need for a targeted approach to economic support and development.
Revisions to Previous Months' Data: Understanding Employment Data Corrections
It's important to note that the April jobs report also included revisions to previous months' data. [Insert details about revisions – e.g., The March jobs report was revised upward by X jobs, indicating stronger-than-initially-reported growth]. These data revisions are a normal part of the process, as more complete data becomes available. These employment data corrections highlight the iterative nature of economic data collection and analysis. Understanding the significance of these revisions is key to interpreting the long-term trends in the job market.
Unemployment Rate Analysis: 4.2% – A Deeper Dive
Understanding the Unemployment Rate: Labor Force Participation and Types of Unemployment
The headline unemployment rate of 4.2% requires further analysis. It's crucial to understand the methodology behind this calculation, which includes surveying households and businesses to determine the number of employed and unemployed individuals. It's also essential to consider different types of unemployment:
- Frictional Unemployment: Unemployment due to individuals transitioning between jobs. This is a natural part of a healthy economy.
- Structural Unemployment: Unemployment due to a mismatch between skills and available jobs. This often requires retraining and workforce development initiatives.
- Cyclical Unemployment: Unemployment tied to the business cycle. This is often higher during economic downturns.
The labor force participation rate (the percentage of the working-age population either employed or actively seeking employment) is another important metric. Analyzing this alongside the unemployment rate provides a more comprehensive picture of the labor market. Examining the employment-population ratio can offer additional context.
Long-Term Unemployment: A Persistent Challenge
The April report should also detail the number of individuals unemployed for extended periods. Long-term unemployment presents a significant challenge, often stemming from structural issues within the labor market. Addressing this requires initiatives focused on skills development, job training, and workforce support programs. The consequences of prolonged unemployment include financial hardship, social isolation, and decreased economic productivity.
Wage Growth and Inflationary Pressures
Average Hourly Earnings: Wage Growth and Its Impact
Average hourly earnings saw a [insert percentage]% increase in April, indicating [insert interpretation – e.g., strong wage growth, moderate wage growth, etc.]. This is a significant metric to watch, as it has implications for inflation. Strong wage growth can fuel inflationary pressures if businesses pass on increased labor costs to consumers through higher prices.
Real Wage Growth: Purchasing Power and Consumer Spending
It is equally important to examine real wage growth – wage growth adjusted for inflation. Real wage growth reflects the actual purchasing power of workers' earnings. If inflation outpaces wage growth, real wages decline, impacting consumer spending and potentially hindering economic expansion. Analyzing inflation-adjusted wages provides a clearer understanding of the impact of wage increases on the overall economy.
Implications and Outlook for the U.S. Economy
Federal Reserve Policy: Monetary Policy and Interest Rates
The April jobs report will significantly influence the Federal Reserve's decisions regarding monetary policy, particularly interest rates. The Fed aims to maintain a healthy balance between economic growth and inflation. Strong employment data, coupled with rising inflation, may lead the Fed to consider further interest rate hikes to cool down the economy and curb inflation. Understanding the relationship between employment data and monetary policy is crucial for anticipating future economic trends.
Future Job Growth Projections: Economic Forecast and Employment Projections
Based on the April data, projections for future job growth suggest [insert projection – e.g., continued moderate growth, a slowdown in growth, etc.]. Several factors could influence this outlook, including economic growth, technological advancements, geopolitical events, and consumer confidence. Careful analysis of these factors is crucial for creating accurate employment projections and formulating effective economic policies. The economic forecast remains uncertain due to these evolving conditions.
Conclusion: Interpreting April's U.S. Jobs Report and What's Next
April's U.S. jobs report reveals a complex picture of the American job market. While the creation of 177,000 jobs and a stable unemployment rate of 4.2% are positive indicators, a deeper dive reveals nuances in sectoral growth, wage increases, and the persistence of long-term unemployment. These findings hold significant implications for the Federal Reserve's monetary policy and future economic growth. Understanding these trends requires continuous monitoring. To stay informed on future U.S. jobs reports and gain a deeper understanding of the U.S. job market, follow the latest employment data and analyze future U.S. job market trends.

Featured Posts
-
 Wbo Interim Championship Fight Parker Vs Bakole
May 04, 2025
Wbo Interim Championship Fight Parker Vs Bakole
May 04, 2025 -
 1 4
May 04, 2025
1 4
May 04, 2025 -
 Wolf Talks Flames Playoff Hopes And Calder Trophy Chances Nhl Com Q And A
May 04, 2025
Wolf Talks Flames Playoff Hopes And Calder Trophy Chances Nhl Com Q And A
May 04, 2025 -
 Fleetwood Macs Chart Triumph Analyzing Their Latest Albums Success
May 04, 2025
Fleetwood Macs Chart Triumph Analyzing Their Latest Albums Success
May 04, 2025 -
 Final Destination Bloodline Trailer Highlights Tony Todds Legacy
May 04, 2025
Final Destination Bloodline Trailer Highlights Tony Todds Legacy
May 04, 2025
