AI In Therapy: Privacy Concerns And The Potential For Surveillance
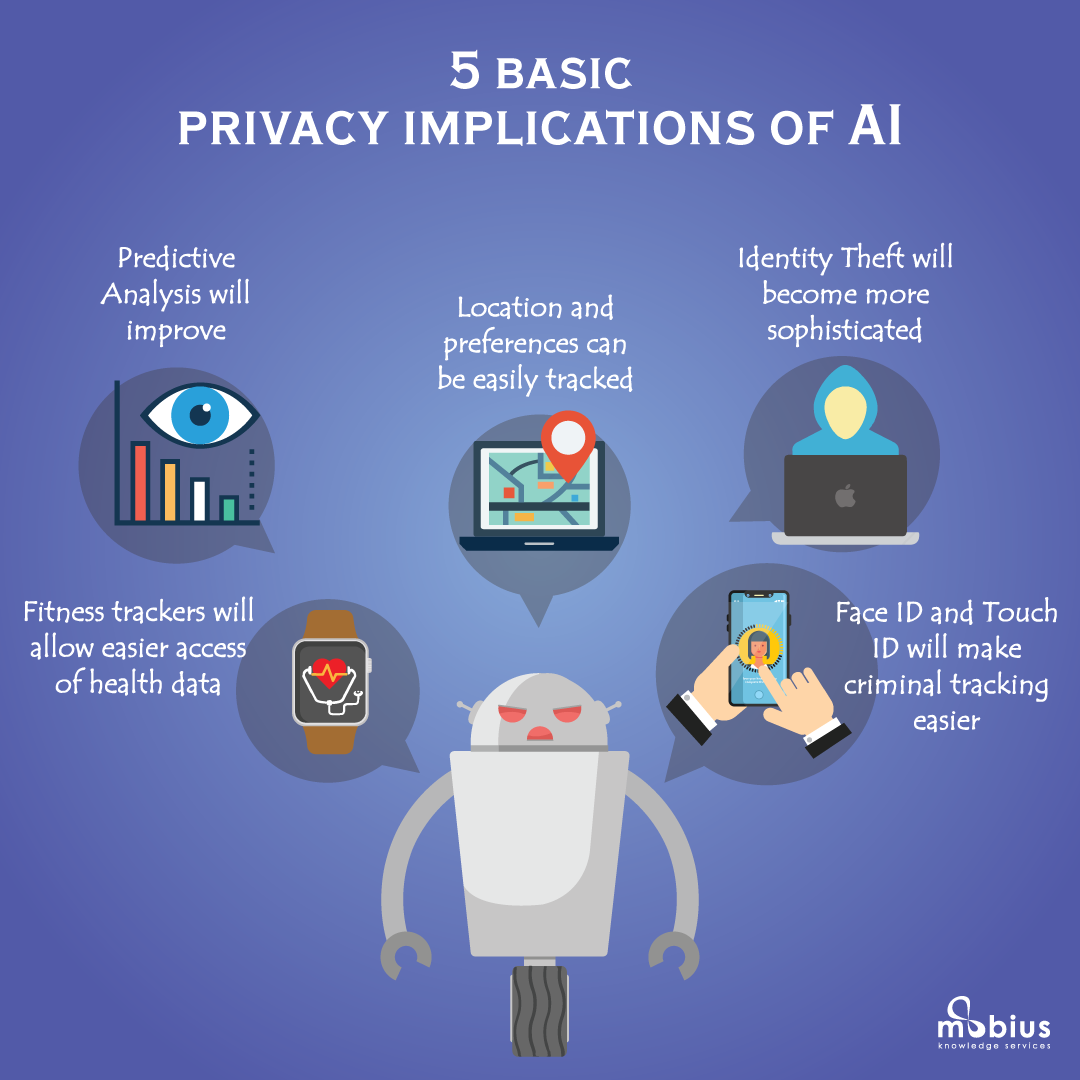
Table of Contents
Data Security and Breaches in AI-Powered Therapy Platforms
The use of AI in therapy necessitates the collection and storage of sensitive patient data, including medical history, psychological assessments, and personal details. This data is incredibly vulnerable, making robust data security paramount. AI platforms, like any digital system, are susceptible to various threats.
- Risk of hacking and data theft: Cyberattacks targeting mental health platforms could expose highly sensitive patient information to malicious actors.
- Potential for unauthorized access to personal information: Breaches could expose medical history, psychological assessments, and personal details, leading to identity theft, discrimination, and emotional distress.
- Lack of robust data encryption and security protocols: Not all AI therapy platforms prioritize comprehensive security measures, leaving patient data vulnerable.
- The legal and ethical implications of data breaches in the context of therapeutic relationships: Data breaches can severely damage the therapeutic relationship, erode patient trust, and have significant legal ramifications under regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
The need for stringent data protection regulations specific to AI in mental healthcare cannot be overstated. Comprehensive cybersecurity measures, including robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, are essential. Furthermore, adherence to existing regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US is crucial for protecting patient data privacy. Robust data security and patient data privacy are not merely compliance issues; they are fundamental to the ethical practice of AI in therapy.
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination in AI Therapy Tools
AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting AI system will likely perpetuate and even amplify those biases. This is a significant concern in the context of AI therapy.
- Bias in training data reflecting societal prejudices: AI models trained on datasets that overrepresent certain demographics or underrepresent others can lead to inaccurate or unfair assessments and treatment recommendations.
- Potential for discriminatory outcomes based on race, gender, socioeconomic status, etc.: Biased algorithms may misdiagnose or undertreat individuals from marginalized groups, exacerbating existing health inequalities.
- Lack of transparency in algorithmic decision-making processes: The "black box" nature of some AI algorithms makes it difficult to identify and correct biases, hindering accountability.
- The impact of biased AI on vulnerable populations: Individuals from already disadvantaged groups are disproportionately affected by biased AI systems, widening the gap in access to quality mental healthcare.
Fairness, accountability, and transparency are critical in the development and deployment of AI therapy tools. Rigorous testing for bias, diverse and representative training datasets, and explainable AI (XAI) techniques are essential steps towards mitigating algorithmic bias and ensuring fairness in AI. The ethical implications of AI necessitate ongoing research and development to address these critical issues.
Surveillance and Monitoring Capabilities of AI in Therapy
While AI offers therapeutic benefits, its capabilities also raise concerns about potential surveillance. The constant data collection inherent in AI-powered platforms could be misused, exceeding the boundaries of legitimate therapeutic practice.
- Data collection and analysis beyond therapeutic needs: AI systems might collect and analyze data beyond what is necessary for treatment, raising privacy concerns.
- Potential for misuse of data by third parties (insurance companies, employers): Patient data could be accessed or used by unauthorized parties for purposes unrelated to mental healthcare.
- Lack of clear guidelines on data retention and disposal: Ambiguity around data retention policies can lead to the indefinite storage of sensitive information, increasing the risk of misuse.
- The erosion of the therapeutic relationship due to lack of trust and autonomy: Patients may feel less comfortable disclosing personal information if they fear that it will be used for surveillance or monitoring.
The potential for AI surveillance necessitates robust safeguards against misuse. Strict regulations on data collection, storage, and use are crucial. Informed consent procedures must be transparent and easily understood, ensuring patients are fully aware of how their data will be used. Clear guidelines on data retention and disposal are essential to protect patient privacy and maintain trust in the therapeutic relationship.
The Role of Regulation and Ethical Guidelines in Mitigating Risks
Mitigating the risks associated with AI in therapy requires a multi-pronged approach involving robust regulations, ethical guidelines, and ongoing dialogue.
- Establishing data protection standards specific to AI in healthcare: Dedicated regulations are needed to address the unique challenges posed by AI in the context of sensitive healthcare data.
- Implementing rigorous auditing and oversight mechanisms: Regular audits and oversight are needed to ensure that AI systems comply with regulations and ethical guidelines.
- Developing ethical frameworks for AI algorithm design and deployment: Ethical frameworks should guide the development of AI algorithms to minimize bias and ensure fairness.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in AI-powered therapy systems: Transparency in algorithmic decision-making and clear accountability mechanisms are essential for building trust.
Collaboration between policymakers, healthcare professionals, AI developers, and ethicists is crucial for responsible innovation. The development and implementation of clear regulations and ethical guidelines are not merely compliance exercises; they are essential for ensuring that AI in therapy benefits patients while protecting their rights and privacy.
Conclusion
AI in therapy presents transformative potential, but responsible implementation requires careful consideration of the inherent privacy concerns and the potential for surveillance. Addressing algorithmic bias, ensuring robust data security, and establishing clear ethical guidelines are crucial for fostering trust and protecting patient rights. The responsible development and deployment of AI in therapy demand ongoing dialogue and collaboration among stakeholders to harness its benefits while mitigating its risks. We must prioritize ethical considerations and patient well-being to ensure that AI in therapy is used responsibly and benefits all. Continued discussion and advocacy concerning the ethical use of AI in therapy are essential. Let's work together to ensure that AI in therapy is developed and implemented ethically and responsibly.

Featured Posts
-
 Could Euphoria Continue Beyond Season 3 Hbos Plans Explored
May 15, 2025
Could Euphoria Continue Beyond Season 3 Hbos Plans Explored
May 15, 2025 -
 The King Of Davoss Decline Power Politics And Ruin
May 15, 2025
The King Of Davoss Decline Power Politics And Ruin
May 15, 2025 -
 Neal Pionk Breaking News And Updates From Around The Nhl
May 15, 2025
Neal Pionk Breaking News And Updates From Around The Nhl
May 15, 2025 -
 Bim In 25 26 Subat Aktueel Katalogu Iste Bu Hafta Indirimde Olanlar
May 15, 2025
Bim In 25 26 Subat Aktueel Katalogu Iste Bu Hafta Indirimde Olanlar
May 15, 2025 -
 Us Canada Trade Fact Checking Trumps Assertions On Essential Imports
May 15, 2025
Us Canada Trade Fact Checking Trumps Assertions On Essential Imports
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Neal Pionks Performance Recent Games And Highlights
May 15, 2025
Analyzing Neal Pionks Performance Recent Games And Highlights
May 15, 2025 -
 Neal Pionk Injury Updates Contract News And More
May 15, 2025
Neal Pionk Injury Updates Contract News And More
May 15, 2025 -
 Is Neal Pionk On The Move Latest Trade Rumors And Analysis
May 15, 2025
Is Neal Pionk On The Move Latest Trade Rumors And Analysis
May 15, 2025 -
 Neal Pionk Recent News Performance And Future Outlook
May 15, 2025
Neal Pionk Recent News Performance And Future Outlook
May 15, 2025 -
 Neal Pionk All The Latest Rumors And Game Highlights
May 15, 2025
Neal Pionk All The Latest Rumors And Game Highlights
May 15, 2025
