$506 Million: Canada's Narrowed Trade Deficit And The Role Of Tariffs
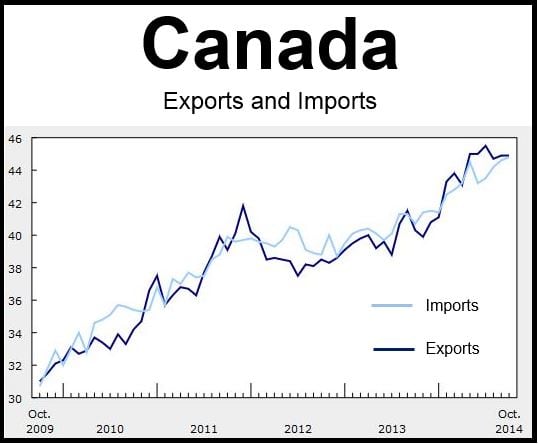
Table of Contents
The $506 Million Reduction: A Detailed Look at the Numbers
The $506 million reduction in Canada's trade deficit represents a significant positive swing in the country's trade statistics. While precise figures require specifying the exact time period (e.g., "during the second quarter of 2024"), the improvement signals a shift toward a more balanced trade balance. This improvement reflects a combination of increased exports and decreased imports.
- Import Decline: Data needs to be inserted here showing the reduction in the value of imports during the specific timeframe. (For example: "Imports decreased by X% compared to the previous quarter, totaling $Y billion.")
- Export Increase: Data needs to be inserted here showing the increase in the value of exports during the specific timeframe. (For example: "Exports saw a Y% increase, reaching a total of $Z billion.")
- Balance of Trade: The improved balance of trade is visually represented with a chart or graph comparing import and export figures over the specified period. (Note: Charts and graphs would be included in an actual published article).
Analyzing these trade statistics reveals a dynamic interplay of economic factors contributing to the improved import decline and export increase. The resulting positive shift in the balance of trade reflects a healthier economic picture for Canada.
The Role of Tariffs in Influencing Trade Balance
Tariffs, taxes imposed on imported goods, are a key instrument of trade policy. Their impact on Canada's narrowed trade deficit is multifaceted.
Impact of Tariffs on Imports
- Decreased Imports: The implementation of import tariffs on specific goods, such as steel or lumber, directly increases their cost for Canadian businesses and consumers. This leads to a decrease in the quantity of those goods imported. Specific examples of tariffs and their effects on import volumes would be included here.
- Protectionist Policies: These protectionist policies aim to safeguard domestic industries by making imported goods less competitive. However, this often comes at a cost:
- Increased Consumer Prices: Higher import tariffs can lead to increased consumer prices, as businesses pass on the added cost. This represents a trade-off between protecting domestic industries and maintaining affordability for consumers. The analysis should include a discussion of the price elasticity of demand for these impacted goods.
Tariffs and Export Competitiveness
While import restrictions via tariffs can help domestic producers, the impact extends beyond national borders.
- Retaliatory Tariffs: Other countries may impose retaliatory tariffs on Canadian goods, harming Canada's export competitiveness in those markets. The article should provide specific examples if available.
- Trade Agreements: Conversely, trade agreements like the CUSMA (formerly NAFTA) can significantly reduce tariffs between participating countries, boosting export growth and overall trade. The effect of these agreements on the recent trade deficit improvement should be discussed. Analysis of the impact of tariffs within the context of international trade agreements is essential.
Other Factors Contributing to the Narrowed Trade Deficit
The improvement in Canada's trade deficit is not solely attributable to tariffs. Several other economic factors played a crucial role.
- Changes in Global Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, especially those of Canadian exports (e.g., oil, lumber, minerals), significantly influence export revenue and, thus, the trade balance.
- Fluctuations in the Canadian Dollar: The value of the Canadian dollar relative to other currencies impacts both exports (making them cheaper or more expensive for international buyers) and imports (making foreign goods cheaper or more expensive in Canada).
- Increased Domestic Demand: Strong domestic consumption can reduce reliance on imports and positively impact the trade balance.
- Specific Industry Performance: The performance of individual industries, particularly export-oriented sectors, plays a critical role.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook
The sustainability of this narrowed trade deficit depends on various factors. The economic forecast needs to consider the ongoing global economic uncertainty, potential future tariff adjustments, and the continued performance of key export sectors.
- Trade Outlook: The article should offer an informed trade outlook, examining the potential for future increases or decreases in imports and exports, and assess the likelihood of a sustained improvement in the trade balance.
- Future of Trade: The discussion needs to cover the long-term future of trade and consider potential challenges, such as trade wars or disruptions to global supply chains.
- Economic Growth: The relationship between the narrowed trade deficit and overall economic growth in Canada needs to be analyzed and future projections provided, considering potential risks and opportunities.
Conclusion: Understanding Canada's Trade Deficit and the Influence of Tariffs
The $506 million reduction in Canada's trade deficit marks a significant positive development. While Canadian tariffs have played a role in this improvement, primarily by influencing import volumes, other economic factors such as commodity prices, exchange rates, and domestic demand were equally important contributors. Understanding this interplay is crucial for developing effective long-term trade policies and ensuring Canada's continued economic growth. To stay informed about Canada's trade deficit and the impact of Canadian tariffs, subscribe to our newsletter or visit [relevant website]. Further research into the dynamics of Canada's trade balance is encouraged.

Featured Posts
-
 Shreveport Police Crack Multi Vehicle Theft Ring Suspects Arrested
May 08, 2025
Shreveport Police Crack Multi Vehicle Theft Ring Suspects Arrested
May 08, 2025 -
 Oklahoma City Thunder Vs Memphis Grizzlies A Crucial Matchup
May 08, 2025
Oklahoma City Thunder Vs Memphis Grizzlies A Crucial Matchup
May 08, 2025 -
 Arsenal Psg Semi Final Why Its A Bigger Challenge Than Real Madrid
May 08, 2025
Arsenal Psg Semi Final Why Its A Bigger Challenge Than Real Madrid
May 08, 2025 -
 Derrota Del Lyon Ante El Psg Analisis Del Encuentro
May 08, 2025
Derrota Del Lyon Ante El Psg Analisis Del Encuentro
May 08, 2025 -
 Surface Pro 12 Inch Specs Price And Review
May 08, 2025
Surface Pro 12 Inch Specs Price And Review
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Quick News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman Updates
May 08, 2025
Quick News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman Updates
May 08, 2025 -
 F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman Quick News Roundup
May 08, 2025
F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman Quick News Roundup
May 08, 2025 -
 Saving Private Ryans Legacy Challenged The Best War Movie Debate Heats Up
May 08, 2025
Saving Private Ryans Legacy Challenged The Best War Movie Debate Heats Up
May 08, 2025 -
 Debate Ignites Has A New War Film Surpassed Saving Private Ryan
May 08, 2025
Debate Ignites Has A New War Film Surpassed Saving Private Ryan
May 08, 2025 -
 A New Challenger Appears Is Saving Private Ryan No Longer The Top War Film
May 08, 2025
A New Challenger Appears Is Saving Private Ryan No Longer The Top War Film
May 08, 2025
