311 Heat-Related Deaths In England: A Public Health Crisis
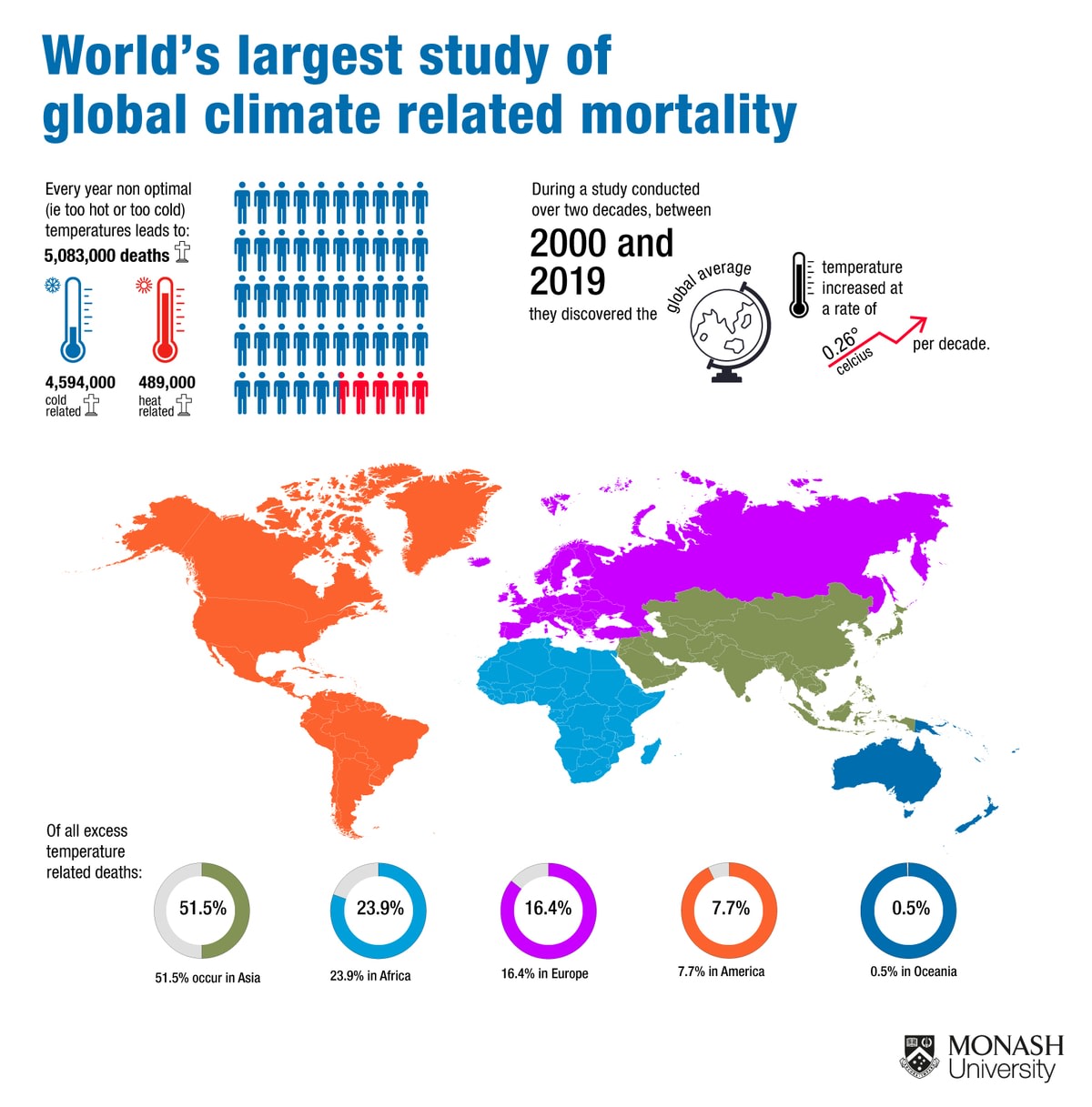
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of the Heatwave
The summer heatwave in England was exceptionally severe, resulting in a significant increase in heatwave mortality. The combination of high temperatures and prolonged duration pushed mortality rates far above the average. Specific data is crucial to understanding the scale of this public health emergency. For example, the highest recorded temperature during the heatwave reached [insert specific temperature and location], and the intense heat persisted for [insert number] days. This period of extreme temperature extremes led to a substantial number of excess deaths directly attributed to heat.
- Number of excess deaths: [Insert precise number if available, or range, citing source].
- Age demographics: The elderly (over 65) and young children were disproportionately affected, highlighting the vulnerability of these groups to heatstroke.
- Geographic areas: [Specify regions of England most impacted, citing data sources]. Urban areas, with their heat island effect, often experienced higher temperatures and consequently, more heat-related deaths.
- Comparison to previous years: The number of heat-related deaths in this recent heatwave significantly surpasses previous years' tolls [cite comparative data from official sources]. This sharp increase highlights the escalating threat posed by extreme heat.
Identifying Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups are inherently more susceptible to heat-related illness and death. Understanding these vulnerabilities is vital for targeted interventions and effective public health strategies. The underlying causes for their increased risk are complex and multifaceted.
- The elderly: Their bodies are less efficient at regulating temperature, and many elderly individuals live alone, leading to social isolation and delayed access to help during heatwaves.
- Individuals with pre-existing health conditions: People with cardiovascular or respiratory diseases, for example, are at significantly higher risk of heatstroke exacerbating their conditions.
- Those living in poorly insulated housing: Inadequate housing insulation contributes to overheating, particularly in vulnerable individuals.
- People experiencing social isolation or homelessness: These individuals lack access to cool spaces and often lack awareness of the dangers of extreme heat. Their lack of access to healthcare worsens their predicament.
The Role of Climate Change and Future Projections
The link between climate change, increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves, and rising heat-related deaths is undeniable. Scientific consensus supports the assertion that global warming is directly contributing to more frequent and more intense heatwaves in England.
- Scientific evidence: [Cite reputable scientific reports and studies linking climate change to heatwaves]. Models predict a substantial rise in average temperatures across the UK.
- Predictions for future heatwave severity: Projections suggest a dramatic increase in the frequency and intensity of future heatwaves in England, leading to a corresponding rise in heat-related deaths.
- The need for long-term adaptation strategies: To adequately address this escalating threat, long-term adaptation strategies must be implemented immediately. These should go beyond short-term emergency responses.
Improving Heat Preparedness and Response
Strengthening heat preparedness and response mechanisms is crucial to mitigating future tragedies. A multi-pronged approach involving public health interventions, improved early warning systems, and increased community support is necessary.
- Strengthening existing heat action plans: England's heat action plans require strengthening, including improved communication strategies and proactive outreach to vulnerable populations.
- Improving public awareness through educational campaigns: Public awareness campaigns are vital in educating the public about the dangers of extreme heat and how to protect themselves.
- Investing in infrastructure: Investments in infrastructure are needed to provide cooling in public spaces (cooling centers) and to improve the energy efficiency and insulation of vulnerable homes.
- Expanding access to healthcare services: Healthcare systems need to be adequately prepared for a surge in heat-related illnesses during heatwaves, with sufficient resources and staffing.
Conclusion
The 311 heat-related deaths in England serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for comprehensive action to address this public health crisis. Vulnerable populations are disproportionately impacted, and climate change exacerbates this risk. Strengthening heat action plans, improving public awareness, investing in infrastructure, and expanding healthcare access are crucial steps to mitigate future tragedies. We must act now to prevent another tragic spike in heat-related deaths in England. Demand effective action on heat-related deaths to protect vulnerable populations and build a more resilient future. We must prioritize heat preparedness and response strategies to protect the lives of our citizens.

Featured Posts
-
 Ulasan Lengkap Kawasaki W175 Cafe Motor Retro Klasik Modern
May 30, 2025
Ulasan Lengkap Kawasaki W175 Cafe Motor Retro Klasik Modern
May 30, 2025 -
 Enjoy Four Days Of Sunshine San Diego Weather Forecast
May 30, 2025
Enjoy Four Days Of Sunshine San Diego Weather Forecast
May 30, 2025 -
 Setlist Fm Se Integra Con Ticketmaster Mejoras Para Los Fans
May 30, 2025
Setlist Fm Se Integra Con Ticketmaster Mejoras Para Los Fans
May 30, 2025 -
 Us Trade Court Rules Against Trump Era Tariffs
May 30, 2025
Us Trade Court Rules Against Trump Era Tariffs
May 30, 2025 -
 Holder Vejret Analyser Af En Potentiel Afvisning Af Danmark
May 30, 2025
Holder Vejret Analyser Af En Potentiel Afvisning Af Danmark
May 30, 2025
