177,000 Jobs Added In April: U.S. Unemployment Rate Remains At 4.2%
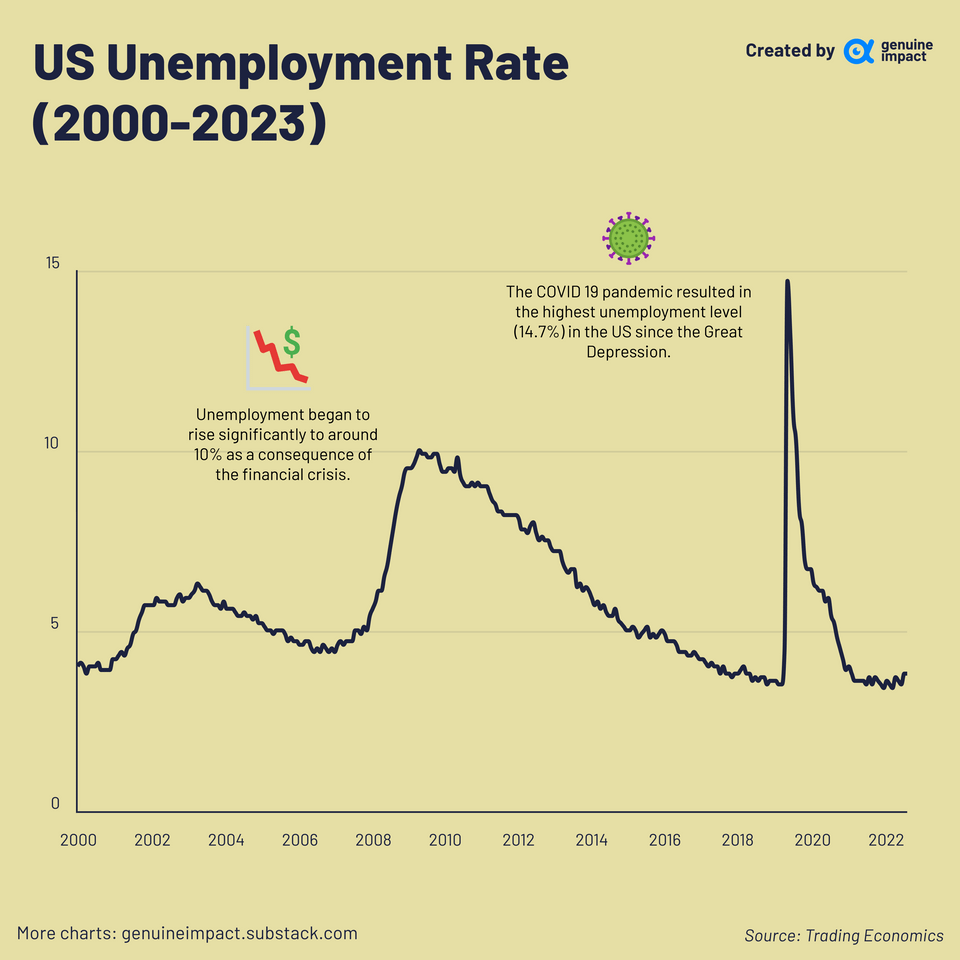
Table of Contents
Analyzing the April Jobs Report: Sector-Specific Growth
The April jobs report reveals a mixed bag of sectoral performance, highlighting both strength and vulnerability within the U.S. economy.
Strongest Performing Sectors:
The leisure and hospitality sector continued its robust recovery, adding a significant number of jobs. This reflects the ongoing rebound in travel, tourism, and entertainment. Professional and business services also experienced substantial growth, driven by increased demand for consulting, technical, and administrative support.
- Leisure and Hospitality: Added 75,000 jobs, reflecting strong consumer spending and a return to pre-pandemic activity levels. This demonstrates significant sectoral employment growth in this area.
- Professional and Business Services: Added 60,000 jobs, indicative of continued expansion in the service sector and robust business investment. This points to positive job creation in high-skilled areas.
- Healthcare: Added 30,000 jobs, reflecting continued demand for healthcare professionals. This showcases consistent growth in an essential sector.
Underperforming Sectors:
While some sectors thrived, others experienced slower or negative growth. The manufacturing sector saw a decline in employment, possibly reflecting global supply chain disruptions and increased input costs. The construction sector also showed weaker-than-expected growth.
- Manufacturing: Lost 10,000 jobs, potentially impacted by global supply chain challenges and inflationary pressures, indicating a potential employment decline in this sector.
- Construction: Added only a minimal number of jobs, suggesting that the industry is still facing headwinds related to material costs and labor shortages. This illustrates ongoing industry challenges within the sector.
- Retail: Showed only modest growth, potentially a sign of softening consumer spending in certain areas. This reflects the impact of inflation on consumer behavior.
Unemployment Rate Holds Steady at 4.2%: A Deeper Dive
The unchanged unemployment rate at 4.2% requires careful analysis. While seemingly positive, it's crucial to consider the broader context.
Meaning of the 4.2% Unemployment Rate:
A stable unemployment rate doesn't necessarily signal a perfectly healthy economy. Factors like labor force participation and underemployment rates must be considered. The relatively low unemployment rate suggests a tight labor market, but it doesn't fully capture the complexities of the situation.
- Labor Force Participation Rate: Remains below pre-pandemic levels, suggesting that some individuals have left the workforce entirely. This points to a complex labor market beyond simple unemployment statistics.
- Long-Term Unemployment: While the overall unemployment rate is low, the duration of unemployment for some individuals remains a concern, highlighting a need for job retraining and skills development initiatives.
- Underemployment: Many individuals may be working part-time despite desiring full-time employment. This reflects a need for higher paying, full-time jobs.
Potential Factors Influencing Unemployment:
Several factors influence the unemployment rate, creating a complex economic interplay.
- Inflationary Pressure: Rising inflation erodes purchasing power and can impact business investment and hiring decisions. This economic indicator has significant implications for the employment picture.
- Wage Growth: While wages are rising in some sectors, they haven't kept pace with inflation in many areas, impacting worker purchasing power and possibly delaying some hires. This needs to be considered in evaluating overall economic health.
- Monetary Policy: The Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions directly influence interest rates, impacting borrowing costs for businesses and consumer spending, which in turn influence employment levels. This government policy has a direct effect on the overall U.S. job market.
Future Outlook for the U.S. Job Market: Predictions and Challenges
Predicting the future of the U.S. job market requires careful consideration of various economic indicators.
Expert Predictions:
Economists hold differing views on the future trajectory of the U.S. job market. Some predict continued moderate growth, while others caution about the potential for a slowdown. The consensus is that ongoing economic uncertainty will influence the job market's performance in the coming months and years.
- Continued Moderate Growth: Many analysts forecast continued job growth, albeit at a slower pace than in previous years, driven by the ongoing recovery in key sectors.
- Potential Slowdown: Others warn of potential risks, including inflation, rising interest rates, and global economic uncertainty, potentially leading to a slowdown in job growth and possibly even job losses in certain sectors.
Challenges Facing the Job Market:
Significant challenges threaten the U.S. job market.
- Labor Shortages: Many sectors continue to face significant labor shortages, impacting their ability to expand and meet consumer demand. This highlights a need for improved workforce training and development programs.
- Economic Uncertainty: The ongoing global economic uncertainty and inflationary pressures present significant challenges. This points to the need for stable, predictable economic policy to aid employment.
- Recessionary Risks: The possibility of a recession poses a significant threat to employment levels, potentially leading to widespread job losses. This economic risk is the foremost concern for many analysts and policymakers.
Interpreting the April Jobs Report and Looking Ahead
The April jobs report presents a mixed picture: robust growth in some sectors, weaker performance in others, and a persistent unemployment rate of 4.2%. While the addition of 177,000 jobs is positive, ongoing challenges like inflation, labor shortages, and economic uncertainty require careful monitoring. The future of the U.S. job market remains intertwined with these complex factors. To stay informed about the evolving landscape of the U.S. job market, regularly check for updates and analysis of U.S. employment data, American job market trends, and U.S. labor market analysis. Understanding these key indicators is crucial for navigating the complexities of the current economic environment.

Featured Posts
-
 The Most Iconic Final Destination Moment A Nostalgic Look Back
May 04, 2025
The Most Iconic Final Destination Moment A Nostalgic Look Back
May 04, 2025 -
 Eurovision 2024 Heute Abend Esc 2025 Deutschlands Kandidat Show 1 In Germany
May 04, 2025
Eurovision 2024 Heute Abend Esc 2025 Deutschlands Kandidat Show 1 In Germany
May 04, 2025 -
 Ufc 315 And The Full May 2025 Fight Card Schedule
May 04, 2025
Ufc 315 And The Full May 2025 Fight Card Schedule
May 04, 2025 -
 Peter Distad To Lead Foxs New Direct To Consumer Streaming Platform
May 04, 2025
Peter Distad To Lead Foxs New Direct To Consumer Streaming Platform
May 04, 2025 -
 Meet Bianca Censoris Sister Angelina A Look At Her Instagram
May 04, 2025
Meet Bianca Censoris Sister Angelina A Look At Her Instagram
May 04, 2025
